Rocks and Weathering

Changing Earth’s Surface
Table of Contents
Rocks and Weathering Chapter
13 Lesson 1
Erosion and Deposition
Chapter 14
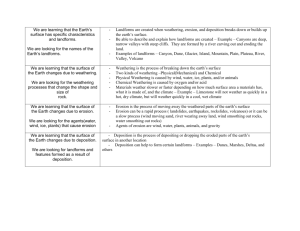
Rocks and Weathering
Cycle of Erosion and Deposition
What are the steps in the cycle of erosion and deposition?
Rocks and Weathering
Forces of Physical
Weathering
Chemical Weathering
• Oxygen causes rust to form which makes rocks soft and a reddish brown color.
• Carbon Dioxide creates carbonic acid which weathers marble and limestone.
• Living organisms can produce weak acids.
• Acid rain is rain combined with pollutants which speeds up weathering.
Rocks and Weathering
Weathering and Surface Area
The diagram shows what would happen if a rock cube broke into smaller cubes. Which rock would have a higher weathering rate?
What does permeable mean?
• How does that change weathering rates?
Rate of Weathering
•
Rate of weathering depends on
CLIMATE
and
TYPE of ROCK
.
•
Chemical weathering occurs faster in climates that are hot and wet.
Water Erosion
Factors Affecting Runoff
What are the five main factors affecting runoff, and what are some examples?
How can we prevent Runoff?
Planting vegetation, decreasing slopes, decreasing size of areas that are just dirt.
Water Erosion
Stream Formation
Which arrows indicate the direction of sheet erosion? Where are rills and gullies in the picture? Streams and rivers?
Tributaries?
Make sure you know the vocab that is in
BOLD .
Water Erosion
Oxbow Lakes
What happens in step 4 of this diagram to form an oxbow lake?
What does an
Oxbow Lake look like?
Alluvial Fan
• A wide sloping deposit of sediment formed when a stream leaves a mountain range.
Water Erosion
Water Deposition
Deposition creates landforms such as the Mississippi River delta.
Water Erosion
Rolling Through the
Hills
Identify the two missing features on the image.
Wave Erosion
Wave Erosion
Where is the greatest energy of the waves concentrated?
Florida Landforms
Florida Landform
Most of Florida is relatively flat, but over time the changing sea levels have shaped a varied landscape.
Florida Landforms
Landforms Across Florida
This map shows a few of Florida’s many landforms.