lesson plan - WordPress.com
advertisement

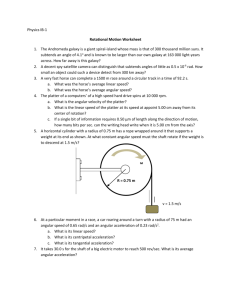
LESSON PLAN This lesson plan is arranged to complete final task Subject : Teaching Physics in English Lecturer : Tatik Juwariyah, M. Sc Name : Indah Putri Pratiwi NIM : 09690033 Major : Physics Education PHYSICS EDUCATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FACULTY ISLAMIC STATE UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA 2012 LESSON PLAN School : Majenang High School Subject : Physics Topics : Circular Motion Grade/Program : X/ Science Semester : 1st Meeting : 6th Time : 4 x 45 minutes (twice meeting) 1. Standard of Competency 1.1 To apply concept and basic principle of kinematics and dynamics body as point. 2. Base Competency 2.1 To analyze physics quantity of circular motion with constant velocity and constant acceleration 2.2 To apply concept of circular motion in daily activities 3. Indicators First meeting (2x45 minutes) 3.1 To define the definition of circular motion. 3.2 To explain the difference between circular motion and rectilinear motion. 3.3 To calculate frecuency, angular speed, period, centripetal acceleration, and angle in the uniform circular motion. 3.4 To indicate the relation between angular speed and linear velocity, angular acceleration and linear acceleration. Second meeting (2x45 minutes) 3.5 To explain the difference between uniform circular motion and nonuniform circular motion. 3.6 To compare the equation of position, velocity, and acceleration in the regular changing rectilinear motion and angle, angular speed, and angular acceleration in the nonuniform circular motion. 3.7 To calculate angle, angular speed, and angular acceleration at t time in the nonuniform circular motion. 3.8 To compare angular speed and linear velocity in the relation of wheels motion. 4. Aims of Instructional First meeting (2x45 minutes) 4.1 Students should be able to explain the difference between uniform circular motion and nonuniform circular motion 4.2 Students should be able to explain the difference between circular motion and rectilinear motion. 4.3 Students should be able to calculate frecuency, angular speed, period, centripetal acceleration, and angle in the uniform circular motion. 4.4 Students should be able to indicate the relation between angular speed and linear velocity, angular acceleration and linear acceleration. Second meeting (2x45 minutes) 4.5 Students should be able to explain the difference between uniform circular motion and nonuniform circular motion. 4.6 Students should be able to compare the equation of position, velocity, and acceleration in the regular changing rectilinear motion and angle, angular speed, and angular acceleration in the nonuniform circular motion. 4.7 Students should be able to calculate angle, angular speed, and angular acceleration at t time in the nonuniform circular motion. The relation of wheels motion. 4.8 Students should be able to compare angular speed and linear velocity in 5. Main of Instructional 5.1 Uniform Circular Motion 5.2 Nonuniform Circular Motion 5.3 The Relation of Wheels Motion 6. Material of Instructional 6.1 Uniform Circular Motion In Uniform circular motion, its linear speed is constant, while its linear velocity always changes. The equation of angle is define by: 𝜃 = 𝜔𝑡 Explanation: θ = angle (rad) ω = angular speed (rad/sec) t = time (sec) The relation between the angle and with the path length is define by: 𝑠 = 𝜃𝑅 The relation between angle degree units and radian 360° = 2𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑 1 𝑟𝑎𝑑 = 360° = 57.3° 2𝜋 The relation between linear speed or translational and angular velocity: 𝑠 = 𝜃𝑅 ∆𝑠 ∆𝜃 = 𝑅 ∆𝑡 ∆𝑡 𝑣 = 𝜔𝑅 Explanation: ω = angular speed (rad/sec) v = linear speed (m/s) In uniform circular motion, there is period T. Period is the time required for one complete revolution. Meanwhile, angular velocity is an angular magnitude which is travel distance per unit time. The relation between angular velocity and period is as follows 𝜔= 2𝜋 𝑜𝑟 𝜔 = 2𝜋𝑓 𝑇 Explanation : T = period (s) f = frequency (Hz) The unit convertion from rps (revolution per second) to rpm (revlution per minute) 1 𝑟𝑝𝑠 = 60 𝑟𝑝𝑚 1 𝑟𝑝𝑠 = 2𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑 𝑟𝑎𝑑 = 120𝜋 𝑠 𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑢𝑡𝑒 Centripetal Acceleration The direction of centripetal acceleration always strives to the center. The centripetal acceleration is formulted 𝑎𝑠 = 𝜔𝑣 = 𝜔2 𝑅 = 𝑣2 𝑅 6.2 Nonuniform Circular Motion • The formulation of speed, path length, and the quantity of traveled angle basically is equal to the formulation for the regular change rectilinear motion. Linear speed and length path after t unit of time is formulated as follows 𝜔𝑡 = 𝜔0 + 𝛼𝑡 1 𝜃 = 𝜔0 𝑡 + 𝛼𝑡 2 2 • The relation between the quantity of angular acceleration and linear acceleration is define by 𝑣 = 𝜔𝑅 ∆𝑣 ∆𝜔 = 𝑅 ∆𝑡 ∆𝑡 𝑎 = 𝛼𝑅 6.3 The Relation of Wheels Two wheels or more that have one axle, will be valid the following relation 𝜔𝐴 = 𝜔𝐵 𝑣𝐴 B A. 