Texas and United States Governments
advertisement

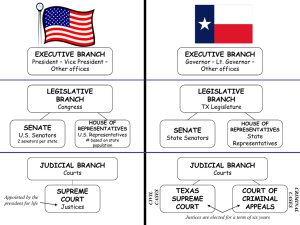
Texas and United States Governments Federalism As a state within the United States, Texas is part of a federal system of government. This means that some powers belong to the federal government and others belong to state governments. Powers for the state are reserved powers, such as establishing legal age for marriage without permission, creating a public school system, and regulating commerce within its borders. Texas cannot create its own money, declare war on other countries or sign treaties. This is reserved for the federal government. Texas Constitution The last constitution written in Texas in 1876 was based on the U.S. Constitution. Role of the constitution is to give government bodies various powers, describe the rights of citizens, and provide a way to make changes through amendments. The constitution emphasizes that political power belongs to the people. (Popular Sovereignty) Separation of Powers The Texas government is like that of the U.S. with its separation of powers by having three different branches of government. Judicial Branch – interprets the laws Legislative Branch – makes the laws Executive Brach – enforces the laws Each branch serves as a check and balance over the other one. Therefore, no branch will gain too much power. The Bill of Rights was added to protect the basic rights of citizens. Judicial Branch Judicial System The judicial branch is made up of courts and judges. It has three purposes: those accused of crimes maybe tried, and if found guilty, punished, and settles disputes. Judicial Branch Civil or Criminal Law Civil law pertains to legal disputes between private citizens, businesses, and governments. Examples of these cases are lawsuits, disputes over money, property, and child cases. Criminal laws are violations against a law. It is concerned with crimes and punishment. There are two types of offenses under criminal law: felony and misdemeanor. Felonies are serious crimes such as murder, arson or kidnapping. This is usually punished by jail time or even the death penalty A misdemeanor is a less serious crime such as gambling, disorderly conduct, or serious traffic violations. These are usually resolved with paying fines, community service or time in county jail. Judicial Branch The Jury System A grand jury considers cases involving felonies and issues an indictment when 9 or more of its 12 members believe the evidence is strong enough to convict. A petite jury decides criminal cases that go to criminal court. Some cases are settled by plea bargaining. This is when the accused confesses for a lesser sentence. Judicial Branch The Court System of Texas Trial Courts – hear cases and reach a decision called a verdict. (with judge or jury) There are three levels of trial courts: municipal (city), county and district. Appeals Courts – hears cases in which the first decision in the first trial is being appealed. Texas has two high courts – Court of Criminal Appeals and the Supreme Court of Texas. Texas Legislature The Function of the Legislative Branch 1. Like that of the U.S. legislature, the Texas legislature is bicameral meaning having two rooms or chambers. The two chambers are the Senate and House of Representatives. (Congress) 2. The legislative branch makes the laws that govern Texas. They approve or reject governors’ appointments, discuss how state money should be spent (schools, prisons, environment) and decide if taxes should be raised or lowered. Texas Legislature The Senate and the House 1. The Senate is composed of 31 members and the House is composed of 150 members all elected by the people. The population count is what determines district lines and the number of legislators in that district. An important duty of the legislature is redistricting. (Redrawing congressional lines determined by population.) Redistricting is important because it could determine what party controls Congress. 2. Congress meets every 2 years unless a special session called by the governor for problems that need immediate solutions. 3. The lieutenant governor is elected by voters of the state, and serves as the Senate’s president. However, the House of Representatives elects a Speaker of the House as their leader. 4. Committees help the legislature carry out the tasks of studying problems and drafting bills. Committees are appointed by the Speaker and lieutenant governor. Texas Legislature How a Bill Becomes a Law 1. There are two major types of proposals. The first is a resolution, used to propose an amendment to the Texas Constitution. The second is a bill, or proposed law. 2. First the bill is introduced to Congress, sent to committee where they hear the pros and cons of the bill. They must then decide if the House or Senate should consider it. Most bills are killed in the committee. 3. If the bill is approved in one house, it must then be sent to the other house for approval. 4. If the House and Senate approve different forms of the same bill, it goes to conference committee which is composed of members from both houses appointed by the lieutenant governor and speaker. They may even alter the bill. If passed there, it must again be passed in both houses. 5. Then the bill goes to the governor for signature. If signed it becomes a law, if vetoed, it does not become a law unless 2/3 of the House and 2/3 of the Senate override the veto. The Executive Branch ► The Function of the Executive Branch The executive branch enforces laws passed by legislature. The Executive Branch The Governor ► The governor is head of the executive branch. The governor serves a 4 year term and there is no limit on the number of terms that can be served. The governor must be a U.S. citizen, 30 or older, and be a resident of Texas for at least 5 years before the election. Our current governor is Rick Perry. The governor makes appointments to boards and commissions which must be approved by 2/3 of the Senate. The governor can also remove officials (ex: judges) with approval of the Senate. The governor can also veto a bill. (cancel) A line item veto allows the governor the reject items in appropriation bills, which deals with how money is spent. The governor can call special sessions where the governor decides what business needs to be discussed. The governor can give pardons or delay an execution. The governor also serves as commander in chief, in control of the Texas Guard.