Convex Mirror
advertisement

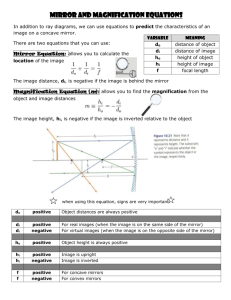
Journal #81 April 22, 2011 You do not need to copy this paragraph Use the concave and convex mirrors on your table. Start with the mirror very close to your eye and slowly back it away. Describe the changes to your image until the mirror is a full arm’s length away Answer to Journal #81 Concave: The image starts off very close to regular size and increases in size. Image becomes completely blurred. Image reforms and is inverted and enlarged. It becomes reduced the farther away you move beyond this point. Convex: The image starts off very close to regular size but reduces as the mirror is pushed back. Also, image is not a true representation of object… slightly skewed. Plane Mirror Reflection is on top of incident light Image formed is: Virtual Upright Same Size Try to fill in this chart from memory… best way to study! Object Placement/Mirror Plane Mirror B/n Concave Mirror and FP At FP of Concave Mirror B/n FP and CC of Concave Mirror At CC of Concave Mirror Beyond CC of Concave Mirror Convex Mirror Real or Virtual Upright or Inverted Size of image compared to size of object Answer Key to Table Object Placement/Mirror Real or Virtual Upright or Inverted Size of image compared to size of object Plane Mirror Virtual Upright Same B/n Concave Mirror and FP Virtual Upright Enlarged At FP of Concave Mirror No Image No Image No Image B/n FP and CC of Concave Mirror Real Inverted Enlarged At CC of Concave Mirror Real Inverted Same Beyond CC of Concave Mirror Real Inverted Reduced Convex Mirror Virtual Upright Reduced How to make a study game Take 4 sheets of blank paper and fold them in half 3 times to create 8 equal sized sections Cut each of the rectangular shapes made by the creases How to make a study game Lay out the individual rectangles in a 4 by 8 grid How to make a study game Remove the bottom row and save them as extras (in case you make a mistake) How to make a study game In the first column, write each of the seven possible situations for mirrors AND/OR draw the set up How to make a study game On the back of those same cards, write IN PENCIL the answers for that card How to make a study game In the other columns, write the three answers each on a separate card for the situation on the left How to PLAY a study game Collect all of the answer cards in a single stack and all of your setup cards in a different stack How to PLAY a study game Shuffle both stacks, then deal out the setup cards in random order How to PLAY a study game Place all of the answer cards on the table Turn over the setup cards and check your answers! Journal #82 April 25, 2011 WITHOUT USING YOUR NOTEBOOK!!! If you know the focal length of a concave mirror, where should you place an object so that its image is upright and larger compared to the object? Will this produce a real or virtual image? Journal #82 Answer Place the object between the focal point and the mirror. The image will be virtual Lens/Mirror Equation (units of length MUST match) f stands for focal length di is the distance from the mirror/lens to the image from do is the distance the mirror/lens to the object 1 i 1 1 o di ( f 1 1 1 o do ( f 1 f (d d ) d ) 1 1 i d ) Image Height Magnification of an image can be found by a series of ratios between the distances of objects and their images and their respective heights as shown below. hi di ho do Helpful Hints for Mirror Probs In the formula, the numbers can tell you the characteristics of the image: Size • Reduced ( |hi| < ho ) • Same Size ( |hi| = ho ) • Enlarged ( |hi| > ho ) Orientation • Upright (hi positive) • Inverted (hi negative) •Focal point for concave mirror is always positive. •Focal point for convex mirror is always negative. Type of Image • Real (di positive, in front of mirror) • Virtual (di negative, behind the mirror) Example problem 1 A concave mirror has a radius of 28cm. An 15cm tall object is placed 25cm from the mirror. Describe the image formed. What will be the height and position of the image? Example problem 2 A convex mirror has a focal length of 32cm. An 17cm tall object is placed 1.0m from the mirror. Describe the image formed. What will be the height and position of the image? HW Problems P. 469 13-16 P. 472 17-21 P. 469 P. 472 Spherical Aberration Special Note: Parallel light rays that are far from the principal axis are not reflected by spherical mirrors to converge at the focal point. This defect is called spherical aberration. To avoid this dilemma, spherical mirrors have been replaced with parabolic mirrors in devices such as telescopes that require extreme accuracy and focus.