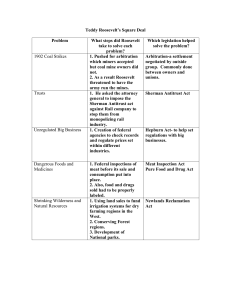
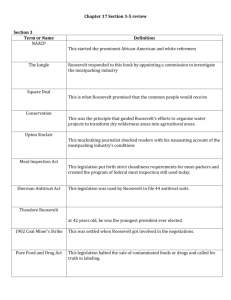
Facts of the Day 6. 77
advertisement

77 Laws separating whites and AfricanAmericans in public facilities and restricting their legal guarantees, such as the right to vote Often part of state statutes Support for these laws were provided in the Plessy v. Ferguson Case, demonstrating the limits of the 14th Amendment Name of the laws are said to be derived from a character in a Minstrel song Restrictions by Southern states on former slaves Designed to replicate the conditions of slavery in the post-Civil War South Various codes prohibited meetings without a WHITE present, while others established SEGREGATED PUBLIC FACILITIES Led to Radical Republican opposition & exclusion of SOUTHERN representation in CONGRESS 78 Also known as the GLASS-STEAGALL ACT Created the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation to guarantee bank deposits (FDIC). The Banking Act of 1933 was part of Roosevelt’s First New Deal. 79 Term used to describe the growth of AFRICANAMERICAN Literature & Arts The center of this movement was Harlem, New York, where many African-Americans moved to during the early 1900s Southern African-Americans brought jazz to Harlem and influenced the music scene; at the same time, writing, sculpting, and photography grew as art forms Writers from the period included Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, and Claude McKay Musicians from this time included Duke Ellington, Bessie Smith, and Louis Armstrong The Great Depression led to the decline of the RENAISSANCE 80 Was a constitution written in 1639 by Connecticut settlers. It was the first formal written CONSTITUTION in the NEW WORLD. The Fundamental Orders of Connecticut stated that a government’s POWER comes from the consent of the governed….not a KING or the BIBLE. 84 Also known as the Ardennes Campaign (1944 – 45) of World War II, this was Adolf Hitler's last counteroffensive in the West by Hitler An attempt to break the Allied lines at the Ardennes Forest. Drive a wedge between the American and British armies Capture the Belgian port of Antwerp Disrupt logistics (supply lines), trap Allied forces – American and British troops Achieve a negotiated peace in the West 86 The 1943 conference was the first time the “BIG THREE”; U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, United Kingdom Prime Minister Churchill, and Soviet Union leader Joseph Stalin. The three leaders planned the D-Day invasion at Normandy and agreed to divide Germany into zones of occupation, if and when the Germany lost WW II. Stalin also agreed to join the war against Japan once German leader Adolf Hitler was defeated. GOAL “Containment” of Communism & the eventual collapse of the Communist world. GOAL spread worldwide Communism 88 Virginia Plan – Called for bicameral legislature based on population and both the chief executive and judiciary to be chosen by legislature New Jersey Plan - called for unicameral legislature with equal representation Plans were united in the GREAT COMPROMISE; the plans form the basis of the modern American legislative structure – US Constitution 89 British impressment of American sailors American frontiersmen wanted more free land, as the West was held by Native Americans and the British The USA suspected the British were encouraging Native American rebellion “War Hawk” Congressional leaders, such as Henry Clay and John Calhoun, pressed for intervention War Hawks desired annexation of Canada & Florida Despite the Embargo Act and Non-Intercourse Act, hostilities could not be cooled The USA sided with France against Britain During the War of 1812, a British ARMADA sailed up the Chesapeake Bay and BURNED the PRESIDENTIAL MANSION (the WHITE HOUSE) Response came in response to the American burning of Toronto The armada proceeded toward Baltimore; America’s Ft. McHenry held firm though bombardment Inspired Francis Scott Key’s “Star Spangled Banner” 90 A proposal to reunite the country AFTER THE civil war by Senators Wade & Davis A proposal to reunite the country by Senators Wade & Davis Required that 50% of a state’s white male voters take a loyalty oath to be readmitted to the UNION Demanded stronger efforts on behalf of states to emancipate slaves Lincoln “pocket-vetoed ” the bill in favor of his “10% Plan” 91 Congressional support agency providing food, clothing, and education for freed slaves AFTER THE CIVIL WAR Ex-slaves states were divided into districts that were managed by assistant commissioners Despite its benefits, the Bureau failed to establish the freed slaves as landowners It organized the African-American vote for the Republican Party, created great animosity toward the Bureau in the South 92 The movement of African-Americans from the South to the industrial centers of the Northeast and the Midwest The African-American population in such cities as Detroit, Chicago, and New York grew during this period The migration led to higher wages, more educational opportunities, and better standards of life for many African-Americans. 93 Further outlined regulations against MONOPOLIES & other UNFAIR business practices, WAS a KEY victory for ORGANIZED LABOR. It exempted labor unions from prosecution under antitrust laws & legalized STRIKES & PICKETING Meant as update for the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 Price discrimination that was destructive to competition was declared illegal Declared interlocking board of directors of direct competitors to be illegal Established Federal Trade Commission to investigate & prosecute instances of unfair competition Served as the grounds for many suits against big corporations 94 95 96 97 Further outlined regulations against MONOPOLIES & other UNFAIR business practices, WAS a KEY victory for ORGANIZED LABOR. It exempted labor unions from prosecution under antitrust laws & legalized STRIKES & PICKETING Meant as update for the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 Price discrimination that was destructive to competition was declared illegal Declared interlocking board of directors of direct competitors to be illegal Established Federal Trade Commission to investigate & prosecute instances of unfair competition Served as the grounds for many suits against big corporations 98 99 100 101 102 American proposal to aid the British, who had little cash for supplies…..during WW II Offered to give the British American supplies in exchange for payment after the war Payment could be made in material goods and services Put the USA on the SIDE of the Allies USA also allowed for Cash & Carry, in which British and French ship could come into the USA’s ports & buy anything that they could carry out GERMANY KNEW of this and was very UNHAPPY! 102 continued In 1941, President Franklin D. Roosevelt forced the LEND-LEASE ACT of 1941 through Congress. The act allowed the president to “lend” or “lease” large amounts of ARMAMENTS to England and other Allied Forces during WW II. To protect these shipments, Roosevelt sent American ships into the war zone, drawing German attacks. The Lend-Lease Act drew the USA away from its position of Neutrality and further involved the nation in World War II prior to the bombing of Pearl Harbor.