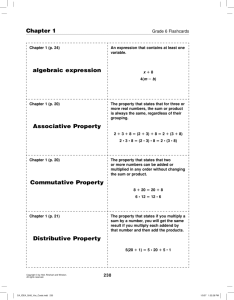
How to Use This Presentation
• To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects
select “View” on the menu bar and click on “Slide Show”,
or simply press F5 on the top row of your keyboard.
• To advance to the next slide click the left mouse button
once.
• From the Chapter screen you can click on any section to go
directly to that section’s presentation.
• Blank or “missing” areas of a slide will remain hidden until
the left mouse button is clicked.
• You may exit the slide show at any time by pressing
the Esc key.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Resources
Bellringers
Chapter Presentation
Transparencies
Standardized Test Prep
Image and Math Focus Bank
CNN Videos
Visual Concepts
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Body Defenses and Disease
Table of Contents
Section 1 Disease
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 1 Disease
Bellringer
Brainstorm as many different names of diseases
as you can. Don’t forget to list both physical
illnesses and mental illnesses. How do you think
people get these diseases?
Record your answers in your science journal.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 1 Disease
Objectives
• Explain the difference between infectious diseases
and noninfectious disease.
• Identify five ways that you might come into contact
with a pathogen.
• Discuss four methods that have helped reduce the
spread of disease.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 1 Disease
Causes of Disease
• Some diseases, such as most cancers and heart
disease, are not spread from one person to another.
They are called noninfectious diseases.
• A disease that can be passed from one living thing to
another is an infectious disease. Infectious diseases
are caused by agents called pathogens.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 1 Disease
Pathways to Pathogens
• Air Some pathogens travel through the air, such as
when someone sneezes.
• Contaminated Objects Drinking glasses,
doorknobs, keyboards, combs, and towels that have
been used by an infected person can all pass
pathogens.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 1 Disease
Pathways to Pathogens, continued
• Person to Person You can become infected with
some illnesses by kissing, shaking hands, or touching
the sores of an infected person.
• Animals Some pathogens are carried by animals.
• Food and Water Bacteria growing in foods and
beverages can cause illness.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 1 Disease
Putting Pathogens in Their Place
• Pasteurization The method of using heat to kill
bacteria is called pasteurization.
• Vaccines and Immunity The ability to resist or
recover from an infectious disease is called
immunity. A vaccine is a substance that helps your
body develop immunity to a disease.
• Antibiotics An antibiotic is a substance that can kill
bacteria or slow the growth of bacteria.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Bellringer
Make a list in your science journal of all the
different ways pathogens might enter the body. Is
there anything that you do to avoid getting sick? Do
you know of anything that your body automatically
does to get rid of pathogens?
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Objectives
• Describe how your body keeps out pathogens.
• Explain how the immune system fights infections.
• Describe four challenges to the immune system.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
First Lines of Defense
• Your skin is made of
many layers of flat
cells. The outermost
layers are dead. As a
result, many
pathogens that land
on your skin have
difficulty finding a live
cell to infect.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Failure of First Lines
• Sometimes, skin is cut or punctured and
pathogens can enter the body. Cell parts in the
blood called platelets help seal the open wound so
that no more pathogens can enter.
• The cells and tissues that recognize and attack
foreign substances in the body belong to the
immune system.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Cells of the Immune System
• Macrophages engulf and digest many
microorganisms or viruses that enter your body.
• T cells coordinate the immune system and attack
many infected cells.
• B cells are immune-system cells that make
antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that attach to
specific antigens.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Responding to a Virus
• If virus particles enter your body, some of the
particles may pass into body cells and begin to
replicate.
• Other virus particles will be engulfed and broken
up by macrophages. This is just the beginning of the
immune response.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Fevers
• A moderate fever of
one or two degrees
actually helps you get
well faster because it
slows the growth of
some pathogens.
• A fever also helps
B cells and T cells
multiply faster.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Memory Cells
• Memory B cells are cells in your immune system
that “remember” how to make an antibody for a
particular pathogen.
