The Excretory System Student Notes
advertisement

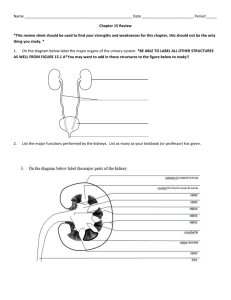
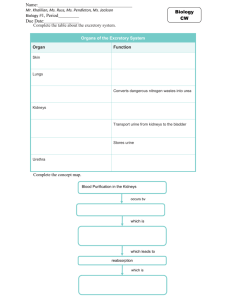
HS 20 - Weir The Excretory (Urinary) System Functions of the Excretory System: The cells of our body obtain energy by converting complex organic compounds into simpler compounds Some of these simpler compounds can be ___________________ to the body Therefore our body must __________________ these waste products MAIN FUNCTION: Removes various ________________ from the blood and ___________ those wastes from the body Wastes are produced by 2 main processes in the body: digestion and metabolic processes MAIN PARTS OF EXCRETORY SYSTEM: ________________________ (main organ) _________________ _________________ _________________ As we know our body breaks down the nutrients we take in ________________________ the breakdown of proteins A byproduct of deamination is _________________ (NH4) Ammonia comes from breaking down proteins and is ______________ Humans convert ammonia into ____________ Urea is produced in the liver Urea is much less toxic than ammonia and your blood can dissolve it. However urea still needs to be expelled from the body Another waste product produced in the body is __________________. Uric acid is a byproduct of your body’s ____________________. This is another waste that needs to be expelled from the body HS 20 - Weir So how do we get these wastes out of our blood and eventually out of our body? Through the ______________ The Kidneys The excretory system _____________ with the kidneys Paired, bean-shaped, size of fist The kidneys have a few functions: Removing ______________ Filtering the _____________ Maintaining _____________ balance Remember: _____________ = relating to the kidneys A cross section of a kidney shows 3 sections: Outer layer of connective tissue = ______________ Inner layer = _____________ Hollow chamber = ____________________ (joins kidney with the ureter) HS 20 - Weir All the ___________ in our body passes through the _______________ several times a day. As the kidneys filter blood they will remove any unwanted wastes Those wastes will eventually be turned into ____________ ___________________________ branch from the aorta (in the heart) and carry blood to the paired kidneys Each kidney is supplied with blood from a single renal artery. The kidneys remove waste from the body by _____________________ the blood However a lot of what the kidneys filtered out ends up being ______________________. **Note: If the kidneys did not reabsorb materials we would produce 120L of urine every minute. If this were the case you would have to consume 1 L of fluids every 10 minutes to maintain homeostasis. Homeostasis = __________________ (we always want our body to maintain homeostasis) Nephrons Kidneys are made up of slender tubules called ________________ These are the ____________________ units of the kidneys. Nephrons are like small ______________ – each kidney has about 1 million nephrons Smaller branches from the renal arteries called afferent arterioles supply the nephrons with blood. Nephron Diagram HS 20 - Weir Glomerulus (Filtration) The afferent arterioles branch into a capillary bed called the ____________________ The glomerulus is the ______________________ of a nephron It is a high pressure capillary bed where the blood is filtered(clusters of capillaries in the kidney) The pressure squeezes some of the fluid out of the blood and into cup-like sac that surrounds the glomerulus….. The Bowman’s Capsule Bowman’s capsule __________________ the glomerulus This capsule ________________ the wastes that are filtered out of the blood The fluid that is filtered from the blood into the bowman’s capsule is now called __________________ – and eventually forms the urine Filtrate is made up of water, urea, smaller ions and molecules. Now the filtrate is ready to be processed and reabsorbed so it exits into the ________________ portion of the nephron Filtrate enters a thin tubule called the _________________ convoluted tubule There are different tubule sections of the nephron – each section performs different types of ______________________ – where substances are transferred back to the blood Loop of Henle (Reabsorption) From the proximal convoluted tubule the filtrate (urine) is carried to the _______________________________ This is where _________ of the reabsorption occurs. Some things that are reabsorbed into the blood include: Glucose, Amino acids, Ions, Minerals, Sodium, Chlorine, Water HS 20 - Weir Dissolved waste materials such as urea are not returned to the blood stream. About 160 liters of water per day soak into the tubules of the nephron The body cannot afford to lose this much fluid so almost ________ of water filtering through the nephrons is reabsorbed into the blood The remaining _______ together with other wastes is turned into urine. Collecting Ducts (Secretion) Filtrate then moves into the distal convoluted tubule - which regulates levels of minerals Filtrate then moves into the ___________________________ –this joins with several collecting ducts to collect the filtrate (urine) – by this point the urine is mainly made up of water, urea and other metabolic waste. Now it is _______________ urine. The collecting ducts collect urine from many nephrons. Urine is a form of waste therefore our body needs to get rid of it. Ureters From the kidneys the urine is transported by 2 thin tubes called _____________. These are approximately 25 – 30cm long in adults Bladder The ureters carry the urine to the bladder – a balloon-like structure A sphincter ______________ at the base of the bladder acts as a valve allowing the ________________ of urine. This muscle is what allows you to hold in urine until you reach the washroom HS 20 - Weir Urethra When the bladder is full the urine is then excreted (removed) from the body through the ____________ In the male the urethra also transports semen. URINE FORMATION: Depends on 3 functions: **Before urine is created our waste goes through these 3 steps 1) ________________________ Completed by the movement of fluids from the blood into the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule 2) ________________________ Involves the absorption of molecules, ions and water from the nephron back to the blood (occurs in tubule portion of nephron – mostly the loop of henle) 3) ________________________ Involves the transfer of materials from the blood to the collecting duct. Complete Excretory System Diagram