Security Awareness Training
advertisement

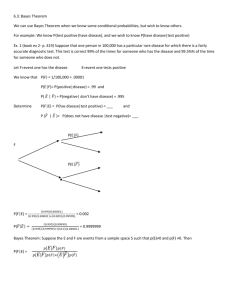
Security Security Awareness Termphong Tanakulpaisal Technical Manager – IT Distribution Co.,LTD Agenda • Introduction to network security – – – – – – How many type of assets in IT system? Which’s the most important asset? Why protect information? (most important one) So we need information security How to achieve the information security >> CIA concept Key success factor summary • Network threats – What’s threat and example? – How to overcome threat? (with security protection concept) – How to overcome threat? (with tools) • Network based protection system • Host based protection system • Case Study Company Assets • Hardware (Physical Assets) • Software • System interfaces (e.g., internal and external connectivity) • Data and information • Persons who support and use the IT system • System mission (e.g., the processes performed by the IT system) • System and data criticality (e.g., the system’s value or importance to an organization) • System and data sensitivity NIST SP 800-30 Information Assets • Information is an asset which, like other important business assets, has value to an organization and consequently needs to be suitably protected » ISO/IEC17799: 2000 Why Information Assets are the most important? • Business Requirements – – – – Client / customer / stakeholder Marketing Trustworthy Internal management tool • Legal Requirements – Revenue Department – Stock Exchange of Thailand – Copyright, patents, …. Why Information Assets are the most important?(2) • Contractual Security Obligations – – – – – – – – Intranet connections to other BU Extranets to business partners Remote connections to staff VPN Customer networks Supplier chains SLA, contracts, outsourcing arrangement Third party access Why we need information Security? • Information security protects information from wide range of threats in order to – Ensure Business Continuity – Minimize Business Damage – Maximize ROI and Business Opportunities • Business : Stable service to customer • Education : Availability of resources and integrity of information e.g. grade, profile, etc. » ISO/IEC17799: 2000 page iii, Introduction How much should we spend on IT security? Q: How much for that each company should spend or plan for their Information System? A: …………… Baht / year Q: How much for that each company should spend or plan for their Information Security? A: …………… Baht / year Why we need information Security?(2) Business impact Analysis How much does it cost per hour if people in your organization cannot access their information? (Business Impact Analysis) One big Organization -> approx 10 mil / day -> working hours 8 hrs -> 1.25 mil / hr -> 10% margin = 125k / hr if we’ve got 10 sale persons it means that we’ve lose 12,500 baht / hr if 1 salesperson can’t access their information …. some more calculations… • 100 people start their day clearing junk mails, each receives 20 junk mails per day, each mail needs 10 seconds to open/read/delete • Each of these staffs gets average THB18,000 income/month from the company – Company pays THB 102.27/staff/hr – 100 people x 10 sec/mail x 20 mails/day x 220 days/yr = 1,222.2 hrs/year – Company pays for this “clearing junk mail” 125,000 Baht/year • Do you believe that – There are only 20 junk mails per day? – Average time spent is only 10 seconds/junk mail? – You pay only 18,000 Baht/month? …. some more calculations… • What is a typical cost when the system is attack by virus / worm? – – – – – Amount of data destroyed and its cost Man-hour of support staff to clean the virus Idle time of other staff waiting for the system to come back Your customers’ satisfaction Your company’s reputation So, a company spends …….. Baht each time the virus attacks Security Concept • Security is preservation of confidentiality, integrity and availability of information • Confidentiality – Ensuring that information is accessible only to those authorized to have access • Integrity – Safeguarding the accuracy and completeness of information and processing methods • Availability – Ensuring that authorized users have access to information and associated assets when required » BS7799-2: 2002 page3, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 Key success to obtain CIA • Policy/Process/Pocedure – Clear – Coverage – Compliance – Legal, Standard, guideline