here - Kent City School District
advertisement
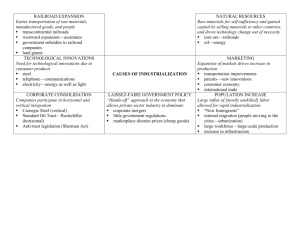
Chapter 6 A New Industrial Age Write a list in your binder of your favorite 5 inventions After the Civil War, America is still an agriculturally based society By the 1920’s America was in the midst of an industrial explosion Reasons for the explosion: 1. Wealth of Natural Resources 2. Government support for business 3. Growing urban population Edwin L. Drake successfully used a steam engine to drill for oil near Titusville, PA This breakthrough started an oil boom that spread to Kentucky, Ohio, Illinois, Indiana, and Texas Petroleum-refining industries arose in Cleveland and Pittsburgh America also had abundant deposits of coal and iron 1887 prospectors discovered iron ore deposits more than 100 miles long and up to 3 miles wide in the Mesabi Range of Minnesota All while coal production skyrocketed; 33millon tons in 1870 to more than 250 million tons in 1900 Iron is a dense metal, but it is soft and tends to break and rust; also contains other elements like carbon Removing the carbon from Iron makes steel Bessemer process was a cheap and efficient manufacturing process to make steel from iron Technique involved injecting air into molten iron to remove the carbon and other impurities Bessemer process was used to make more than 90% of America’s steel Railroads, became the biggest customers for steel http://www.jmhdezhdez.com/2013/06/home-insurance-building-chicago.html New inventions affected the very way people lived and worked Thomas Alva Edison 1. Established the world’s first research lab 2. Perfected the incandescent light bulb 3. Made electricity safer and less expensive with the help of George Westinghouse Harnessing electricity completely changed the nature of business Electricity now appears in the workplace and in homes Allowed for faster urban travel, and manufacturers to locate plants anywhere Christopher Sholes, typewriter, changed the world of work Alexander Graham Bell, telephone, created a platform for a global communications network Both inventions create new jobs Chapter 6 A New Industrial Age 1. 2. 3. A National Network Romance and Reality Railroad Time Local transit becomes faster and reliable Westward expansion becomes possible Realizing the importance of railroads, the government made huge land grants and loans to railroad companies May 10, 1869 crowds cheered as the Central Pacific and Union Pacific Railroads met at Promontory, Utah This meeting was the first transcontinental railroad http://www.history.com/shows/america-the-story-of-us/videos/transcontinentalrailroad?m=5189719baf036&s=All&f=1&free=false ROMANCE Dreams of… Available land Adventure A new life A fresh start REALITY Dreams made possible by… Harsh lives of railroad workers Chinese and Irish immigrant labor More than 2,000 employees killed More than 20,000 injured Communities still operated on its own time Noon in Boston was nearly 12 minutes later than in New York 1869 Professor C.F. Dowd proposed the 24 time zones Railroads strongly backed Dowd’s idea 1918 Congress officially adopts “railroad time” 1. 2. 3. New Towns and Markets Pullman Credit Mobilier Industry grows rapidly trying to keep pace with RxR’s demand for parts RxRs inspire growth, new towns establish new markets and new economic opportunities RxRs ignite trade and interdependence by connecting previously isolated cities, towns and settlements Towns began to specialize in particular products (Chicago/Stockyards, Minneapolis/Grain) Without the RxR, cities like: 1. Abilene, Kansas 2. Flagstaff, Arizona 3. Denver, Colorado 4. Seattle, Washington would not be in existence. Built a factory for manufacturing railroad cars Built a nearby town for his employees; modeled after European industrialist concepts Pullman provided almost all of workers’ basic needs Town strictly under the control of Pullman, created for Pullman’s want of control and profit Desire for profit and control leads RxR magnates and wealthy industrialists toward corruption Company made up by stockholders in the Union Pacific RxR Scandal included 20 members of congress Stockholders of the Union Pacific Railroad used the company to make huge, unearned profits for themselves http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Spgdy3HkcSs Move to 5:30 1. 2. 3. 4. RxR abuses Granger Laws Interstate Commerce Act Panic and Consolidation The Grangers, members of the Grange were farmers disturbed by railroad corruption Began demanding governmental control over the industry Sold cheaply purchased governmental lands to other businesses rather than to settlers Fixed prices helping keep farmers in debt Discriminated rates; charged different customers different prices; charged more for short hauls than long. A response to railroad abuses Established maximum freight and passenger rates and prohibit discrimination Made constitutional in the case of Munn v Illinois; states now regulate the RxRs This act established the right of the federal government to supervise railroad activities and established a five-member Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC). Not until 1906 did the ICC grow any real power; thanks to President Theodore Roosevelt, who allowed the ICC