𝑅𝐴 𝑣 = 𝑅𝐵 ; 𝑣𝐴 ≠ 𝑣𝐵 𝐵 Two wheels or more that have contact will be valid the following equation 𝜔𝐴 ≠ 𝜔𝐵 𝑣𝐴 = 𝑣𝐵 𝑜𝑟 𝜔𝐴 𝑅𝐴 = 𝜔𝐵 𝑅𝐵 B A. Two wheels or more that connected with a rope will be valid the following equation 𝜔𝐴 ≠ 𝜔𝐵 B A. 𝑣𝐴 = 𝑣𝐵 𝑜𝑟 𝜔𝐴 𝑅𝐴 = 𝜔𝐵 𝑅𝐵 7. Instructional Model 7.1 Mind Map 7.2 Direct Instruction 7.3 Discussion 8. Learning Activities First meeting (2x45 minutes) Teacher’s activities Opening Students’s activities Greeting Respon greeting Pray together Pray together Checking of student’s Raise the hand Time if persence his/her name was called Tell about the purpose of Listen seriously lesson and give to students motivation study more and more Ask some questions Give attention about circular motion that Answer will give aperception to questions students their knowledge teacher’s according 15 minuets Main activities Explain about material Give attention globally by using mind 60 map. Explain circular about motion and the difference Listen well and attentively between circular motion and rectilinear motion. Give time to students for Think about what that asking unknowns something that unknowns from the material that have been told by teacher Continuing study about Listen uniform circular motion attentively well and and its quantity, such as angle, frequency, angular speed, periode, centripetal and acceleration. Also give example, and the way how to solve that Give time to students for Think about what that asking unknowns something that unknowns from the material that have been told by teacher Indicate the relation between angular speed and linear Listen well and attentively velocity, angular acceleration and linear acceleration. Organize students to form Collect with their group some group Give tasks about the material that have been Do the tasks with their group minutes told and ask students to discuss that Closing Give time to each group Give attention and ask to present their answer as what the result of discussion. from the tasks Guide to students conclude the materi that have been told that Conclude unknowns the materi that have been studied and 15 discussed Ask students to restudy minutes Listen well about material that have been studied Closing saying by hamdallah and salam Say hamdallah and answering salam Second meeting (2x45 minutes) Techer’s activities Opening Students’s activities Greeting Respon greeting Pray together Pray together Checking of student’s Raise the Time 15 minuets hand if persence his/her name was called Tell about the purpose of Listen seriously lesson and give to students motivation study more and more Review about the Listen well previous material Main activities Explain Nonuniform about circular motion and indicate the difference between uniform circular motion and nonuniform circular Listen seriously well and 60 minuets motion. Give time to students for Think about what that asking unknowns something that unknowns from the material that have been told by teacher Continuing study about Listen the attentively equation nonuniform of well and circular motion, such as angle, angular speed, and angular acceleration at t time. Also give example, and the way how to solve that Give time to students for Think about what that asking unknowns something that unknowns from the material that have been told by teacher Compare velocity the and linear angular Listen well and attentively speed in the relation of wheels motion principle. Give tasks about the material that have been Write the question told Give time to student to Do the task Pay answer the task Ask some students to come forward to write their answer in the white board. attention and compare their answer with answer their friends’s Explain the right answer Listen well and the materi attentively Closing Guide to students conclude the materi that Conclude that have been studied 15 minuets have been told. Ask students to restudy Listen well about material that have been studied Closing by saying hamdallah and salam Say hamdallah and answering salam 9. References 9.1 Purwanto, Budi. 2009. Theory and Application of Physics for Grade X of Senior High School and Islamic Senior High School. Solo: Tiga Serangkai. 9.2 Students worksheet 10. Evaluation 10.1 Cognitif Assessment Put a cross mark (x) on letter a, b, c, d, or e in the correct answer. 