• If the pathogen shows up again, the memory B cells
produce B cells that make enough antibodies in just 3
or 4 days to protect you.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Primary and Secondary Immune Response
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
You may stop the video at any time by pressing
the Esc key.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Challenges to the Immune System
• Allergies happen when the immune system
overreacts to antigens that are not dangerous to the
body.
• Autoimmune Disease is a disease in which the
immune system attacks the body’s own cells. In an
autoimmune disease, immune-system cells mistake
body cells for pathogens.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Challenges to the Immune System,
continued
• Cancer is a disease in which the cells begin
dividing at an uncontrolled rate and become invasive.
• AIDS The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
causes acquired immune deficiency syndrome
(AIDS). HIV infects the immune system itself, using
helper T cells as factories to produce more viruses.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Body Defenses and Disease
Concept Map
Use the terms below to complete the concept map on
the next slide.
hemophilia
pathogens
immune system
fungi
viruses
protists
infectious diseases
noninfectious diseases
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Concept Map
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Concept Map
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
End of Chapter 27 Show
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Body Defenses and Disease
CNN Videos
• Scientists in Action: In Search of Nature’s Cures
• Science, Technology, and Society: Computer
Healing
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
Reading
Read each of the passages. Then, answer the
questions that follow each passage.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
Passage 1 Bacteria are becoming resistant to many
human-made antibiotics, which means that the drugs
no longer affect the bacteria. Scientists now face the
challenge of developing new antibiotics that can
overcome the resistant strains of bacteria. Antibiotics
from animals are different from some human-made
antibiotics.
Continued on the next slide
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
Passage 1, continued These antibiotics bore holes
through the membranes that surround bacterial cells,
causing the cells to disintegrate and die. Bacterial
membranes don’t mutate often, so they are less likely
to become resistant to the animal antibiotics.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
1. In this passage, what does mutate mean?
A to change
B to grow
C to form
D to degrade
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
1. In this passage, what does mutate mean?
A to change
B to grow
C to form
D to degrade
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
2. Based on the passage, which of the following
statements is a fact?
F Bacterial membranes are on the inside of the
bacterial cell.
G Bacterial membranes are on the outside of the
bacterial cell.
H All strains of bacteria mutate.
I Bacterial membranes never change.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
2. Based on the passage, which of the following
statements is a fact?
F Bacterial membranes are on the inside of the
bacterial cell.
G Bacterial membranes are on the outside of the
bacterial cell.
H All strains of bacteria mutate.
I Bacterial membranes never change.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
3. Based on the passage, which of the following
sentences is false?
A Antibiotics from animals are different from humanmade antibiotics.
B Antibiotics from animals bore holes in bacterial
membranes.
C Bacterial membranes don’t change very often.
D Bacteria rarely develop resistance to human-made
antibiotics.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
3. Based on the passage, which of the following
sentences is false?
A Antibiotics from animals are different from humanmade antibiotics.
B Antibiotics from animals bore holes in bacterial
membranes.
C Bacterial membranes don’t change very often.
D Bacteria rarely develop resistance to human-made
antibiotics.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
Passage 2 Drinking water in the United States is
generally safe, but water lines can break, or treatment
plants can become flooded, allowing microorganisms to
enter the public water supply. Bacteria growing in foods
and beverages can cause illness, too.
Continued on the next slide
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
Passage 2, continued Refrigerating foods can slow the
growth of many of these pathogens, but meat, fish, and
eggs that are not cooked enough can still contain
dangerous bacteria or parasites. Leaving food out at
room temperature can give bacteria such as salmonella
time to grow and produce toxins in the food. For these
reasons, it is important to wash all used cooking tools.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
1. Which of the following statements can you infer from
this passage?
A Treatment plants help keep drinking water safe.
B Treatment plants never become flooded.
C Eliminating treatment plants would help keep water
safe.
D New treatment plants are better than old ones.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
1. Which of the following statements can you infer from
this passage?
A Treatment plants help keep drinking water safe.
B Treatment plants never become flooded.
C Eliminating treatment plants would help keep water
safe.
D New treatment plants are better than old ones.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
2. Which of the following statements can you infer
from the passage?
F Bacteria that live in food produce more toxins than
molds produce.
