Here's
advertisement

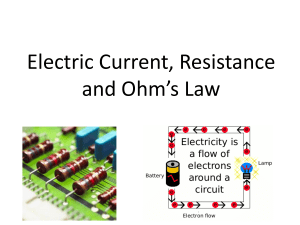
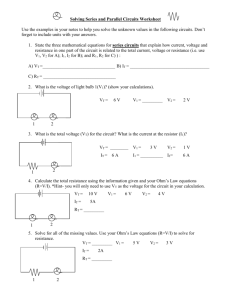
Electronic Technology Welcome to Lesson #1 DC Review – LU 1101 (with Mr. Cooper) Lesson Plan – Kevin C. Cooper Electronic Technology – LU 1101- Introduction and DC Review First Cycle Objectives – Pg. 1 of 2 - Students will: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. List items required for daily shop activities. List the 10 most important shop rules. Identify and follow all safety rules. State the procedure for extra help and make up. Review the shop grading policy. Review Basic Atomic Structure. Review Ohm’s Law, Watt’s Law, Kirchoff’s Laws. Review resistor networks and the use of DVOM’s. Calculate, construct and test series circuits. Calculate, construct and test parallel circuits. Lesson Plan – Kevin C. Cooper Electronic Technology – LU 1101- Introduction and DC Review First Cycle Objectives – Pg. 2 of 2 - Students will: 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Calculate, construct and test combination circuits. Troubleshoot various faults in DC circuitry. Simulate various DC circuits on computers. Practice clean, safe, mature, proper use of lab equipment. Maintain complete, accurate, neat, permanent notes. Write a “Type-5” technical Lab Report. Develop a list of on-line resources. Begin an electronic student portfolio. Pass three written tests. (Safety, Series, Parallel) Identify schematic symbols and diagrams, reactive components, time constants, complex DC circuitry. Things you need every day! • Clean Shop Tee Shirt or Shop Sweat Shirt......every day, no exceptions!!! • Notebook (3 ring binder with paper). • Scientific Calculator. • Pencil and Pen. • Text Book. • Items specified in your student handbook. • Small hand tools and Safety Glasses. • BRAIN. Shop Rules • • • • • • • • • • Follow dress code. (Shop Shirts, No Jackets…) Maintain a business like atmosphere. No horseplay or throwing things. No video games or illegal software. Follow safety rules. Take and keep all notes. Clean the lab every afternoon. Respect the property of others. No food in the lab. No talking while the instructor is talking. Things you need to know: • Mr. Cooper is available for extra help after school every day upon request. • If you are absent for one day, get the notes you missed from another student, and the lab you missed from Mr. Cooper as soon as possible. • If you are not sure what to do, ask your instructor. There are no stupid questions. • Request extra help before you fall behind. Grading Policy • • • • • • • • Student Written Notebook: 10% Student Electronic Portfolio: 10% Daily Theory & Book Assignments: 10% Daily Computer & Web assignments: 10% Daily Lab Circuits & Experiments: 20% Weekly Written Tests: 20% Weekly Lab Reports: 20% Extra projects & missions: +/- 10% Meet this awesome atom. Notes on Mr. Atom: • All materials are made of atoms. • Protons and Neutrons reside in the Nucleus. • Electrons orbit around the nucleus at the speed of light. • Current flow is the movement of free electrons. • Like charges repel, unlike charges attract. (Coulomb’s Law) More notes on Mr. Atom: • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the electrical properties. • Conductors have 1 – 3 valence electrons. • Semiconductors have 4 valence electrons. • Insulators have 5 – 8 valence electrons. • Balanced atoms have an equal