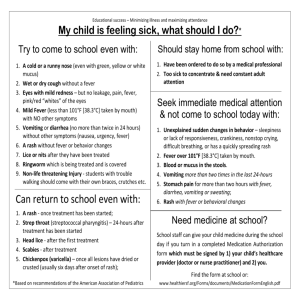
Those Bumps Aren't Moguls!
advertisement

Those Bumps aren’t Moguls! An Algorithmic Approach to Rashes David Robinson MD Department of Emergency Medicine University of Texas Medical School at Houston 31rst Annual Emergencies in Medicine Conference Park City, Utah General ‘Bump’ Terms • Rash: An eruption on the skin; more extensive than a single lesion • Lesion: Single small, diseased area • Macule: Circumscribed area of change without elevation • Papule: Solid raised lesion ≤1 cm • Plaque: Circumscribed elevated confluence of papules ≥1 cm • Nodule: Solid raised lesion ≥1 cm • Pustule: Circumscribed area containing pus • Vesicle: Circumscribed fluid-filled area ≤1 cm • Bulla: Circumscribed fluid-filled area ≥1 cm • Petechia: Small red/brown macule ≤1 cm that does not blanche 4 Major Rash Algorithms a. Erythematous b. Vesiculo-bullous c. Petechiae/Purpura d. Maculopapular Your working at ABEM general when… • ‘sick baby with red skin in room 5’ • Red Skin, ‘skin is peeling off – when I push on it’, blisters • Fever • The 2 key historical points? Erythematous Rashes Erythema (from the Greek erythros, meaning red) is redness of the skin, caused by hyperemia of the capillaries in the lower layers of the skin Erythematous Rash Type of rash? Fever? Special Finding? Nikolsky sign Yes Staphylococcal SSS (children) TEN (adults) Yes No Erythematous Rash TSS Kawasaki disease Scarlet fever Yes TEN No Anaphylaxis Scombroid Poisoning Alcohol Flush No Erythematous Rash with fever Positive Nikolsky Sign – the sick ones • Staph SSS (children <5) – Aka dermatitis exfoliativa neonatorum – Diffuse scarlatiniform erythema – No mucous membranes – Shallow skin cleavage • TEN (adults) – MC associated with sulfa drugs – First around face/eyesshoulders and UE – Mortality 30-35% Erythematous Rash with fever No Nikolsky sign • Toxic Shock Syndrome – Diffuse erythematous rash • Kawasaki Disease – High fever x 5 days – Red eyes, Cracked lips, Dry tongue • Scarlet Fever – Pink-red ‘sandpaper’ rash – Flushed face, strawberry tongue – Follows sore throat or impetigo Erythematous Rash Type of rash? Fever? Special Finding? Nikolsky sign Yes Staphylococcal SSS (children) TEN (adults) Yes No Erythematous Rash TSS Kawasaki disease Scarlet fever Yes TEN No Anaphylaxis Scombroid Poisoning Alcohol Flush No Erythematous Rash, No Fever and No Nikolsky Sign • Anaphylaxis – 2 or more body systems • Scombroid poisoning – Spoiled dark fleshed fish – Intense histamine reaction 30-40 min after ingestion – Flushing, headache, abd cramps – Self limited, antihistamines • Alcohol Flush – MC seen in Asians (East) – Self limited http://dermatology.cdlib.org/126/case_presentations/scrombroid/ferran.html Erythematous Rash, +/- Fever and (+) Nikolsky Sign • Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) – Associated with drugs – Life threatening shearing of epidermis from dermis in more than 30% of body – Affects mucous membranes – TX: plasmaphoresis, IVIG, stop drug, ICU admit http://dermatology.cdlib.org/126/case_presentations/scrombroid/ferran.html A two-fer… Bed 3 • 6 yo with fluid filled vesicles on face, scalp, torso, upper arms • Fever • unvaccinated What are the diagnostic clues ? Bed 9 • 60 yo with sharp back and chest pain • Blisters over specific area of chest – follows dermatome • No fever Fever and rash distribution Vesiculo-Bullous Rash Definitions: Circumscribed fluid filled sac less than 1 cm (vesicle) or greater than 1 cm (bullous) Bullous erythema multiforme Vesicles of Hand, foot and mouth Vesiculo-Bullous Rash Type of rash? Fever? Special Finding? Necrotizing fasciitis Hand, Foot, and Mouth Distribution Localized Varicella/Chicken Pox Small Pox Disseminated GC Yes Purpura Fulminans/ DIC Diffuse Vesiculo-Bullous Rash