lect - 9 genital system
advertisement

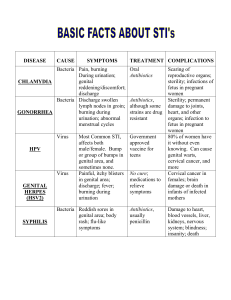
Anatomy of Genital System BMS 231: 2015/2016 DR SOBIA IKRAM DR AQEELA BANO DR SADIA FARHAN Table of Contents 1. Objectives for this lesson 2. Function of the Reproductive system and the organs involved in both Male and Female genital system. 3. Gross Anatomy and functions of the Organs involved in male genital system. 4. Gross Anatomy and functions of the Organs involved in Female genital system. Objectives When you finish this lesson, you should be able to • Describe the Functions of the Male and Female Reproductive system • Identify the Gross Anatomy and Explain the Functions of the organs involved in the Male Genital system. • Identify the Gross Anatomy and Explain the Functions of the organs involved in the Female Genital system. Functions of genital system To ensure survival of the species To produce egg and sperm cells To transport and sustain these cells Production of hormones Hormones permits the secondary sex characteristics, such as breast development in women and beard growth in men. GROSS ANATOMY OF GENITAL SYSTEM Male & Female genital system Composed of : 1. Reproductive organs called gonads that produce gametes (reproductive cells) and hormones 2. Ducts that transport gametes 3. Accessory glands and organs that secrete fluids Male genital system Functions – To produce, maintain and transport sperm (the male reproductive cells) and protective fluid (semen) – To produce and secrete male sex hormones responsible for maintaining the male reproductive system Male genital organs Consists of 1. A pair of testes 2. A network of excretory ducts • • • 3. 4. 5. 6. Epididymis Ductus deferens Ejaculatory ducts Seminal vesicles Prostate Urethra Penis Male Genital system Testes / testicles (Gonads) Produce sperm (Spermatogenesis) Sperm production begins at puberty and continues throughout the life of a male Male Genital system Testes / testicles (Gonads) Produce testosterone • Hair patterns and voice changes • Development of the male accessory organs (prostate, seminal vesicles etc.) • Stimulates the effect of protein building in the body that is responsible for the greater muscle development and strength of the male Male Genital system • Duct System – Epididymis • Sperm mature in epididymis – Ductus Deferens • Transports mature sperm to the urethra – Ejaculatory ducts • empty into the urethra Male Genital system Seminal vesicles – Attached to vas deferens – Produce a sugar rich fluid (fructose) that provides energy to sperm Male Genital system Prostate Gland Makes seminal fluid . Male Genital system Urethra Tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body Also carries semen out of the body Female genital system Functions 1. Produces the female egg cells 2. Transports the eggs to the site of fertilization 3. The fertilization of an egg by a sperm, occurs in the fallopian tubes Female genital system Functions 1. After fertilization, provides a place for a baby to develop 2. If fertilization does not take place, the system is designed to menstruate 3. Produces female sex hormones that maintain the reproductive cycle. Female genital system Consists of 1. Uterus (corpus and cervix) 1. vagina 2. Ovaries 3. Fallopian tubes Female genital system Coronal section Sagittal section Female genital system Uterus – Hollow, pear-shaped organ that is the home to a developing fetus • Divided into two parts: – the cervix, the lower part that opens into the vagina – Main body of the uterus, called the corpus. – The corpus can easily expand to hold a developing baby. – A channel through the cervix allows sperm to enter and menstrual blood to exit Female genital system Vagina – Canal that joins the cervix (the lower part of uterus) to the outside of the body – Also is known as the birth canal. Female genital system Ovaries – Oval-shaped glands that are located on either side of the uterus – Produce eggs and hormones. Female genital system Fallopian Tubes – Narrow tubes that are attached to the upper part of the uterus and serve as tunnels for the egg cell to travel from the ovaries to the uterus – Fertilization of an egg by a sperm, normally occurs in the fallopian tubes – The fertilized egg then moves to the uterus, where it implants into the lining of the uterine wall