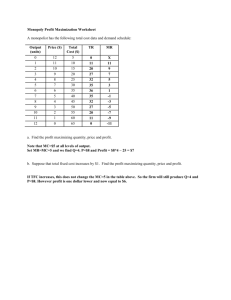
Profit Maximization in a Monopoly
advertisement

Profit Maximization in a Monopoly Profit Maximization in a Monopoly • A firm with market power will price above cost but by how much? • A firm with no competition still faces a demand curve—so as it raises its price, it will sell fewer units • Higher prices are not always better for a seller – raise the price too much and the profits will fall, lower the price and profits will fall Profit Maximization in a Monopoly • To maximize profit: – A firm should produce until revenue from an additional sale is equal to the cost of an additional sale – MR = MC • For a smaller firm, revenue = price (MR=P) • When a firm’s output of a product is large relative to the entire market’s output of that product, an increase in the firm’s output will cause the MP of that product to fall Profit Maximization in a Monopoly • So….a firm that produces a large share of the markets total out of a product, revenue from the sale of an additional unit is less than the current market price (MR < P) • To calculate the firm’s profit maximization: – 1. first need to figure out marginal revenue Using Market Power to Max. Profits • Marginal Revenue is the revenue gain on new sales plus the revenue loss on previous sales • Shortcut to find MR: • If the demand curve is a straight line, then the revenue curve is a straight line that begins at the same point on the vertical axis as the demand curve but with twice the slope Using Market Power to Max. Profits Elasticity of Demand • Consumers with serious diseases are relatively insensitive to the price of lifesaving pharmaceuticals – will continue to buy in large quantities even when the price increases • When consumers are relatively insensitive to the price, what type of demand? Inelastic demand Elasticity of Demand • “You can’t take it with you” and “other people’s money” are two influences on demand that make the demand curve more inelastic • The more inelastic the demand curve, the more monopolist will raise its price above MC Elasticity of Demand The Costs of Monopoly • Monopolists gain less from the monopoly pricing than the consumer loses • Monopolies are bad because compared with competition, monopolies reduce total surplus, the total gains from trade (consumer surplus plus producer surplus) The Costs of Monopoly • Key Point: – SOME of the consumer surplus has been transferred to the monopolist as profit. – But some of the consumer surplus is not transferred, it goes to neither the consumer nor to the monopolist, it goes to no one and is lost – Deadweight loss The Costs of Monopoly Profit Maximization in a Monopoly Notes Profit Maximization in a Monopoly • A firm with market power will price above cost but by how much? • A firm with no competition faces a _____________as it raises it price, it will sell fewer _________ • Higher prices are not always better for a seller – raise the price too much and the profits will ___________, lower the price and profits will ___________ Profit Maximization in a Monopoly • To maximize profit: – A firm should produce until revenue from an additional sale is equal to the cost of an additional sale – ______________________ • For a smaller firm, ___________ (MR=P) • When a firm’s output of a product is large relative to the entire market’s output of that product, an increase in the firm’s output will cause the MP of that product to fall Profit Maximization in a Monopoly • So….a firm that produces a large share of the markets total output of a product, revenue from the sale of an additional unit is less than the current market price (___________) • To calculate the firm’s profit maximization: – 1. first need to figure out ___________ Using Market Power to Max. Profits • Marginal Revenue is the revenue gain on new sales plus the revenue loss on previous sales • Shortcut to find MR: Using Market Power to Max. Profits Elasticity of Demand • Consumers with serious diseases are relatively insensitive to the price of lifesaving pharmaceuticals – will continue to buy in large quantities even when the price increases • When consumers are relatively insensitive to the price, what type of demand? Elasticity of Demand • “______________________” and “______________________” are two influences on demand that make the demand curve more inelastic • The more inelastic the demand curve, the more monopolist will ________ its price above MC Elasticity of Demand The Costs of Monopoly • Monopolists ___________from the monopoly pricing than the consumer ______ • Monopolies are bad because compared with competition, monopolies reduce ___________, the ___________from trade (______________________plus ______________________) The Costs of Monopoly • Key Point: – SOME of the consumer surplus has been transferred to the monopolist as profit. – But some of the consumer surplus is not transferred, it goes to neither the consumer nor to the monopolist, it goes to no one and is lost – ______________________ The Costs of Monopoly