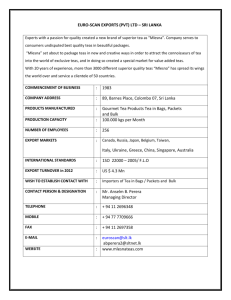
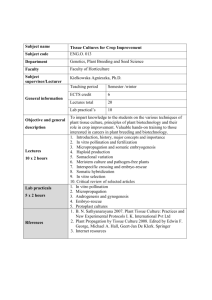
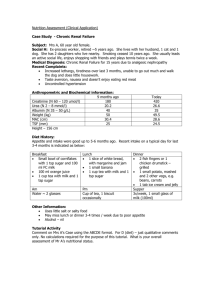
Diapositiva 1
advertisement

ANTIMICROBIAL PROPERTIES OF VARIOUS GREEN TEA PRODUCTS WITH AND WITHOUT THE ADDITION OF SUGAR T3 Members: Samantha Acevedo, Conan Chen, Ethan France, Brian Goldspiel, Anna Kim, Amanda Li, Florence Ma, Sana Siddiqui, Stephanie Tarlowe, Anthony Yakely, Leanna Zhan Advisor: Mrs. Rachel Sandler Assistant: Gillian Bradley What is Green Tea? • Camellia sinensis plant leaves • Fermentation – Green, oolong, and black teas • Types – – – – – – Matcha: powdered leaves Sencha: Uji leaves Loose: dried leaves Bagged: filtered tea bag Bottled: Snapple ® brand Instant: powdered mix http://www.plantoftheweek.org/week046.shtml Chemical Composition http://www.nature.com/onc/journal/v25/n13/fig_tab/1209227f1.html Streptococcus mutans http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Streptococcus_mutans_Gram.jpg • Gram-positive bacteria produce lactic acid – Breaks down tooth enamel – Causes cavities and bad breath • Unique genes serve as drug targets Health Benefits • Multiple studies have been conducted – – – – – LDL Obesity Diabetes Cancer Dental Health • Antimicrobial properties due to low degree of fermentation – May destroy catechins http://www.bostonteacampaign.com/en-us/7_5/encyclopedia-of-tea.html http://www.bitemarket.com/store/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1_40&products_id=237 http://awesomebeautysupply.com/diet-snapple-singles-to-go-antioxidants-green-tea/ Preparation of Teas • 240 mL boiled, deionized water • Cooled to 90° • Steep 15 minutes • 15 g sugar per sample • Diet Snapple ® Onthe-Go powder Process of Diffusion • Cover plates with bacterial lawn – None on control • Soak disks 5 minutes • Place on plate • Incubate ~48 hours at 37° C • Measure zones of inhibition In Vitro Procedure • Sterilize loop • Inoculate and make line on plate • Submerge loop in liquid – 2 minutes – 10 second intervals • 5 in liquid, 5 in air – Stir gently • Scope ® – 30 seconds – Constant agitation • Swab loop and make line on plate Paper Disk Diffusion: Zone of Inhibition • Scope ® mouthwash – 1.77 cm diameter • Antimicrobial compounds – – – – Alcohol Poloaxamer Polysorbate Sodium benzoate • No observable zone of inhibition around disks of any teas Paper Disk Diffusion: Possible Errors • Contaminated plates – Open disks exposed to fungus in lab – Lapses in aseptic technique – Excess liquid on disks Paper Disk Diffusion: Zone of Growth • Lipton ® tea with sugar – 0.95 cm diameter • No growth on control • Sugar may have boosted • Inconclusive Gram stain • More research needed In Vitro: Results • Control had more bacteria before than after • All results compared to control – Less bacteria not necessarily significant • Sugar appeared to have no effect Control (Water) Matcha with Sugar In Vitro: Best Results Loose Leaves Scope ® In Vitro: Results Discussion • More subjective and qualitative – Visual observation • Little clear evidence of antimicrobial benefits against S. mutans • Loose tea leaves had strongest effect In Vitro: Alternate Method for Scope ® • Known antibacterial agent • Loop immersed in Scope ® for 30 seconds • Simulated difference between rinsing with mouthwash and sipping a beverage • May have attributed to differing results In Vitro: Errors • Preparation method • Small sample size • Discrepancies Future Research • Different preparation methods • Potency of green tea on other microbes • Chemical compositions of teas – Loose leaf tea (in vitro) • Effects of sugar • Modeled after realistic experience • Different concentrations Conclusions • Scope ® is most effective • Loose sencha leaves (in vitro) • Sugar inconclusive – Possibly detrimental in one case Acknowledgements • • • • • • • • • • • John and Laura Overdeck The Crimmins Family Charitable Foundation NJGSS Alumni and Parents (1984-2011) Bristol-Myers Squibb Roche Kinder Morgan Bain Capital GlaxoSmithKline Novartis Bayer HealthCare Dr. Miyamoto, Dr. Surace, Dr. Quinn, Myrna Papier, Mrs. Sandler, Gillian Bradley