A&P II Exam 3 Name Russo Matching Questions Figure 20.1 Using
advertisement
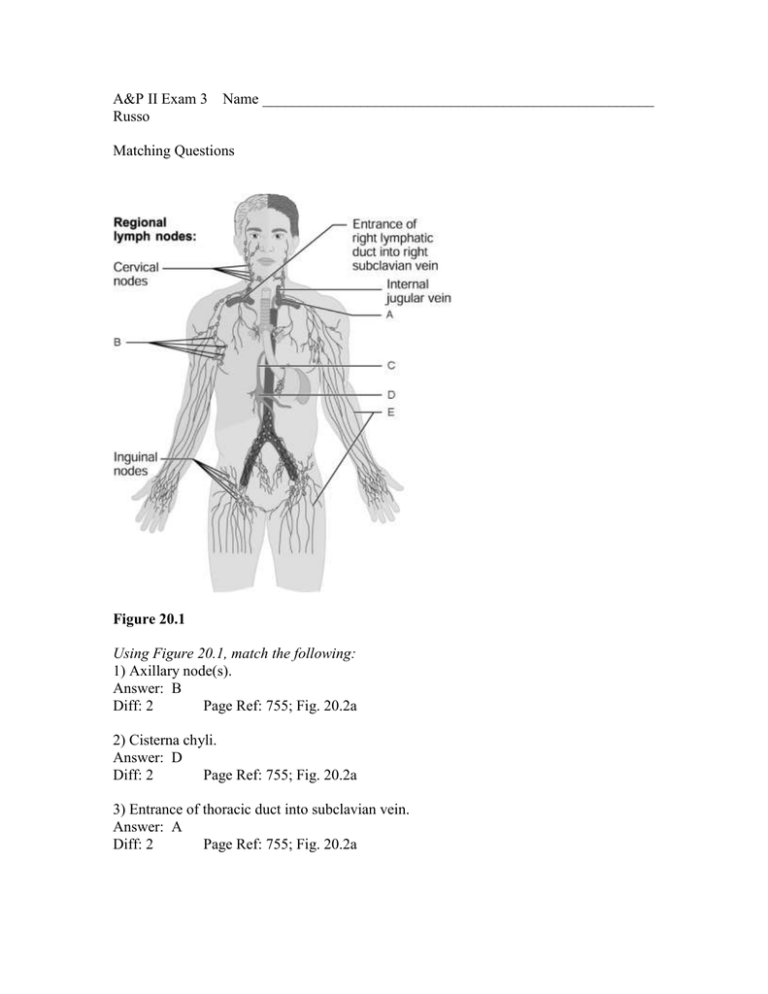
A&P II Exam 3 Russo Name ____________________________________________________ Matching Questions Figure 20.1 Using Figure 20.1, match the following: 1) Axillary node(s). Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 755; Fig. 20.2a 2) Cisterna chyli. Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 755; Fig. 20.2a 3) Entrance of thoracic duct into subclavian vein. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 755; Fig. 20.2a 4) Thoracic duct. Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 755; Fig. 20.2a 5) Lymphatic collecting vessels. Answer: E Diff: 3 Page Ref: 755; Fig. 20.2a T/F 6) The lymphatic capillaries function to absorb the excess protein-containing interstitial fluid and return it to the bloodstream. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 753-754 7) Lymph always flows away from the heart. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 753 8) Lymphatic capillaries are permeable to proteins. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 754 9) Digested fats are absorbed from the intestine by the lymph capillaries. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 754 10) Chyle is delivered to the blood via the lymphatic system. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 754 11) About 3 liters of fluid are lost to the tissue spaces every 24 hours and are returned to the bloodstream as lymph. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 754 12) Because lymph vessels are very low-pressure conduits, movements of adjacent tissues are important in propelling lymph through the lymphatics. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 754 Multiple Choice 13) Both lymph and venous blood flow are heavily dependent on ________. A) the pumping action of the heart B) skeletal muscle contractions and differences in thoracic pressures due to respiratory movement C) contraction of the vessels themselves D) two-way valves Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 754 14) Which lymphatic structure drains lymph from the right upper limb and the right side of the head and thorax? A) lumbar trunk B) thoracic duct C) right lymphatic duct D) cisterna chyli Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 754 15) The lymphatic capillaries are ________. A) more permeable than blood capillaries B) less permeable than blood capillaries C) as permeable as blood capillaries D) completely impermeable Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 753-754 16) Select the correct statement about lymph transport. A) Under normal conditions, lymph vessels are very high-pressure conduits. B) Lymph transport is faster than that occurring in veins. C) Lymph transport is only necessary when illness causes tissue swelling. D) Lymph transport depends on the movement of adjacent tissues, such as skeletal muscles. Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 754 17) Lymph capillaries are absent in all but which of the following? A) bones and teeth B) bone marrow C) CNS D) digestive organs Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 753-754 18) Which of the following is not a method that maintains lymph flow? A) skeletal muscle contraction B) breathing C) valves in lymph vessel walls D) smooth muscle contraction Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 754 19) Which of the following is not a normal component of lymph? A) water B) plasma proteins C) red blood cells D) ions Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 753 20) Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system? A) draining excess interstitial fluid B) carrying out immune responses C) transporting dietary fats D) transporting respiratory gases Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 753 Figure 21.2 Using Figure 21.2, match the following: 21) Area where B cells become immunocompetent. Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 778; Fig. 21.8 22) Area where T cells become immunocompetent. Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 778; Fig. 21.8 23) Area where activated immunocompetent B and T cells recirculate. Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 778; Fig. 21.8 24) Area seeded by immunocompetent B and T cells. Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 778; Fig. 21.8 25) Area where antigen challenge and clonal selection are most likely to occur. Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 778; Fig. 21.8 Match the following: A) Inflammatory response and skin and mucous membranes B) Immune response C) Inflammatory response D) Intact skin and mucous membranes 26) First line of defense. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 767 27) Second line of defense. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 767 28) Third line of defense. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 767 29) Innate defense system. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 767; Fig. 21.1 30) Adaptive defense system. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 767 Answers: 26) D 27) C 28) B 29) A 30) B T/F 31) The respiratory burst produced by some macrophages releases free radicals. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 768 32) The directional movement of cells in response to chemicals is called chemotaxis. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 773 33) Substances capable of triggering the adaptive immune system and provoking an immune response are called antigens. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 776 34) Some immunocompetent cells will never be called to service in our lifetime. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 779 35) Adaptive immunity is provided only by lymphocytes that secrete antibodies. