Lesson 6 Grammar PowerPoint
advertisement

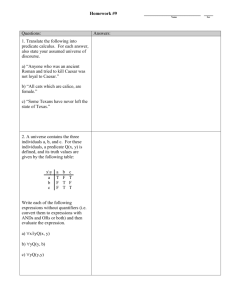
Simple and Compound Sentences Simple Sentences A simple sentence is a sentence that only has one clause which contains one subject and one predicate. The dog ran. Subject: dog Predicate: ran What is a subject and predicate? The subject tells what or who the sentence is about, while the predicate describes the action of the subject. The penguin listens to music. Subject: penguin Predicate: listens to music Simple Sentence Examples The chair is red. Subject: the chair Predicate: is red The baby cried. Subject: the baby Predicate: cried He plays baseball. Subject: he Predicate: plays baseball Mike hurt his leg. Subject: Mike Predicate: hurt his leg Simple sentence practice: Decide if the underlined part of the sentence is the subject or the predicate. The girl sang loudly. A) Subject B) Predicate The music sounded great. A) Subject B) Predicate I had a lot of fun. A) Subject B) Predicate Next Great job! Sorry, that’s incorrect Compound Sentences A compound sentence is a sentence that connects two independent causes with a comma and a coordinating conjunction or a semicolon. Jason was tired, and he didn’t feel well. or Jason was tired; he didn’t feel well. Subject: Jason, he Predicate: was tired, didn’t feel well Coordinating Conjunction: and Coordinating Conjunctions Use the acronym to help you remember the seven coordinating conjunctions. For And Nor But Or Yet So Coordinating Conjunctions For- same as because And- means in addition Nor- negative choice But- same as however Or- same as either Yet- means contrast So- the result Things to Remember when Using Coordinating Conjunctions 1) Don’t start a sentence off with a coordinating conjunction. Instead of starting a sentence with these words Use these words and also but however or otherwise so as a result 2) Use a comma before the coordinating conjunction. Example: Kathryn loves to roller blade, but she likes ice skating better. Compound Sentence Examples The game was fun, but it could have been better. or The game was fun; it could have been better. Subject: the game, it Predicate: was fun, could have been better I do not like singing, nor do I like dancing. or I do not like singing; I do not like dancing. Subject: I, I Predicate: do not like singing, do like dancing Compound Sentence Examples I am not as fast as Johnny, yet I am still one of the fastest runners in the class. or I am not as fast as Johnny; I am still one of the fastest runners in the class. Subject: I, I Predicate: am not as fast as Johnny, am still one of the fastest runners in the class Are you going to baseball practice, or are you going to the movies? or Are you going to baseball practice; are you going to the movies? Subject: you, you Predicate: are going to baseball practice, are going to the movies Is it a simple sentence or compound sentence? 1. The boy ran home. A) Simple Sentence B) Compound Sentence 2. We went shopping, and then we went to the party. A) Simple Sentence B) Compound Sentence 3. Ella worked hard, so she got a good grade. A) Simple Sentence B) Compound Sentence 4. I stumped my toe on a really big rock. A) Simple Sentence B) Compound Sentence 5. The stairs are windy, long, and wide. A) Simple Sentence B) Compound Sentence 6. She bought new shoes, but they were too small. A) Simple Sentence B) Compound Sentence Next Slide Great job! Sorry, that’s incorrect I hope you understand simple and compound sentences purr-fectly!