oneM2M-REQ-2012-0019R03
advertisement

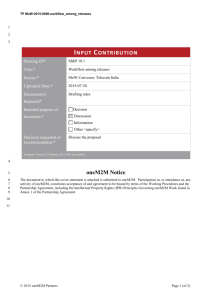
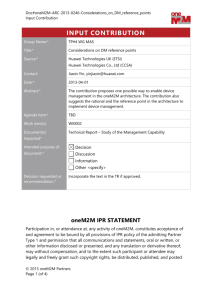
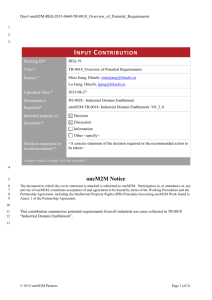
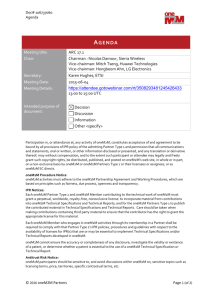
BENEFITS OF ONEM2M TECHNOLOGIES Group Name: oneM2M WG1 Requirements Source: Phil Hawkes, Rapporteur “Benefits of oneM2M technology” TR, phawkes@qti.qualcomm.com Meeting Date: 2012-10-23 Agenda Item: 7 “Contributions” Scope • Audience: Vertical industry segment stakeholders • Purpose: Trigger feedback from [the Audience] • Content: Highlights potential benefits of oneM2M communication technology to [the Audience] • Note: current title of presentation is a placeholder only 2 Outline • Motivators: – Audience Priorities oneM2M intends to address • • • • Description of oneM2M Technology Benefits of oneM2M Details of the oneM2M Functionalities Terminology 3 Motivators • oneM2M believes that [the Audience] wants improvements in the following aspects of the M2M ecosystem: – Improved Functionality-Price-Quality (FPQ) tradeoffs: • improved FPQ tradeoffs in sourcing, development and integration of the Components comprising their M2M solutions • “Price” includes impact of CAPEX, OPEX and Time-to-market [1] – Enhanced Scalability: • Scales to large deployments – Greater Choice: • a range of providers from which to source Components comprising their M2M solutions • range of options for structuring their deployment – Greater Opportunities: • For example, [the Audience] would like the ability to share data and other resources by partnering with other stakeholders. Byproducts include improved FPQ tradeoffs and new revenue streams 4 One sentence description of oneM2M technology Easy-to-digest description of oneM2M technology DESCRIPTION OF ONEM2M TECHNOLOGY 5 One sentence description oneM2M aims to enable improved Functionality-Price-Quality tradeoffs of future end-to-end M2M solutions, whilst providing scalability, greater choices and opportunities for [the Audience] by standardizing a set of valuable, Generic M2M-communication Capabilities that incorporate the necessary interactions with Underlying Networks. 6 Easy-to-digest description of oneM2M • Figure & text showing relationship between – Applications – oneM2M Technology – Underlying Networks • Should not imply an architecture 7 Example only M2M App Interface to capabilities Interface to capabilities M2M App oneM2M Capabilities Underlying Networks 8 Goal of this document • Background – This document provides a broad description of how the aims of oneM2M might be met by potential capabilities and features that oneM2M is considering for the upcoming release. All capabilities and features in this document should be treated as potential only. • Objective – Request feedback in order to help oneM2M prioritize its work. 9 BENEFITS OF ONEM2M 10 Summary of Benefits 1. Benefits of standardizing generic capabilities 2. Benefits of incorporating interactions with underlying networks 3. Benefits of valuable capabilities directly addressing the Motivators 11 Benefits of Standardizing Generic Capabilities Economies of scale Specifications can be used as the basis for certifying # interoperability & quality Improved FPQ Tradeoffs # Note: Interoperable Components from multiple providers Extensive Application Development Ecosystem Greater Choice Greater Opportunities Enhanced Scalability at the time of writing, it is not clear if oneM2M will provide certification. Even if oneM2M does not provide the certification, one or more other groups may certify against part or all of the oneM2M specifications. 12 Benefits of Incorporating Interactions with Underlying Networks Application developers can ignore details of usage of underlying network, simplifying development while benefiting from integrated efficiency & reliability Improved FPQ Tradeoffs Greater Choice Wider range of options for the [Audience] in selecting an underlying network Greater Opportunities Enhanced Scalability 13 OTE: Initial text to explain artitioning of features. Capabilities Capability Features Sharing Sharing of content between M2M Applications. Support for sharing with partners. Content is opaque. Standardized metadata provides control. Content-Aware Processing Sharing Capability features plus processing with varying degree of “understanding” of