European Government and Society
advertisement

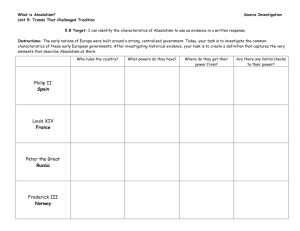
ABSOLUTISM What are the rights of a citizen? What are the responsibilities of the government? How are they different? ABSOLUTISM AND ENLIGHTENMENT European Government and Society EUROPE IN THE 1600S ABSOLUTISM IN EUROPE A form of government in which: • The leaders are monarchs (kings and queens) • They have absolute or total control over the country. • This may also be referred to as “totalitarian” government or regime. FRANCE Louis XIV Fought lots of wars. • Wanted to expand French territory. No religious toleration • Only Catholicism • Revoked the Edict of Nantes which gave Calvinist Protestants (Huguenots) rights. FRANCE Louis XIV Raised taxes on Peasants Made the Palaces of Versailles the residence of the Royal family Believed in the Divine Right of Kings RUSSIA Peter the Great Czar (Tsar) Romanov family Wanted to Westernize Russia • Travelled abroad to learn about the latest trades, techniques and technology. RUSSIA Peter the Great Secular • Worldly; not as religious • Took over Russian Orthodox Church Not democratic • Didn’t free serfs (slaves) • Didn’t make gov’t more open. PRUSSIA The Hohenzollerns Frederick I • Created a New Gov’t. • Created a New State w/ New Laws. • More open than Russia. PRUSSIA Hohenzollern Castle Society and Government Military is center of Prussian Society Ruler has tremendous power Russia and France rely on local officials for governing. AUSTRIA The Habsburgs Maria Theresa Enemies with Prussia Her father passes the Pragmatic Eventually all of Europe is Sanction allowing her to become involved in conflict between the two ruler of the Austrian Empire. countries. • The Seven Years War (originated in North America as the French and Indian War) • Pragmatic sanction is an edict that ensured that hereditary (family) possessions could be inherited by a daughter. ENGLAND Constitutional Monarchy King • Head of the Church of England Parliament • Congress- lawmakers *England is the first sort of democratic country in Europe