etc. • People – Awareness (e.g. Password on screen) – Discipline • Technology – Enablers – Management Tools What is Threat? • Could be anything that harm your system e.g. – – – – – User Hacker/ cracker Virus Spam Etc. Key Factors Driving Threat over network • Internet connection speeds are increasing for SMB as prices and technology improves: – DSL, cable modem, T1 (business class connection services) • Increase in real-time Internet applications – Web apps, VoIP, downloads, etc. require real-time security processing • Everything become online Nowadays threat to you IT system • Non-Computerized system – – – – Masquerade Social Engineering Theft System malfunction (disaster, power interruption) • IT Network Threat – Network Level – Application Level Threat – Network Level • Denial of Services – Services has been disable by excessive workload. • Information sniffing – Information has been tapped and viewed by unauthorized person • Unauthorized access – Low level worker can access to critical information. Sample of Threats Snooping 202.104.10.5 m-y-p-a-s-s-w-o-r-d 203.152.145.121 Telnet 203.152.145.121 username:daeng password: Sample of Threats (cont.) 3-way handshake 3-way handshake SYN REQ SYN ACK ACK DATA TRANSFER WWW Sample of Threats (cont.) SYN attack 203.152.145.121 2 202.104.10.5 SYN ACK D=202.104.10.5 S=203.152.145.121 WAIT Internet WWW Attacker 1 SYN REQ D=203.152.145.121 S=202.104.10.5 Sample of Threats (cont.) Smurf Attack ICMP REPLY D=203.152.149.1 S=192.168.1.1 ICMP REPLY D=203.152.149.1 S=192.168.1.2 ICMP REPLY D=203.152.149.1 S=192.168.1.3 ICMP REPLY D=203.152.149.1 S=192.168.1.4 Internet 203.152.149.1 ICMP REPLY D=203.152.149.1 S=192.168.1.5 ICMP REPLY D=203.152.149.1 S=192.168.1.6 ICMP REPLY D=203.152.149.1 S=192.168.1.7 ICMP REPLY D=203.152.149.1 S=192.168.1.8 192.168.1.0 ICMP REQ D=192.168.1.255 S=203.152.149.2 Threat – Application Level - Virus • Virus vs Worms..? – Virus • Viruses are computer programs that are designed to spread themselves from one file to another on a single computer. • A virus might rapidly infect every application file on an individual computer, or slowly infect the documents on that computer, • but it does not intentionally try to spread itself from that computer to other computers. – Worms • Worms, on the other hand, are insidious • because they rely less (or not at all) upon human behavior in order to spread themselves from one computer to others. • The computer worm is a program that is designed to copy itself from one computer to another over a network (e.g. by using e-mail). Threat – Application Level – Spam Mail • E-mail spoofing – Pretend to be someone e.g. bill_gate@microsoft.com, • Spam Mail – Unsolicited or unwanted e-mail or Phising Threat – Application Level - Desktop Desktop Threat Viruses, worms, Trojan, Backdoor Cookies Java Script and Java Applet Zombies network Key logger (Game-Online) How to overcome Threat? • We need “control” which are – Policy & Process security control to provide guideline and framework – People to control user behavior – Technology will be a tool in order to enforced Policy throughout the organization effectively. Policy & Process Control • Policy Compliance – ISO 17799 • Compliance Checking – CobiT Audit Tools • NIST security standard guideline – NIST – 800 series • Organization Control – Business Continuity Plan People Control • Security Awareness Training • Security Learning Continuum – Awareness, Training, Education • Responsibility Control – Need to know basis People Control - Example (2) • Don't install free utilities on your computer • Run the current version of supported antivirus software and set it for regular, automatic updates • Assign a complex, hard-to-guess password to your computer (on-screen, pool) • Be alert for "phishing" scams that can result in identity theft • Promptly apply security "patches" for your operating system. • Activate your system’s firewall (Windows XP & Macintosh OS X) Technology Control • Computer Security is the process of preventing and detecting unauthorized use of your computer • Prevention measures help you to stop unauthorized users (intruders) from accessing any part of you computer network • Detection helps you to determine whether or not someone attempted to break into your system, if they were successful, and what they may have done. • Network and Host Based Security – Security Devices (Hardware) or Security Software Network Security Protection • • • • • Firewall (Access control) IDS/IPS VPN & SSL VPN (Data Encryption) Anti-Spam (preventing un-wanted email) QoS (Quality of Services - Bandwidth Management) • Web Content Filtering • IM & P2P Firewall (Access Control) Web Traffic— customers, partners, employees Email Traffic Applications/Web Services Traffic partners, customers, internal Remote user VPN Traffic remote and mobile users Internal security threat Contractors/disgruntled employees Type of firewall Packet Filter • Type of firewall – Packet filtering – Application Firewall – Stateful Inspection • Type of implementation – – – – Packet Filter Screened host Dual home Host Screen Subnet (DMZ) References: CISSP Certification Screened Host Dual home Host Screened Subnet Basic Firewall Implementation Intrusion Detection & Intrusion Prevention Solution Known Attacks Laptop Desktop Host IPS Zero-day Attacks Server Core DOS/DDOS Edge Branch Office Network IPS IDS/IPS • Detection & Prevention System • Signature & Behavior & Anomaly based Virtual Private Network (VPN) • Encryption & Decryption • Public Key & Private Key • Encryption Technology – DES – 3DES – AES Anti-Spam Source: Symantec/ Brightmail How serious spam is? • Why do they spam? – 0.0005$ vs 1.21$ -> 0.02B vs 48.4B – 1/100,000 count as success • How much does spam is? <spamcorp.net> – ~6 e-mail/sec 360 e-mail/min 21,600 e-mail/hr • How do they get my e-mail? – Webboard, forum, etc. • Does spam legal? • How to Protect yourself from getting spam? Why Spam Matters for Business • Before: a nuisance -> Today: a serious business problem Problems 1) Lost Employee Productivity Symptoms • Employees deleting spam • Employees complaining about spam 2) Unnecessary IT Costs • • • • 3) Phishing and email fraud • Employees and customers falling victim to fraud and identify theft IT administrator salary Mail server CPU Storage Bandwidth Business Impacts • Employees are spending 50 or more hours per year dealing with spam • With AntiSpam solutions costing $10-15 per year – significant positive ROI • IT administrators responding to help desk tickets to fight spam with no tools • Spam requiring constant upgrading of mail infrastructure capacity • Damage to brand • Support cost Phising Example Phising Example Phishing Example (2) Spam control Web-Content Filtering • Cracks and Hacks Tools Website – Spyware, Trojan, Virus, etc. • Banner & Advertising – Adware, Toolbar, Spam – Subscribe, Credit card no., etc. • Drugs, Gambling, Weapon, etc. • Pornography, Nude, Adult Materials • Shopping Online (Credit card issues) FortiGuard Web Filtering Enhancements • Block Override – Authoritative user logs in to enable site block override – Bypasses filter block on a user’s session and lasts until timer expires • Rate Image – URL rating capabilities are extended to include image URLs contained in web page – rates gif, jpeg, png, bmp, and tiff images • Web Filter Consolidation – Web filter menu items of URL Exempt, URL Block, and Web Pattern have been consolidated to a single menu item to speed configuration • Active Directory Integration – Single sign-on – Policy based on AD User/Group – Requires FSAE agent software Web Filtering: Banned Word Desktop Security • • • • • Anti – Virus VPN - Client Personal Firewall IDS Web-Filtering – Small group, Home used, Computer Laboratory, etc. URL Filtering Instant Messaging(IM)/Peer-to-Peer(P2P) • IM – Virus – Exploit – Voice Chat • P2P – Bandwidth Usage – Spyware – BackDoor Enterprise IM, P2P Challenges Viruses, worms Worms programmed to chat Virus via malicious URL Rootkit via file install Internet Traffic bottlenecks Confidentiality breech Lack of visibility / management tools • • • • Lack of usage & user controls Protecting against new threats Gaining control of bandwidth usage Management & reporting insight IM & P2P Access Control Gartner’s Analysis Regulations Don’t Matter, but Auditors Do Convergence Brings Evolutionary Efficiencies Cyberthreat Hype Cycle Conclusion • PPT • Security system without performance degradation • "You don't put brakes on a car to go slower, you put brakes on a car to go faster, more safely. Along the same lines, IT security is not meant to slow down a company, but rather to enhance and facilitate the growth of a company... safer growth."--Quoted from Gartner Group's Information Security Show, June 2001