Radio Waves - Solon City Schools
advertisement

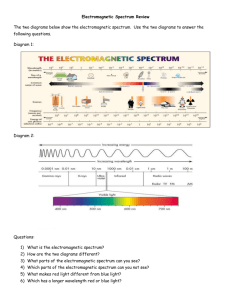
Created by: Mrs. Radney’s SI Class Attention! You will have a short quiz over the following information on Wednesday 1/12! The Waves are listed in order from low frequency to high frequency! Cool Website with Info on EM spectrum EM Spectrum Radio Waves Electromagnetic waves that have longer wavelength than microwaves and are used in communication and RADAR. The frequency range of radio waves is 103-109 Hz. This shows the paths that radio waves take around and above Earth’s surface. Radio Wave Facts Radio waves carry signals for TV, AM and FM radio and cell phones. Radio waves have the longest wavelength of the EM spectrum. Radio waves are used in RADAR which is Radio Detection and Ranging for locating various objects and prediction of storm patterns. By: Stephen Dayneka, Madeline Taylor, Katie Hanrahan, Eric Seifert Microwaves Microwaves = radio waves with the shortest wavelengths. 10^10 Hz Microwave Facts Microwaves are not easily blocked by trees, buildings, and mountains. This is why they are used for cell phone communication. Stars give off microwaves. Prolonged exposure to microwaves is known to cause "cataracts" in your eyes, which is a clouding of the lens, preventing you from seeing clearly. By: Mrs. Radney (whoever had microwaves never turned their project into my inbox!!) Infrared Waves Infrared Waves- electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths slightly longer than visible red light. Frequency Range .003 – 4 x 1014 Hz Image of 2 people in mid-infrared light 1) Infrared waves give off heat. 2) Heat can be seen with specific devices and photographic film. 3) Used in night vision goggles & telling the weather. Katie Riordan, Jenny Yang, Jiayu Liang, Ben Richards Visible Light Visible light is a certain range of waves in the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. The range of visible light is from 4 - 7.5 x 1014 Hz Here is visible light on the EM spectrum Information Light is a wave and a photon. In space light moves at about 300,000 km /second. Albert Michelson first discovered this speed by doing a rotating mirror experiment. Glass prisms work by separating white light. White light is made from multiple colors. These colors move at different speeds so when split at a angle, they split into different colors. By: Adam Katz, Jacob Rogers, Daniel Axner, & Da Gengster Ultraviolet Waves (UV) Definition: The waves of the electromagnetic spectrum just above the frequency of visible light. Frequency Range: 7.5x1014 to 3.0x1016 Hz Ultraviolet flashlight (UV waves can let humans see things they couldn’t normally see Ultraviolet Waves 10 nm to 400 nm in wavelength. It can cause skin and eye damage if exposed. It has more energy and a shorter wavelength than visible light. By: Shannon Finnerty, Ellie Gulling, Lily Li X- Rays A form of electromagnetic radiation which have very high frequencies. The frequency range is 3 x 10^16 Hz to 3 x 10^19 Hz (30 petahertz to 30 exahertz). This is the electromagnetic spectrum, where X-rays are highlighted in the red box. Shreyas + Jordan + Monika = Shrodanika 1. X-rays are also called Rontgen radiation, named after its discoverer. 2. X-rays are used in medicine to generate images of the human body behind the skin. 3. X-rays have more energy and shorter wavelengths than UV, visible, Infrared, Microwave, and Radio light. Shreyas + Jordan + Monika = Shrodanika Gamma rays- A high energy short wavelength wave used for medical purposes, generally for killing cancerous cells or sterilizing medical equipment. Frequency range- 3*10^18<f<3*10^22 This is where gamma rays lie on the electromagnetic scale. 1. Gamma rays have the capability to kill cells. 2. Gamma rays have more energy than any other light ray in the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Gamma rays are produced by violent events such as super nova explosions or radioactive decay. By: Catherine Chervenak, Krish Lamba, Mark Oet