Content data elements: e.g. data type, data value and/or semantics. Security Framework & Access Control Provisioning, access control, authentication and security mechanisms for protecting oneM2M capabilities. Support for enabling App-to-App security. Remote Device Management Provisioning. Remote reporting from Device (e.g. for maintenance) and remote configuring (e.g. settings, software and firmware management). Communication Efficiency & Reliability Selecting and establishing connectivity on an underlying network. Scheduling communication. Delivery confirmation/progress reporting. Robustness in the presence of lossy links. Broadcast/multicast support. Possible processing of visible data includes: filtering; aggregating; simple arithmetic ops (average, sum, etc.) 14 Benefits of Valuable Capabilities Remote Device Management Security Framework and Access Control Communication Content-Aware Efficiency & Reliability Processing Sharing Reduced traffic volume Reduced field agent call-outs Improved end-product quality Improved FPQ Tradeoffs Better power consumption Greater Choice More value extracted from underlying network Greater Opportunities Ability to share data & assets with partners Enhanced Scalability 15 DETAILS OF ONEM2M CAPABILITIES 16 Sharing Capability Functions Sharing Content-Aware Processing Security Framework and Access Control Remote Device Management Communication Efficiency & Reliability Field/Cloud to Field/Cloud Sharing Event Notification Metadata-aware Processing Filtering/Searching Aggregating content Simple Arithmetic on metadata (sum, mean, max, min) Content Origin Metadata Entity Descriptions Metadata Searchable Tags Content Delivery Guidance 17 Content-Aware Processing Sharing Content-Aware Processing Security Framework and Access Control Remote Device Management Communication Efficiency & Reliability Data-TypeAware Processing SemanticsAware Processing Data-Type-Aware Description Language Data-Type-Aware Procedure Language Semantics-Aware Description Language Simple Arithmetic Operations (sum, mean, max, min) Filtering/Searching Aggregating content Semantics-Aware Procedure Language 18 Security Framework and Access Control oneM2M-to-oneM2M class Sharing Security Framework Classes App-to-oneM2M class App-to-App class Content-Aware Processing Passphrase High-Entropy Key Security Framework and Access Control Remote Device Management Communication Efficiency & Reliability Authentication Framework Certificate Static root of trust Dynamic root of trust Static Identity Identity Access Control Dynamic Identity TBD (another page?) 19 Remote Device Management Sharing Content-Aware Processing Security Framework and Access Control Remote Device Management Communication Efficiency & Reliability Log Reports Reporting Data from Devices Controlling Data on Devices Maintenance Reporting Fault Reports Performance Reports Reporting Configuration Settings Updating Configurations Managing Software & Firmware Adding new Software (E.g. Applications) Software/Firmware updates Removing Software 20 Communication Efficiency Sharing Content-Aware Processing Security Framework and Access Control Remote Device Management Communication Efficiency & Reliability Delivery confirmation /Progress reporting Robustness in the presence of lossy links Selecting an appropriate underlying network & scheduling Support for Content Delivery Guidance metadata Interface to M2M-specific features of the underlying network (e.g. triggering, location broadcast) 21 Terminology References APPENDICES 22 Terminology Name Description M2M Application (App) TBD App-to-App Capability TBD Component Hardware, software and services that combine to produce an M2M solution Content Data produced or consumed by Applications Content-Aware Aware of the data model and/or semantics of Content Generic Common to two or more applications or vertical segments Underlying networks Access networks, core networks, busses and other technology assisting in data transport 23 References 1. “oneM2M Standardization”, 2012-04-24. Available from ftp://ftp.onem2m.org/Primary_Deliverables/ Material_for_Verticals/oneM2M Standardization_2012-04-24.zip 24 Saved here in case they are useful in future. OLD SLIDES – DELETE BEFORE PUBLICATION 25 Figure by Farooq Bari, AT&T 26 Figure by Tim Carey, ALU 27