1. In Uniform circular motion the following quantities which are constant, except... a. Frequency b. Centripetal acceleration c. speed d. angular velocity e. linear velocity 2. An object is bind with a rope, then it is spinning horizontal. If the object is spinning with constant frequency and the rope length is twice from the beginning, the quantity of the object linear velocity becomes... a. Twice from the beginning b. Three from the beginning c. Four from the beginning d. Five from the beginning e. Six from the beginning 3. In uniform circular motion, the centripetal acceleration is... 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. a. Its direction always touches the path b. Its direction alwayscome out the circle c. Changes the quantity of linear velocity d. Changes the angular velocity e. Changes the direction of linear velocity An object rotates with speed 20 rps. If the path radius is 50 cm, the centripetal acceleration of the object is... a. 80 π m/s2 b. 160 π m/s2 c. 800 π m/s2 d. 800 π2 m/s2 e. 1.600 π2 m/s2 A particle rotate with 2 rps in the circular path with the radius 8 m.The particle has angular velocity andlinear velocity as muc as.... a. 4 π rad/s and 32 π m/s b. 8 π rad/s and 4 π m/s c. 16 π rad/s and 32 π m/s d. 24 π rad/s and 16 π m/s e. 32 π rad/s and 4 π m/s In the Bohr atom model, an electron move around the proton in circular orbit with the 5.29 x 10-11 m and its speed are 2.18 x 106 m/s. The centripetal acceleration of the electrons is... a. 10.21 x 1021 ms-2 b. 9.89 x 1022 ms-2 c. 8.09 x 1022 ms-2 d. 8.98 x 1022 ms-2 e. 7.98 x 1022 ms-2 A satellite orbited on the earth surface in the 600 km high. The time needed to travel one time rotation is 90 minutes. The satelite speed is... a. 986 m/s b. 968 m/s c. 869 m/s d. 689 m/s e. 698 m/s A wheel rotated with 1,800 rpm speed slowing down with homogenous speed into 900 rpmin 2seconds. Amount rotation that the wheel travelled in 2 seconds is... a. 415/ π b. 45 c. 45/ π d. 90 e. 90/ π Wheel A and B are contacted each other so if A rotates, B will rotate too. The radius of wheel A is 6 cn, and the radius of wheel B is 4 cm. If the wheel A frequency is 8 Hz, the angular speed of wheel A and B are... a. 16 π rad/s and 26 π rad/s b. 16 π rad/s and 24 π rad/s c. 24 π rad/s and 16 π rad/s d. 24 π rad/s and 36 π rad/s e. 36 π rad/s and 45 π rad/s 10. Wheel B and C have one axis and rotate together. Wheel A and B are conected chain. If RA = 25cm, RB=15 cm, RC=40 cm, and wheel C is turning 60 rpm, the angular velocity of wheel A is... a. 5 π/6 rad/s b. 6 π/5 rad/s c. 3π/2 rad/s d. 2 rad/s e. 5 π rad/s Solve the problems based on the instruction. 1. A wheel with radius 20 cm, rotating on its axis with speed 6,000/ π rpm. Determine a. Its angular speed, frequuency, and period; b. A linear speed of a point on a wheel and the travel path length in 10 seconds; c. Rotation number in 10 seconds 2. A wheel has radius 1 m, is moving with the first speed 50 rot/s. In 10 seconds, speed became 20 rot/s. Howmuch is a. The linear speed of a point on the radius end; b. The linear acceleration or the angular acceleration; c. How long the wheel will stop; d. The revolution until it will stop. 3. An antique bicycle moves with the speed 36 km/hour. Yhe bicycle has big radius as R1= 50 cm and small radius R2= 10 cm. a. Calculate the turning speed of wheel 1 and wheel 2 b. Calculate the rotation number of wheel 1 and wheel 2 in 15 minutes. 10.2 Phycomotoric Assessment Score Num Performance ber 1 1. Skill on experiment 2. Cooperation on experiment 2 Assessment directive : Num Aspect Criteria Score ber 1. 2. Skill on measurement dan doing Fast and correct the task Do not quite fast and corret Cooperation in experiment 4 3 Slow and correct 2 Good cooperation 4 Do not quiet cooperation 3 No coopertaion 2 Maximum Score 8 Psycomotoric Score = 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑡 𝑠𝑡𝑢𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡 ′ 𝑣 𝑔𝑜𝑡 𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 × 100 Psycomotoric Score > 80, passed score 60 – 74 =C score 75 - 85 =B score 86 - 100 =A 10.3 Affective Assessment Score Num Attitude ber 1 1 Attendance 2 Manner in learning proses 3 Manner on asking 4 Cooperation 2 3 Num Aspect Criteria Score ber 1 2 3 4 Attendance Manner in learning proses Manner on asking Cooperation Discipline 3 Do not quite discipline 2 Indisciplinary 1 Good manner 3 Do not quite manner 2 Impolite 1 Good manner 3 Do not quite manner 2 Impolite 1 Favourable 3 Do not quite favourable 2 Unfavourable 1 Maksimum Score 12 Affective Score = Criteria of Score : 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑡 𝑠𝑡𝑢𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡 ′ 𝑣 𝑔𝑜𝑡 𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 Score 86 - 100 = A Score 75 - 85 = B Score 60 – 74 =C Score < 60 =D × 100 Yogyakarta, 15 Januari 2012 Headmaster Teacher ............................... Indah Putri Pratiwi, S.Pd.Si. NIP. NIP.