Chapter 25.3 - CPO Science
advertisement

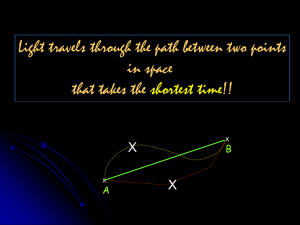
LIGHT 25.3 Chapter Twenty-Five: Light 25.1 Properties of Light 25.2 Color and Vision 25.3 Optics Chapter 25.3 Learning Goals Explain how basic optical devices function. Compare and contrast the interactions of light and matter. Distinguish between concave and convex lenses. 25.3 Basic optical devices Three useful optical devices are: 1. lenses 2. mirrors 3. prisms 25.3 Basic optical devices A magnifying glass is a converging lens that can be used in survival situations to make a hot spot. Mirrors can attract the attention of rescue teams from great distances. 25.3 Four ways light is affected by matter All four interactions almost always happen together. Green colored paper absorbs some light, reflects some light, and is partly translucent. Can you tell which colors are reflected and which are absorbed? 25.3 Four ways light is affected by matter A glass window is mostly transparent, but also absorbs, scatters, and reflects some light. See if you can identify where certain colors are absorbed and reflected in this picture. 25.3 Light rays Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface and when light bends while crossing through materials. 25.3 Reflection There are two types of reflection; but not all reflections form images. Rays light that strikes a shiny surface (like a mirror) create single reflected rays. This type of reflection is called specular reflection. 25.3 Reflection A surface that is dull or uneven creates diffuse reflection. When you look at a diffuse reflecting surface you see the surface itself. 25.3 Law of reflection A ray diagram is an accurately drawn sketch showing how light rays interact with mirrors, lenses, and other optical devices. 25.3 Refraction Materials with a higher index of refraction bend light by a large angle. The index of refraction for air is about 1.00. Water has an index of refraction of 1.33. 25.3 Refraction Vegetable oil and glass have almost the same index of refraction. If you put a glass rod into a glass cup containing vegetable oil, the rod disappears because light is NOT refracted! 25.3 Lenses An ordinary lens is a polished, transparent disc, usually made of glass. The shape of a converging lens is described as being “convex” because the surfaces curve outward. 25.3 Lenses The distance from the center of the lens to the focal point is the focal length. Light can go through a lens in either direction so there are always two focal points, one on either side of the lens. 25.3 Lenses For a converging lens, the first surface (air to glass) bends light rays toward the normal. At the second surface (glass to air), the rays bend away from the normal line. Searching the Cosmos Astrophysicist Dr. Hakeem Oluseyi (Oh-lu-SHAY-ee) is fascinated by stars. A physics and space science professor at the Florida Institute of Technology, he has invented several new instruments to give astronomers a closer look at the cosmos.