PowerPoint - Mrs. Anderson's ABC of Business
advertisement

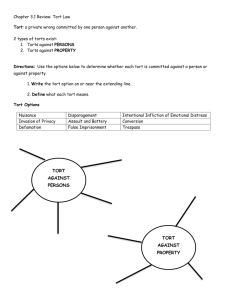
BUSINESS LAW Unit 5 Crime Vs. Tort Crime is against society-public wrong Tort is a private or civil wrongindividual issue Judgments-can sue and get damages Elements of a Tort Duty-legal obligation to do or not do something 1. Not to injure another. 2. Not to interfere with property rights of others. (trespass) 3. Not to interfere with economic rights of others. (contracts) Elements of a Tort Breach-a violation of the duty Intentional-do on purpose Negligence-carelessness Mental state of the person is important Elements of a Tort Injury-a harm that is recognized by the law. Results from the breach of duty Elements of a Tort Causation-breach of the duty caused the injury. Proximate cause is when the law recognized that the cause if great enough that injury occurred. Vicarious liability –when someone else is responsible or liable for the actions of another Ex. Parents are responsible for kids Elements of a Tort Duty Breach Injury Causation Common Intentional Torts Intentional Torts are torts in which the defendant possessed the intent or purpose to inflict the resultant injury. Assault Definition-one person intentionally puts another in reasonable fear of an offensive or harmful bodily contact. Threat-words or gestures BelievableRaise a fist or attempt to strike Battery Definition-a person who has a duty to refrain from harmful or offensive touching of one another-but does not. Actual hit, touch or thrown item at person If hit from behind-is battery without assault False Imprisonment Definition-intentional confinement of a person against their will. Defamation Definition-false statement about a person that can injure a person Slander-is spoken Libel-is written or printed Have to be 1. False 2. Be communicated to a third person 3. Bring the victim into disrepute, contempt or ridicule by others. Invasion of Privacy Definition-uninvited intrusion into an individuals private matters (relationship and activities) Trespass to Land Definition-entry onto the land without the consent of the owner (intentional) Fraud Definition-the intentional misrepresentation of a important fact Negligence Definition-most common tort Intent to injure is not required Carelessness has to be displayed Reasonable person standard Professionals/Tradesmen have a higher standard Negligence Contributory negligence if person is not as careful or at partial fault Comparative negligence-plaintiff is at partial fault-can have damages reduced Assumption of risk-aware of danger, but still attempt-Ex. Skiing, Skydiving Strict Liability is when you have a dangerous item and must handle items very carefully-Ex-wild animals Types of Remedies for a Civil Law Suit Injunction person must do or not do a certain act. Damagesmonetary award to compensate for the loss. Actual/Compensat ory Civil Trial Procedures Judge or Jury(6-12)-does not have to be unanimous Depends on the case-which one you would want Plaintiff vs. Defendant Tort Trial Procedures Opening Statements Evidence is then presented Testimony-statements of written Witness-someone who has personal knowledge of the facts Experts-Engineers, Scientists Subpoenas are issued to get people to court to testify Contempt of Court-if do not show up to testify Tort Trial Procedures Closing Statements-by both sides Judge then gives direction to jury to decide the case Jury does not have to unananimous-10 out of 12 or 5 out of 6 Damages are awarded-based on the jury’s decision-not set amounts are given