G Cooking food thoroughly kills bacteria living in the
food.
H Some bacteria are helpful to humans.
I Illnesses caused by bacteria living in food are
seldom serious.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
2. Which of the following statements can you infer
from the passage?
F Bacteria that live in food produce more toxins than
molds produce.
G Cooking food thoroughly kills bacteria living in the
food.
H Some bacteria are helpful to humans.
I Illnesses caused by bacteria living in food are
seldom serious.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
3. According to this passage, what do pathogens
cause?
A disease
B flooding
C water-line breaks
D water supplies
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
3. According to this passage, what do pathogens
cause?
A disease
B flooding
C water-line breaks
D water supplies
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
Interpreting Graphics
The graph below shows the reported number of people
living with HIV/AIDS. Use the graph to answer the
questions that follow.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
1. When did the number of
people living with HIV/AIDS
reach 5 million?
A 1985
B 1986
C 1987
D 1988
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
1. When did the number of
people living with HIV/AIDS
reach 5 million?
A 1985
B 1986
C 1987
D 1988
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
2. When did the number of
people living with HIV/AIDS
reach 30 million?
F 1996
G 1997
H 1998
I 1999
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
2. When did the number of
people living with HIV/AIDS
reach 30 million?
F 1996
G 1997
H 1998
I 1999
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
3. When was the rate of
increase of people with
HIV/AIDS the greatest?
A from 1980 to 1982
B from 1984 to 1986
C from 1988 to 1990
D from 1998 to 2000
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
3. When was the rate of
increase of people with
HIV/AIDS the greatest?
A from 1980 to 1982
B from 1984 to 1986
C from 1988 to 1990
D from 1998 to 2000
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
4. What percentage of the
people who are infected
with HIV do not yet have
AIDS?
F 10%
G 24%
H 75%
I There is not enough
information to determine
the answer.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
4. What percentage of the
people who are infected
with HIV do not yet have
AIDS?
F 10%
G 24%
H 75%
I There is not enough
information to determine
the answer.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
5. If the virus continued to
spread as the graph indicates,
in the year 2002, about how
many people would be
infected with HIV?
A 30 million
B 35 million
C 39 million
D 60 million
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
5. If the virus continued to
spread as the graph indicates,
in the year 2002, about how
many people would be
infected with HIV?
A 30 million
B 35 million
C 39 million
D 60 million
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
6. Which part of the graph
indicates the rate of infection?
F x-axis
G y-axis
H slope of the line being
graphed
I number of years in the sample
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
6. Which part of the graph
indicates the rate of infection?
F x-axis
G y-axis
H slope of the line being
graphed
I number of years in the sample
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
Math
Read each question, and choose the best answer.
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
1. Suppose you have 50,000 flu viruses on your fingers
and you rub your eyes. Only 20,000 viruses enter your
eyes, 10,000 dissolve in chemicals, and 10,000 are
washed down into your nose. Of those, you sneeze out
2,000. How many viruses are left to wash down the
back of your throat and possibly start an infection?
A 50,000
B 10,000
C 8,000
D 5,000
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
1. Suppose you have 50,000 flu viruses on your fingers
and you rub your eyes. Only 20,000 viruses enter your
eyes, 10,000 dissolve in chemicals, and 10,000 are
washed down into your nose. Of those, you sneeze out
2,000. How many viruses are left to wash down the
back of your throat and possibly start an infection?
A 50,000
B 10,000
C 8,000
D 5,000
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
2. In which of the following lists are the numbers in
order from smallest to greatest?
F 0.027, 0.072, 0.270, 0.720
G 0.270, 0.072, 0.720, 0.270
H 0.072, 0.027, 0.270, 0.720
I 0.720, 0.270, 0.072, 0.027
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
2. In which of the following lists are the numbers in
order from smallest to greatest?
F 0.027, 0.072, 0.270, 0.720
G 0.270, 0.072, 0.720, 0.270
H 0.072, 0.027, 0.270, 0.720
I 0.720, 0.270, 0.072, 0.027
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Section 2 Your Body’s Defenses
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 27
Standardized Test Preparation
Chapter menu
Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.