to create maximum railroad rates RxR companies faced many problems 1. ICC (tiny problem) 2. Corporate abuses 3. Mismanagement 4. Overbuilding 5. Competition Many companies were on the brink of bankruptcy Financial problems contributed to a nationwide economic collapse; the Panic of 1893 Firms such as J.P. Morgan & Company reorganized the RxRs Seven powerful companies held sway over 2/3’s of the nation’s tracks Chapter 6 A New Industrial Age Someone read the bottom of 241-top 242 Entered the steel business in 1873 Witnessed the Bessemer process first hand in Britain brought it to America By 1899 Carnegie produced more steel than all of Britain with his Carnegie Steel Company Searched to find ways to make better products more cheaply Attracted talented people by offering them stock in the company, while also encouraging competition within his company Vertical Integration – When a company expands into areas that are at different points on the same production path; a manufacturer owns its supplier and/or distributor. helps companies reduce costs and improve efficiency by decreasing transportation expenses and reducing turnaround time Example of Vertical Integration The merger of Live Nation and Ticketmaster created a vertically integrated entertainment company that manages and represents artists, produces shows and sells event tickets. Horizontal Integration - The acquisition of additional business activities that are at the same level of the value chain in similar or different industries. If the products offered by the companies are the same or similar, it is a merger of competitors. If all of the producers of a particular good or service in a given market were to merge, it would result in the creation of a monopoly Someone read this section of the book Carnegie’s success was contributed too 1. Hard work 2. Shrewd investments 3. Innovative business practices Others believed it was Social Darwinism Grew from Charles Darwin’s theory of biological evolution Some individuals of species flourish and pass their traits along to the next generation, while other do not “Natural selection” weeded out less-suited individuals and enabled the best-adapted to survive Herbert Spencer used Darwin’s biological theories to explain the evolution of human society Became a way for economists to justify laissez faire economics William G. Sumner – success and failure in business were governed by natural law What personal qualities do you think a person would need to become a billionaire in today’s world? Forbes 400 4,000 new millionaires since the Civil War Hard work pays off Riches were a sign of God’s favor The poor must be lazy or inferior people who deserved less Read the top of 243 If you can’t beat’em, join’em Many industrialists often pursued horizontal integration in the form of mergers A firm that bought out all its competitors could achieve a monopoly Complete control over an industry’s production, wages, and prices Holding company – a corporation that did nothing but buy out the stock of other companies (JP Morgan) Trusts – joining with competing companies and turning over stock to a groups of trustees, who ran all the companies as one corporation (Rockefeller) 1880 Rockefeller’s Standard Oil company controls 90% of the refining business Paid employees extremely low wages Undercut employees by selling his oil at cheap costs. Once he controlled the market, prices soared Made it illegal to form a trust that interfered with free trade between states or with other countries. Did not work easily though, it was difficult to determine what a trust was; the Supreme Court did not rule on the side of the federal government in cases brought against trusts The South had a devastated economy from the Civil War It was at the mercy of Northern railroad companies goods to markets. It also paid added costs for raw materials due to high tariffs Read this section Workers learn from ownership and join there forces Exploitation and unsafe working conditions drew workers together across regions Workers labored 6-7 days a week, for 12+ hours No vacation, sick leave, or reimbursement for injuries suffered on the job Injuries were common at work Poor working conditions and mindless tasks were major factors in work related deaths 1882 – 675 laborers were killed in work=related accidents each week First large-scale national organization of laborers, the National Labor Union (NLU) Formed in 1866 the NLU persuaded Congress to legalize an 8 hour work day for government workers Samuel Gompers – led the Cigar Makers’ International Union to organize with other unions American Federation of Labor (AFL) President Focused on collective bargaining or negotiation between labor and management Craft Unions only focused on skilled laborers Many felt skilled and unskilled laborers needed representation Eugene V. Debs – American Railway Union (ARU) 1894 led workers on a strike for higher wages and won “The strike is the weapon of the oppressed” Debs and other labor activists turned to Socialism Socialism – an economic and political system based on government control of business and property and equal distribution of wealth Socialism at its extreme = communism Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), aka