Bullous Pemphigus Pemphigus Vulgaris Diffuse No Contact Dermatitis Zoster Localized Burns Dyshidrotic Eczema Vesiculo-Bullous rash Febrile and Localized • Necrotizing Fasciitis – Rapidly progressing – Polymicrobial, gpA strept IV ABX • Hand, Foot and Mouth – – – – Children <10 Coxsackie A16 Vesicles to hands, feet Symptomatic tx http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6a/Necrotizing_fasciitis Vesiculo-Bullous rash Febrile and Diffuse • Varicella/ Chicken pox • Smallpox – Variola v – Born after 1972? • Disseminated GC – Also seen as palpable purpura • Purpura Fulminans / DIC – Fever, shock, rapid SQ hemorrhage, tissue necrosis, DIC – MC meningococcal or G(-) organisms – Trauma, multiorgan failure Vesiculo-Bullous Rash Type of rash? Fever? Special Finding? Necrotizing fasciitis Hand, Foot, and Mouth Distribution Localized Varicella/Chicken Pox Small Pox Disseminated GC Yes Purpura Fulminans/ DIC Diffuse Vesiculo-Bullous Rash Bullous Pemphigus Diffuse No Pemphigus Vulgaris Contact Dermatitis Zoster Localized Burns Dyshidrotic Eczema Vesiculo-Bullous rash Not Febrile and Localized • Contact Dermatitis – Often linear at point of irritation • Zoster – VZV – Follows dermatome pattern • Burns • Dyshidrotic Eczema – Pruritic blisters on hands and feet, possibly scaly – Unknown etiology Vesiculo-Bullous rash Not Febrile and Diffuse • Bullous Pemphigus (~60s) – Neg Nikolsky’s, pruritic – Oral lesions in 1/3 • Pemphigus Vulgaris (>40 y) – Autoimmune blistering of skin (flaccid bullae) and mucous membranes – Penicillamine, ACE inh – Treat as burns, immunosuppressant therapy Hey Doc…I got these Bumps on my skin • Afebrile • What are the distinguishing features for these ‘bumps’ • Are they Bumps? – Palpable or Nonpalpable? • Do they Blanch? Petechial / Purpuric rash Petechia: small (< 3 mm) red or purple spot on body due to minor hemorrhage of blood vessel Purpura: Larger hemorrhagic lesions (3-10mm) Ecchymosis: largest (>10mm) Petechial / Purpuric rash Type of rash? Fever? Special Finding? Meningiococcemia Palpable? Disseminatd GC Endocarditis RMSF Palpable Yes HSP TTP Purpura Fulminans/DIC Petechial / Purpuric Rash Not palpable HSP ITP Not palpable No Vasculitis Palpable Palpable • • • • • Petechial / Purpuric rash Febrile and… Meningococcemia – Hemorrhagic, petechial with bullae – From endotoxin release Disseminated GC Endocarditis – Osler’s nodes, roth spots, palpable purpura RMSF – Early: Small, flat non-pruritic macules on wrists forearms and ankles – Late: spreads to trunk, petechial HSP – Kids (2-10) – Vascular palpable purpura – Assoc. GI and joint pain Petechial / Purpuric Febrile and Not Palpable • TTP – Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, neurologic sx, HUS – Tx with plasma exchange, immunosuppressants – 2° TTP assoc with ca, platelet agg inh, immunosuppresants, HIV, SLE • Purpura Fulminans / DIC – Associated with G- sepsis – Debridement, eschar/amput often necessary • HSP (anaphylactoid purpura) – Systemic vasculitis, children – Associated with infection (pharyngitis) – Triad: purpura, arthritis, abd pain Petechial / Purpuric rash Type of rash? Fever? Special Finding? Meningiococcemia Palpable? Disseminatd GC Endocarditis RMSF Yes Palpable HSP TTP Purpura Fulminans/DIC Petechial / Purpuric Rash Not palpable HSP ITP Not palpable No Vasculitis Palpable Petechial / Purpuric rash Not Febrile and… Palpable • Vasculitis – Vascular damage to capillary sized vessels Not Palpable • ITP (idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura) – Autoimmune in 60% – ½ new cases in children, 70% end in remission What are these bumps? Macule: Circumscribed area of change without elevation Papule: Solid raised lesion ≤1 cm Nodule: Solid raised lesion ≥1 cm Plaque: Circumscribed elevated confluence of papules ≥1 cm Morbilliform: has both macular and papular features Drug eruption Pityriasis Maculopapular Rash Type of rash? Fever / ill? Yes Special Finding? Distribution? other finding? Yes: Central SJS, EM Target lesions? Peripheral Maculopapular Viral exanthum Lyme Disease (erythema migrans) No: Meningococcemia RMSF Syphilis Lyme disease (erythema migrans) Rash Flexor: Peripheral No Scabies, Eczema Lesion Distribution? Extensor: Psoriasis Central Drug reaction Pityriasis Maculopapular Rash and Fever Type of rash? Fever / ill? Yes Special Finding? Distribution? other finding? Yes: Central SJS, EM Target lesions? Peripheral Maculopapular Viral exanthum Lyme Disease (erythema migrans) No: Meningococcemia RMSF Syphilis Lyme disease (erythema migrans) Rash Flexor: Peripheral No Scabies, Eczema Lesion Distribution? Extensor: Psoriasis Central Drug reaction Pityriasis Maculopapular Rash with Fever and Central distribution • Viral exanthum – From Gr: ‘breaking out’ – Measles, rubella, erythema infectiosum, roseola… • Lyme Disease (erythema migrans) – Target lesions (EM) 3-30 d after bite – Progresses to neuro (10-15%), cardiac complications Maculopapular Rash with Fever and Peripheral Distribution Target Lesions • Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) – Caused from drugs, infections, malignancies No Target Lesions • Meningococcemia • RMSF • Syphilis • Lyme Disease • Erythema multiforme Clinical presentation, history, and presence of toxicity or neurologic deficits will clue the practitioner to the correct diagnosis Maculopapular Rash and No fever Type of rash? Fever / ill? Yes Special Finding? Distribution? other finding? Viral exanthum Lyme Disease (erythema migrans) Yes: Central SJS, EM Peripheral Target lesions? No: Meningococcemia RMSF Syphilis Lyme disease (erythema migrans) Maculopapular Rash Flexor: Peripheral No Scabies, Eczema Lesion Distribution? Extensor: Psoriasis Central Drug reaction Pityriasis Maculopapular Rash No Fever and Central Lesions • Drug Reaction – Fixed or centrally located • Pityriasis rosea – Assoc. with URI, ha, n,v – Herald’s Patch (2-10 cm oval red) seen – Last 6 weeks Maculopapular Rash No Fever and Peripheral Lesions Lesions on Flexor Surfaces • Scabies • Eczema Lesions on Extensor Surfaces • Psoriasis – Immune mediated, pruritic – Red and white scaly plaques, patches – 30% with arthritis – Tx with ointments, cr, phototherapy Bonus clues to bump identification Clues to Diagnosis Rash Patient Age 0 to 5 years: Meningococcemia, Kawasaki disease, viral exanthem >65 years: Pemphigus vulgaris, sepsis, meningococcemia, TEN, SJS, TSS Rash Characteristics Diffuse erythema: Staphylococcal SSS, staphylococcal or streptococcal TSS, necrotizing fasciitis Mucosal lesions: EM major, TEN, SJS, pemphigus vulgaris Petechiae/purpura: Meningococcemia, necrotizing fasciitis, vasculitis, DIC, RMSF Symptom Hypotension Meningococcemia, TSS, RMSF, TEN, SJS Key Summary Points • Rash with fever is a bad thing • Organize rashes to the 4 major types: – – – – erythematous macular/papular petechial/purpura vesicular-bullous • Secondary signs (Nikolsky, distribution, location (peripheral vs central, extensor vs flexor) Now, go hit those bumps References and Acknowledgments • Hanson, S, Nigro, J. Pediatric Dermatology. Medical Clinics of North America. 82(6):1381-1403, 1998 • Lampell, MS.Childhood Rashes that Present to the ED. Pediatric EM Practice. EBMedicine.net 4:3,2007 • CDC homepage (www.cdc.gov/meningitis) • Papulosquamous Diseases. dermatitis emedicine.medscape.com/article/1108312-overview • Murphy-Lavoie, HM. “Approach to Rashes”. Notes from lecture Oct 27,2008 . ACEP Scientific Assembly • Special thanks to Dr. Ronald Rapini, MD Chair, Dermatology at University of Texas Medical School at Houston for various photos