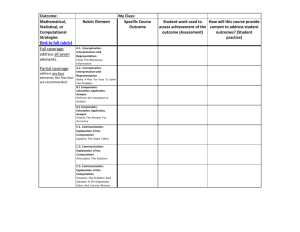
Computation - Personal Web Pages
advertisement

Welcome to EGR 106
Foundations of Engineering II
Course information
Today’s specific topics:
Computation and algorithms
– MATLAB
Basics
Demonstrations
Material in textbook chapter 1
–
Computation
What is computation?
Examples:
Computation = “transformation from one or
more inputs to an output”
3+2
tan 40o
Human Computation
“Simple” computations (trivial to us)
–
–
–
Adding 2 single digit numbers
Recognizing a letter of the alphabet
Comparing 2 numbers for <, =, >
“Harder” computations (based on simple)
–
–
–
Adding 3 or more numbers
Reading a word
Sorting a list of numbers
Algorithms
Definition: “a set of directions for carrying out
a computation in terms of other, simpler
computations”
“Simpler computations” = ones that we
already know how to do
Example
Memorizing
addition
tables in
grammar
school
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
3
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
4
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
5
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
6
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
7
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
8
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
9
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Permits multi-digit addition
Computer Computation
Very fast at arithmetic operations
Algorithms = computer programs
–
–
–
Need to understand what computations are
“simple” for the computer
Need to write a clear set of directions to be
followed
Build more complicated computations from
intermediate ones
Examples
Find the smallest in a list of number
Sort a list of numbers
Some for discussion/thought
(first two from Kaplan, Introduction to Scientific Computation and
Programming)
Start with the list and 2 variables, P and S
Find the
Smallest of
a List:
Set P=1, S=first number on list
Increase P by 1
Set S equal to the smaller of S and the
Pth number on the list
Done with
list?
yes
Stop
no
Example: list = 7,1,5
Step
P
S
1
1
S=7
2
2
3
4
S = smaller(7,1) = 1
3
5
S = smaller(1,5) = 1
6
stop
Sort a List
of Numbers:
Start with your list and an empty list
Let S = the smallest number in the list
Note reuse!
Delete S from the old list;
Append S to the new list
Done with
list?
yes
Stop
no
Example: list = 8,5,1,2
Step
S
1
1
2
3
8,5,2
1
8,5
1,2
8
1,2,5
5
6
7
8
New List
2
4
5
Orig List
8
1,2,5,8
Some Others….
Adding numbers expressed in Roman
numerals
LXVI + XXXIV = ???
Find the 2nd smallest number in a list
Convert the month/day into day of the year
Feb 15 = day 46
MATLAB – What is it ?
Name is from matrix laboratory
Powerful tool for
–
–
–
Computation and visualization of engineering and
science mathematics
Communication of ideas
Programming:
Built-in editor, debugger, and help
Many predefined functions (grouped in toolboxes)
Interpreted or compiled programs
Today is “beginning MATLAB”, sort of like
“beginning French”:
–
–
–
We start with basic terminology
We consider the simplest of computations
We do computation in interpreter mode (the
“enter” key invokes/runs/executes the operation
requested)
Chapter 1 of Gilat
–
Pages 5-22
The MATLAB Environment
Data represented in arrays
–
–
Organized by row and column indices
Use variable names for them
More next
week
Multi-paned desktop:
–
–
–
–
Command window
Workspace browser
Current directory
Other windows: Figure, File Editor, Help, …..
The Command Window
Command prompt >>
Basic math operations are available:
addition +
subtraction –
division /
multiplication *
exponentiation ^
“enter” key “executes” or “runs” or “invokes” the
operation
Operator precedence: PEMDAS
5–4+3^4/(3–1)=?
Finite precision
mathematics !!
By default, 5
significant digits are
shown, with
exponential notation
as needed
Results of NaN, Inf,
possible
Allows Stored Variables
The equal sign is an assignment operator
c = 7.5
bob3 = 3.7789
There are naming restrictions:
Connected symbols, starting with a letter
Make them unique
Some are predefined for special values
or uses:
pi inf flops j i ans for
Combining Operations and =
Generally, computation requires 3
pieces of information:
–
–
–
Specified on the
The operator?
right hand side of
an equal sign
The inputs?
What to do with the output?
MATLAB storing the result in a variable
Accomplished by the equal sign, =
For these examples, 2 and 4 are the input
and addition is the operation
No specification of the output;
the default is to put it into the
variable named ans
The output is assigned to the
variable named bob
bob is again the destination of
the result, we’ve just used
functional style notation for
the computation
Note that = is not really an equal sign, but is
an assignment operator
The computation on the right
can be trivial
Here the computation is done
using bob, then the result is
put into variable bob
An error results since we’ve
got things on the wrong sides
of the assignment operator
Other Useful Operations
abs(x) ceil(x)
sign(x) floor(x)
sqrt(x) conj(x)
sin(x)
sinh(x)
asin(x) acosh(x)
sind(x)
many more exist !!
exp(x)
log(x)
log10(x)
tan(x)
atan(x)
fix(x)
round(x)
rem(x,y)
atan2(x,y)
sec(x)
Examples
Square roots
Note that trig functions
generally work in radians, not
degrees
In general, all variables are
complex numbers
Bits and Pieces
Other useful system commands:
– clear, clc
– diary
– help, lookfor
– who, whos
Semicolon (;) suppresses the displaying of the result
of a computation
Arrow keys allow for editing of prior commands
PC version (network license) is available from ECC
help desk for $10
Plotting Basics
Figure window commands:
figure, figure(3), clf, close
plot(x,y) in which x and y are “arrays”
Annotation commands:
title('the title goes here')
xlabel('the x axis label goes here')
ylabel('the y axis label goes here')
Now for Some Demos!
Simple demos of variables and math
“Demos” at the command line
A simple gui of a bouncing ball