Wobblies – miners, lumberers, and cannery and dock workers Created by a group of radical unionists and socialists in Chicago Led by William “Big Bill” Haywood Allowed African Americans to join Unionization spreads to the West and is successful 1,000 Japanese and Mexican workers unionize and strike in the Sugar Beet fields in California Chinese and Japanese miners in Wyoming strike searching for the rights that other unions are receiving. This movement aids in strengthening labor unions Read about – The great Strike of 1877 The Haymarket Affair The Homestead Strike http://www.history.com/topics/knights-oflabor/videos#homestead-strike and The Pullman Company Strike Class Discussion to follow Eugene V. Debs Mary Harris (Mother) Jones Take out a sheet of paper and we will construct an answer to the question listed below as a class What appears to have been the chief goal of big business during the late 1800s, and why did the government begin making efforts to prevent big business from achieving this goal? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Make sure these terms and names are in your Binder Sherman Antitrust Act Samuel Gompers Thomas Alva Edison American Federation Alexander Graham Bell of Labor George M. Pullman 10. Mary Harris Jones Transcontinental 11. Triangle Shirtwaist railroad Factory (249) Interstate Commerce Act Andrew Carnegie 7. 8. 9. The Expansion of Industry (pages 230-233) - How did the growth of the steel industry influence the development of other industries? Answer The growth of the steel industry influenced the development of other industries because steel created demand for coal and iron ore; it was used extensively in the railroad, agriculture , food, and construction industries The Expansion of Industry (pages 230-233) - How did inventions and developments in the late 19th century change the way people worked? Answer Inventions and developments in the late 19th century changed the way people worked by creating new jobs for women, drew people to cities, and made jobs less backbreaking The Expansion of Industry (pages 230-233) What factors allowed the United States to industrialize very rapidly during the last half of the 19th century Answer The factors that allowed the United States to industrialize very rapidly during the last half of the 19th century were abundant natural resources, such as coal and iron. These resources gave inventors and entrepreneurs the means to develop and implement new products and production methods. The explosion of new inventions and manufacturing processes enabled industry to grow rapidly. The harnessing of electricity allowed business owners to locate their factories wherever they wanted and to produce more goods more efficiently than ever before. A rapidly growing urban population provided potential markets for new inventions and industrial goods, as well as a steady supply of cheap labor for industry. Government policies, including laws and Supreme Court decisions, generally favored business and industry - The Age of the Railroads (pages 236-240) - Why did people, particular farmers, demand regulation of the railroads in the late 19th century? Answer People particularly farmers demanded regulation of the railroads in the late 19th century because railroad companies were very powerful and often corrupt The Age of the Railroads (pages 236-240) - Why were attempts at railroad regulation often unsuccessful? Answer Attempts at regulating the railroads were often unsuccessful because railroads had a great deal of political power and fought legal battles against regulation. Big Business and Labor (pages 241-249) - Why were business leaders such as John D. Rockefeller called robber barons? Answer Business leaders such as John D. Rockefeller were called robber barons because of the use of ruthless tactics to earn great wealth Big Business and Labor (pages 241-249) - Why did the South industrialize more slowly than the North did? Answer The South industrialized more slowly than the North did because the Southern economy and terrain had been devastated by the Civil War and had to be rebuilt. The South had less capital for investment Big Business and Labor (pages 241-249) - Why did workers form unions in the late 19th century? Answer Workers formed unions in the late 19th century because workers realized that they needed to unite to protect themselves and to increase wages, shorten work hours, and improve working conditions. Big Business and Labor (pages 241-249) - What factors limited the success of unions? Answer The factors that limited the success of unions were government support of management, the use of violence and scabs to break strikes. Big Business and Labor (pages 241-249) How did 19th century industrialists encourage competition? How did they discourage competition? Answer 19th century industrialists encouraged competition by running their businesses in such a way that their own employees competed with one another and other businesses were forced to cut costs, run more efficiently, and create better products to compete. 19th century industrialists discouraged competition by driving their competitors out of business by developing monopolies and trusts that destroyed compeition. -