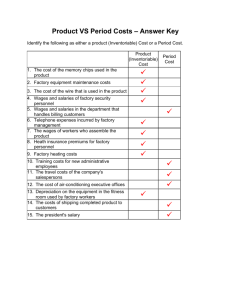
11 cost sheet analysis
advertisement

COST SHEET Samir K Mahajan COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST Prime cost or Direct cost : It is the aggregate of direct material cost, direct labour cost and direct expenses. i.e. Prime cost or Direct cost = Direct materials + Direct labour + Direct expenses (Direct materials = Purchases + Opening stock of Raw materials – closing stock of Raw materials ) Factory cost or “works cost” or “manufacturing cost”: It is the aggregate of prime cost and factory overheads. i.e. Works cost or Factory cost or Manufacturing cost = Prime cost + factory overheads COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST contd. Office cost or cost of production or administrative cost : It is the aggregate of factory cost and office and administration overheads. i.e. Office cost or cost of production = Factory cost + Administration overhead Cost of production of goods sold /cost of production of sales = Cost of goods available for sale − Closing stock of finished Goods = (Office cost + Opening stock of finished goods) − Closing stock of finished goods COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST Total cost or Cost of sales : It is the aggregate of office cost and selling and distribution overheads. This is also called cost of sales Cost of sales or Total cost = cost of production of sales + Selling and Distribution overheads Profit Or Loss : The difference between the cost of sales and selling price represents profit or loss. COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST contd. In the determination of different components of cost, certain adjustments have to be carried out for inventories of raw materials, work-in-progress and finished goods as follows: Consumption of raw material (or) material used: It has to be adjusted with inventories of raw materials Raw materials used = Opening stock + Purchases − Closing stock =Opening stocks of Direct material + Purchase of direct material − Closing stock of direct material COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST contd. Work in Progress: It has to be adjusted with works cost (i.e., after computation of prime cost but before determining works cost) Gross Work cost = Works cost + Opening work-in-progress − Closing work-in-progress Stock of finished goods: It has to be adjusted with cost of production (i.e., after computation of works cost but before determining cost of production) and Cost of production of goods sold/sales. CONVERSION COSTS Conversion costs are those costs required to convert raw materials into finished goods that are ready for sale. The concept is used in cost accounting to derive the value of ending inventory, which is then reported in the financial statements. It can also be used to determine the incremental cost of creating a product, which could be useful for price setting purposes. Conversion costs are all manufacturing costs except for the cost of raw materials. Conversion costs = Direct labour + Manufacturing overhead = (Prime cost – direct materials – direct expenses ) + Manufacturing overhead Examples of costs that may be considered as conversion costs are direct labour and related benefits equipment depreciation, equipment maintenance, factory rent, factory supplies, factory insurance, machining Inspection, production utilities, production supervision, Small tools charged to expense. CONVERSION COSTS contd. Illustration: ABC International incurs a total of $50,000 during March in direct labour and related costs, as well as $86,000 in factory overhead costs. ABC produced 20,000 units during March. Therefore, the conversion cost per unit for the month was $6.80 per unit (calculated as $136,000 of total conversion costs divided by the 20,000 units produced). Illustration 1. Find the Prime Cost, Works Cost, Cost of production, total Cost and profit from the following:- Direct Materials Rs.20000; Direct Labour Rs. 10000; Factory Expenses Rs. 7000; Administration Expenses Rs. 5000; Selling Expenses Rs. 7000 and Sales Rs.60,000. Solution: Prime Cost = Direct Materials + Direct Labour = Rs.20,000 + Rs.10,000 = Rs.30,000. Works Cost = Prime Cost + Factory overheads = Rs.30,000 + Rs.7,000 = Rs.37,000. Cost of Production = Works Cost + Administration Expenses=Rs.37000+ Rs.5, 000 = Rs.42, 000. Total Cost or Cost of sales= Cost of Production + Selling Expenses = Rs.42, 000+ Rs.7, 000 = Rs.49, 000. Profit = Sales - Total Cost = Rs.60,000 - Rs.49,000=Rs.11, 000. Illustration 1. Find the Prime Cost, Works Cost, Cost of production, total Cost and profit from the following:- Direct Materials Rs.20000; Direct Labour Rs. 10000; Factory Expenses Rs. 7000; Administration Expenses Rs. 5000; Selling Expenses Rs. 7000 and Sales Rs.60,000. Cost Sheet: Analysis of Components of Cost Cost sheet or Statement of Cost: When costing information is set out in the form of a statement, it is called “Cost Sheet”. It is usually adopted when there is only one main product and all costs almost are incurred for that product only. The information incorporated in a cost sheet would depend upon the requirement of management for the purpose of control. An analysis of the total cost of production and cost of sales is carried out by preparing “Cost sheet”. A Cost sheet is an important document prepared by the costing department. Cost sheet is prepared to analyse the components of total cost, thereby determining (i) prime cost, (ii) works cost, (iii) cost of production, (iv) cost of sales and (v) profit. FORMAT OR SPECIMEN OF A COST Cost Sheet or Statement of Profit and Cost Direct Material Direct Labour Direct Expenses XXX XXX XXX PRIME COST XXX XXX Add: Factory overhead WORKS COST (or) FACTORY COST Add: Administration overhead XXX XXX XXX COST OF PRODUCTION Add: Selling and distribution overhead TOTAL COST (or) COST OF SALES XXX XXX PROFIT XXX SALES XXX Ex 1: Calculate (i) prime cost, (ii) works cost, (iii) cost of production and (iv) cost of sales, from the following particulars: Raw materials consumed 30,000 Wages paid to labourers 12,000 Chargeable expenses—Direct 1,000 Wages of foreman 2.000 Wages of store keeper 1,000 Electricity : Factory 2,500 Office Rent : Factory Office Depreciation: Plant and machinery Office furniture 500 1,500 500 600 200 Consumable stores 1,000 Manager’s salary 3,000 Office printing and stationery 500 Solution: Example 2: From the following particulars, calculate: Cost of raw-materials consumed, prime cost, Works/manufacturing cost, cost of production , cost of production of goods sold, total cost and Profit Opening stock Raw materials 10,000 Office management salaries 5,000 Finished goods 5,000 Office printing and stationery 300 Raw material purchased 60,000 Salesmen salary 3,000 Wages paid to labourers 25,000 Travelling expenses 1,200 Directly chargeable expenses 3,000 SALES 1,75,000 Rent, rates and taxes 4,000 Power 2,500 Factory heating and lighting 2,000 Factory insurance 1,000 Sale of wastage of materials 500 Closing stock Raw materials 7,000 Finished Goods 10,000 Solution: Example 2 Particulars Step 1: Direct material : Cost of Raw material Consumed (i)Opening Stock 10000 (ii) Add: Purchase 60000 70000 iii)Less: Closing stock 7000 (iv) Less: Sale of wastage materials Step2: Direct labour Step 3: Direct Expenses –chargeable Step 4: Prime Cost (step 1+ step 2+ step 3) Amount (Rs) 63000 500 Amount (Rs) 62500 25000 3000 90500 Solution: Example 2 Particulars Amount (Rs) Amount (Rs) Step 5: Add Production overheads (factory) (i) Rent, rate and taxes (ii) Power (iii) Factory heating and lighting (iv) factory insurance Step 6: Factory cost (step 4 + step5) 4000 2500 2000 1000 95000 Step 7: Add Administrative overheads (i) Office management salary (ii) Office printing and stationary Step 8: Total cost of production (step 6+ step 7) 5000 300 100000 5300 105300 Step 9: Add: Opening stock of finished goods 105300 5000 110300 Step 10: Less closing stock of finished goods Sept 11: Cost of production of goods sold 10000 100300 Step 12: Add: Selling and Distribution overheads (i) Salaries of salesmen (ii) Travelling expenses Step 13: Cost of sales /total cost (Step 11+ step 12) Sept14: Profit (step 15- step 14) Step 15: Sales 3000 1200 42000 104500 70500 175000 Solution: