African Societies Similarities and Differences
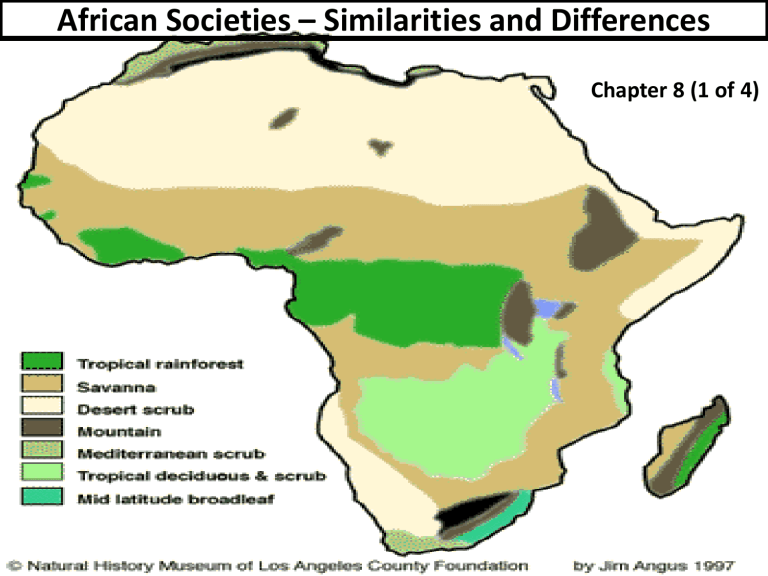
African Societies – Similarities and Differences
Chapter 8 (1 of 4)
Diverse =
Different
African Diversity
There was no dominant state or religion in Africa
Africans very diverse making it hard to generalize about them
(each group different)
Stateless Societies
States emerged, but many stateless
No central power
Power shared by families
Could be large
Disputes settled easily, lot of open land to move to
No kings, so no need for taxes
Difficulties = hard to raise army and defend itself vs. organized states or raise money for public works
Though Diverse, some similarities Existed in African Society
Animism common throughout Africa – though local practices differed
Bantu people spread out, so language similar
Many believed in creator god and lesser gods
Believed in good and evil (witches evil and had to be eliminated) – similar view to Europeans
Ancestors who founded land seen as holy, so land was holy (religion, economics, and history closely linked)
Overall, African religion = provided view of how world worked and code of ethics
Even as Islam spread to Africa, these beliefs still held
North Africa
Had been involved in trade with other parts of the world for a while
Agriculture and skilled ironwork spread rapidly throughout
Sub-Saharan
Africa
Economies varied greatly from region to region
Trade (especially w/Arabs increased greatly - led to some big cities w/professional traders – women involved too)
Africa at Trade Disadvantage
Traded away valuable resources
(gold, ivory, salt) for expensive manufactured goods
Africa didn’t gain much new technology and manufacturing through this trade
Islam Comes to North Africa in the 600s
North
Africa had been part of classical world for a long time already
Christianity had already spread to the area towards the end of the Roman era
By 670,
Muslims controlled northeast
Africa , called
Ifriqiya
Soon after,
Muslims got control of northwest
Africa, called
Maghrib
The North
Africans converted rapidly to
Islam
The Berbers
Berbers = Africans from Sahara
Desert (indigenous people)
The Berbers created states in
North Africa
Almoravids
Reform movement within the Berbers. Practiced stricter version of Islam and spread religion through jihad.
Almohadis
Islamic reformers within the Berbers, key to spreading Islam to sub-
Saharan Africa and Spain through jihad
Islam Attractive to Africans
Example of social stratification that still existed = punishment for killing man twice as much as for killing woman
Egalitarian, so
African converts would be equal to Arab Muslims
(though stratification still existed)
The kings and rulers were the first to convert
(they used Islam to enhance their power)
Christianity Arrives 1
st
in Africa (Before Islam)
Egypt and Ethiopia =
Christian, even before
Romans converted
Coptic Christians =
Christians of Egypt, 1 st universal religion in Africa
Coptic Christians had spread Christianity from
Egypt up the Nile to Nubia
Arabs conquered Egypt, but Copts remained
Click map for video on Coptic Christians
EGYPT
ETHIOPIA
Ethiopia
Formed from the trading kingdom of
Axum
Ethiopia grew when King
Lalibela conquered surrounding lands from
Axum
Ethiopia
The Ethiopian Highlands -
Ethiopians lived in mountainous area so they learned to use terrace farming
Ethiopians built many great buildings, especially massive churches which they built from rock terrace farming
Ethiopian Religious Isolation
Ethiopia was cut off from other Christian areas (like
Byzantine Empire) so it developed Christianity independently
Ethiopia was (and still is) surrounded by Muslims countries, which caused friction (and still causes problems today)
Ethiopia Surrounded
Ethiopia almost conquered by
Muslims in
1542, but
Portuguese helped stop the takeover
Portuguese tried to bring the Ethiopians into the
Roman
Catholic
Church, but failed
Ethiopia remained an independent, and Christian kingdom, and is mostly
Christian to this day