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 777 Multiple Choice 36) B lymphocytes develop immunocompetence in the ________. A) thymus B) spleen C) bone marrow D) lymph nodes Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 777 37) Which of the following is not a function of the inflammatory response? A) prevents the spread of the injurious agent to nearby tissue B) replaces injured tissues with connective tissue C) disposes of cellular debris and pathogens D) sets the stage for repair processes Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 769 38) The redness and heat of an inflamed area are due to a local hyperemia caused by ________. A) vasodilation B) vasoconstriction C) phagocyte mobilization D) production of complement and interferon Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 769-770 39) In clonal selection of B cells, which substance is responsible for determining which cells will eventually become cloned? A) antigen B) interferon C) antibody D) complement Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 780 40) Which of the following statements regarding NK cells is a false or incorrect statement? A) NK cells are a type of neutrophil. B) NK cells are present in the blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow. C) NK cells attack cells that display abnormal MHC antigens. D) NK cells attack cancer cells and virus-infected body cells. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 768-769 41) The process whereby neutrophils and other white blood cells are attracted to an inflammatory site is called ________. A) diapedesis B) chemotaxis C) margination D) phagocytosis Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 773 42) Small molecules that bind with self-proteins to produce antigenic substances are called ________. A) haptens B) antibodies C) ions D) reagins Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 776 43) Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in phagocytosis? A) adherence, digestion, killing, ingestion, chemotaxis B) chemotaxis, ingestion, digestion, adherence, killing C) chemotaxis, adherence, ingestion, digestion, killing D) ingestion, adherence, chemotaxis, digestion, killing Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 768; Fig. 21.2 Figure 22.2 Using Figure 22.2, match the following: 44) Tidal volume. Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 825; Fig. 22.16 45) Inspiratory reserve volume. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 825; Fig. 22.16 46) Residual volume. Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 825; Fig. 22.16 47) Expiratory reserve volume. Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 825; Fig. 22.16 48) Air that does not participate in the exchange of gases. Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 825; Fig. 22.16 T/F 49) The lungs are perfused by two circulations: the pulmonary and the bronchial. The pulmonary circulation is for oxygenation of blood. The bronchial circulation supplies blood to the lung structures (tissue). Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 818 50) Intrapleural pressure is normally about 4 mm Hg less than the pressure in the alveoli. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 819 51) Smoking diminishes ciliary action and eventually destroys the cilia. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 813 52) Tracheal obstruction is life threatening. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 813 53) The average individual has 500 ml of residual volume in his lungs. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 824 54) Atelectasis (lung collapse) renders the lung useless for ventilation. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 820 55) The walls of the alveoli are composed of two types of cells, type I and type II. The function of type II is to ________. A) secrete surfactant B) trap dust and other debris C) replace mucus in the alveoli D) protect the lungs from bacterial invasion Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 815 56) Complete the following statement using the choices below. Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is A) less than the pressure in the atmosphere. B) greater than the pressure in the atmosphere. C) equal to the pressure in the atmosphere. D) greater than the intra-alveolar pressure. Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 820 57) Unlike inspiration, expiration is a passive act because no muscular contractions are involved. Expiration, however, depends on two factors. Which of the choices below lists those two factors? A) the recoil of elastic fibers that were stretched during inspiration and the inward pull of surface tension due to the film of alveolar fluid B) the expansion of respiratory muscles that were contracted during inspiration and the lack of surface tension on the alveolar wall C) the negative feedback of expansion fibers used during inspiration and the outward pull of surface tension due to surfactant D) combined amount of CO2 in the blood and air in the alveoli Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 822 58) Which of the following maintains the patency (openness) of the trachea? A) surface tension of water B) surfactant C) cartilage rings D) pseudostratified ciliated epithelium Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 813 59) Intrapulmonary pressure is the ________. A) pressure within the pleural cavity B) pressure within the alveoli of the lungs C) negative pressure in the intrapleural space D) difference between atmospheric pressure and respiratory pressure Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 819 60) The relationship between the pressure and volume of gases is given by ________. A) Boyle's law B) Henry's law C) Charles' law D) Dalton's law Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 820 Xtra credit (1 point each) 1) Which of the choices below describes the forces that act to pull the lungs away from the thorax wall and thus collapse the lungs? A) the natural tendency for the lungs to recoil and the surface tension of the alveolar fluid B) compliance and transpulmonary pressures C) the natural tendency for the lungs to recoil and transpulmonary pressures D) compliance and the surface tension of the alveolar fluid Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 819 2) The factors responsible for holding the lungs to the thorax wall are ________. A) the smooth muscles of the lung B) the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles alone C) the visceral pleurae and the changing volume of the lungs D) surface tension from pleural fluid and negative pressure in the pleural cavity Answer: D Diff: 3 Page Ref: 818 3) Most inspired particles such as dust fail to reach the lungs because of the ________. A) ciliated mucous lining in the nose B) abundant blood supply to nasal mucosa C) porous structure of turbinate bones D) action of the epiglottis Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 806