number of protons and electrons. • An atom that loses an electron is a positive ion. An atom that gains an electron is a negative ion. Mr. Ohm is our good friend! • Ohm’s Law defines the relationship between Current, Voltage, and Resistance. • Ohm’s Law states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. • Current flow is the movement of free electrons (from negative toward positive). The unit for current flow is the Ampere. The letter “I” stands for Current. Ex: I = 1.5 A. Mr. Ohm is so cool! • Voltage is the force that moves electrons. The unit for voltage is the Volt. The letters “E” and “V” both stand for Voltage. • Resistance is the opposition to current flow. The unit for resistance is the Ohm (shown as the Greek letter Omega). The letter “R” stands for resistance. • Formulas you need to know forever: E=I*R, I=E/R, R=E/I. Mr. Watt is also very cool! • P = Power in Watts. P=I*E • Here’s those groovy magic pies again! • Note: E = V • Note: There are three power Formulas… P = I*V, P = I^2*R, P = E^2/R Metric Prefixes are great! • • • • • • • Mega = 1,000,000 = 1 EE 6 = M Kilo = 1,000 = 1 EE 3 = K (Units Volt, Ohm, Amp have no exponent.) milli = 0.001 = 1EE-3 = m micro = 0.000 001 = 1 EE-6 = u nano = 0.000 000 001 = 1 EE-9 = n pico = 0.000 000 000 001 = 1 EE-12 = p Color First Stripe Second Stripe Third Stripe Black 0 0 x1 Brown 1 1 x10 Red 2 2 x100 Orange 3 3 x1,000 Yellow 4 4 x10,000 Green 5 5 x100,000 Blue 6 6 x1,000,000 Purple 7 7 Gray 8 8 White 9 9 Fourth Stripe Gold 5% Silver 10% Lots of Resistors!!! • Series resistors: Rt=R1+R2+R3 • Parallel resistors: Rt=1/(1/R1+1/R2+1/R3) LOVE YOUR METER! • An ammeter must be connected in series to measure current!! • A voltmeter is connected in parallel to measure voltage! • An ohmmeter must never be connected to a “live” circuit when measuring resistance!! Series circuits are very exciting! • Current flow is constant in series. • Voltage drops add up to the total voltage. • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Rt = R1+R2+R3 It = Et/Rt It = IR1 = IR2 = IR3 ERx = IRx*Rx PRx = IRx*ERx Calculate the EIRP values! • • • • 1. Rt=R1+R2+R3=3K-Ohms 2. It=Et/RT=4mA 3. It=IR=IR2=IR3=4mA 4. ER1=IR1*R1=4V, ER2=IR2*R2=4V, ER3=IR3*R3=4V • 5. P=I*E=16mW each=64mW total Parallel circuits are super awesome! • Voltage drops in a parallel circuit are constant. • Branch currents in a parallel circuit add up to the total current. • • • • • 1. Et=ER1=ER2=ER3 2. IRx=ERx/Rx 3. It=IR1+IR2+IR3 4. RT=ET/It 5. PRx=IRx*ERx Calculate the EIRP values! • 1. ET=ER1=ER2=ER3=12V • 2. IR1=ER1/R1=1mA, IR2=ER2/R2=1mA, IR3=ER3/R3=1mA • 3. It=IR1+IR2+IR3=3mA • 4. Rt=Et/It=4K-Ohms • 5. P=I*E=3mW each=9mW total. • Check: RT=1/(1/R1+1/R2+1/R3) DC Review Assignments: • • • • • Assignments: Read Chapters 1 – 8. Do Chapter Self-Tests. (1-8) Write Q&A. Open Basic Circuit Challenge. Do the following assignments. Have your instructor verify and record each assignment before proceeding to the next. • Color Code, Ohm’s Law 1, Ohm’s Law 2, Power 1, Power 2, Series Sources, Series 1, Series 2, Parallel 1, Parallel 2, S-P 1, S-P 2. More fantastic DC circuits! • Do the following assignments. Have your instructor verify and record each assignment before proceeding to the next. • Open DC Circuits Challenge. • Complete: Series 1,2,3; Parallel 1,2,3; Series-Parallel 1,2,3,4,5; Basic Networks; TS Series; TS Parallel; TS S-P.