Kinetic Energy
advertisement

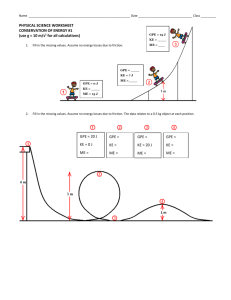
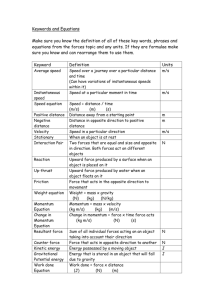
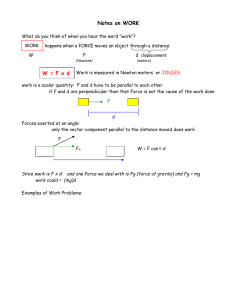
Calculating Energy What did you notice about the TOTAL ENERGY during the skatepark lab? • Total Energy does NOT change! • The amount of KE, PE and THERMAL change, but always add up to the same total! THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it only changes forms Potential Energy Stored Energy Any energy that is STORED UP is Potential Energy! • Gravitational PE – Determined by an object’s height • Elastic PE – Stretching or Compression • Chemical PE – Food (not yet eaten) – Gasoline (not yet burned) – Battery (not yet used) Gravitational PE • Any time an object has height above a reference point. • GPE = M*G*H – Mass (in kilograms) – G (acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s2) – Height (in meters) The UNIT for Energy is JOULE (J)! EXAMPLE 1 • A 0.5-kg squirrel sits at the top of a 10meter tall tree eating an acorn. How much Gravitational Potential Energy does the squirrel have? Step 1: Write the given information and the formula M = 0.5 kg H = 10 m G = 9.8 m/s2 GPE = mgh Step 2: Substitute the given values into the formula GPE = 0.5kg x 9.8 m/s2 x 10 m Step 3: Solve the problem (with units!) GPE = 49 Joules Practice on Your Own 1. Nijah drives her 1000-kg Mini Cooper to the top of a hill 7 meters tall. How much GPE does the Mini have at the top of the hill? 2. Ronnie throws a 1-kg football straight up in the air. How much GPE does the football have when it is 9 meters high? 3. Keanna jumps on a trampoline. If she has a mass of 65 kg and jumps 5 meters into the air, how much GPE can she obtain? Kinetic Energy Energy of Motion Which has more kinetic energy: • A falling ping pong ball or • A falling bowling ball? • Increasing mass increases KE! • How do you get your bike to go really really fast down a hill? • Increasing speed increases KE! How much kinetic energy an object has depends on 2 things: • Its MASS (kg) and • Its VELOCITY (m/s)! KE = ½ * M * 2 V The UNIT for Energy is JOULE (J)! EXAMPLE • A 3000 kg delivery truck drives down the street at 15 m/s. How much Kinetic Energy does it have? Step 1: Write the given information and the formula M = 3000 kg V = 15 m/s KE = 1/2mv2 Step 2: Substitute the given values into the formula KE = ½ x 3000kg x (15 m/s)2 Step 3: Solve the problem (with units!) KE = ½ x 3000kg x 225 = 337,500 J Practice on Your Own 1. Debra pedals her bike at 20 m/s. If she and her bike have a mass of 100 kg, how much KE does she have? 2. A 6-kg alley cat is chasing a mouse at a speed of 4 m/s. How much KE does the cat have? 3. Timara kicks a 1.5-kg soccer ball giving it a velocity of 3 m/s. How much KE does the ball have?