The Desert Biome - ashleyapenvironmentalscience
advertisement

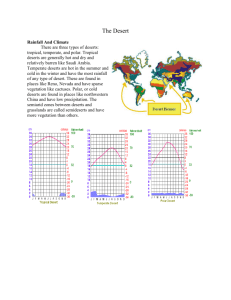
By: Max Garfinkle Low latitude climate that has an average temperature of 64 degrees Fahrenheit. Has very low temperatures at night and very high temperature during the day due to the lack of precipitation. Only about 1 inch of rain falls in these areas a year. BARREL CACTUS(FEROCACTUS WISLIZENI) Two to five tall, cylinder with numerous parallel ridges that run down the sides. These ridges are topped with dangerously sharp 34 inch spines. The barrel cactus is also a flowering plant. It has rings of yellow-green or red blossoms at its top. DESERT IRONWOOD(OLNEYA TESOTA) From the pea family. The leaves and flowers resemble those of the sweetpea. They're the tallest trees in the Sonoran Desert, reaching heights of 15 to 25 feet, but they can grow as tall as 30 feet. They are very slow growing, with bluish gray-green leaves, and a wide, spreading crowns. and can live as long as 1,500 years. PALO VERDE(CERCIDIUM MICROPHYLLUM) Has low hanging, dense and twiggy branches and a strange irregular shape. Six to four major stems sprout out about 8 inches (20 cm) from the ground. The crown is 12 to 18 feet (3.7 - 5.5 m) wide. Palo verde can get to be 10-20 feet tall, but grow very slowly and are considered climax species in the desert. CACTUS WREN(CAMPYLORHYNCHUS BRUNNEICAPILLUS) 7-9 inches (18-22 cm) long, the Cactus Wren is the largest wren in the United States. Both sexes look alike. Both are brown and have a white stripe running over each eye. Their throats are white, and their beaks are dark, long and slightly curved. They are very active and curious birds. They quickly investigate anything new in their territory. COYOTE(CANIS LATRANS) Has a tan coat mixed with hairs of rusty brown and gray, and the ends of the hair may be black. The different colors help to hide the coyote in the underbrush, rocks, and grasses. Has large, pointed ears and a bushy tail. Known for their sharp eyesight, keen hearing and a keen sense of smell. Adults can grow to be 4 feet long (including the tail which can be 11 - 16 inches long). They can be 2 feet tall and weigh up to 30 pounds. THORNY DEVIL (MOLOCH HORRIDUS) Has conical spines all over, including spines above each eye and a hump behind its head which is spiny. The tail is also spiny. Its spines make it easy to identify. The color changes on the Thorny Devil's body from yellow to reddish brown to black, depending on which type of soil it is crossing. Lays about 3 to 10 eggs underground, between September and January. The eggs hatch 3 to 4 months later. They reach maturity after 3 years. The Thorny Devil lives for about 20 years. This a basic food web that has general categories which deal with the desert biome. The flora and fauna that I have chosen are interchangeable in this diagram. Most deserts have a lot of mineral deposit due to ground water evaporating out of the soil. These mineral deposits can be mined for our benefit. A good amount of oil is found in the desert biomes due to evaporation of lakes and streams which at one point in time contained a lot of organic material. This oil can be processed and sold. Lastly a lot of history is related to the deserts which gives it a large aesthetic value, especially the deserts in Egypt. Lack of rain water and rapid temperature change provides a difficult climate for plants to grow in. The soil is mostly composed of sand which promotes plant life to store water in their stems for long periods of time. Weather can change very quickly so plant and animal life must be tough enough to withstand this to grow and live. Plant and animal life are quickly fading due to human impact. Mining these deserts for oil and minerals takes away from the delicate balance the plant and animal life must survive because of the harsh climate. Global warming is increasing the extremes of temperature which can cause depletion of aquifers and kill off certain key plants. Desertification is occurring in areas surrounding deserts due to a lack of rain and water in the surrounding areas. Many cultures have made the desert their home throughout history. They have made this environment hospitable by building their homes out of clay and using advanced systems of irrigation to water plants. In other cases people have become nomadic and travel their entire lives through the desert searching for food and water.