DECISION MAKING
advertisement

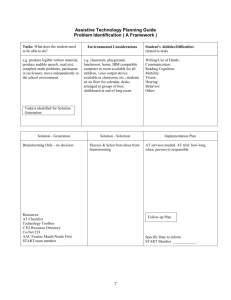
DECISION MAKING LEARNING OBJECTIVES/OUTCOMES Explain why decision making is an important component of good management. Discuss the difference between programmed and non-programmed decision and the decision characteristics of certainty and uncertainty. Explain the process by which managers actually make decisions in the real world. Identify the six steps used in managerial decision making. Describe four personal decision styles used by managers and explain the biases that frequently cause managers to make bad decisions. Identify and explain techniques for innovative group decision making. DECISION – is a choice made from available alternatives. DECISION MAKING – is the process of identifying problems and opportunities and then resolving them TYPES OF DECISIONS AND PROBLEMS Programmed Decisions Non-programmed Decisions Programmed Decisions Nonprogrammed Decisions Problem situations that occur often to enable rules situations that are unique or poorly defined and unstructured Procedure Dependence on policies, rules, and definite procedures. Necessity for certainty, intuition, tolerance for ambiguity, creative problem solving. Business firm Periodic reorders of inventory. Diversification into new products and markets. University Necessary grade-point average for good academic standing. Construction into new classrooms and facilities. Health care Procedure for admitting patients. Purchase of experimental equipment. Government Merit system for promotion of state employees. Reorganization of state government agencies. Examples Why do we need to make tough decisions? Decision Making in Today’s Environment FACING CERTAINTY AND UNCERTAINTY Certainty: the information needed is available Risk: the future outcome is subject to chance regardless of the information available Uncertainty: goals are clear but information about future events are incomplete Ambiguity: the goals and/or problem are unclear and difficult to define CONDITIONS THAT AFFECT THE POSSIBILITY OF DECISION FAILURE Organizational Problem LOW Certainty Possibility of Failure Risk Uncertainty Programmed Decisions HIGH Ambiguity Nonprogrammed Decisions Problem Solution AGING AND DECISION MAKING: HOW AGING AFFECTS DECISIONS UNDER UNCERTAINTY (Research Study) (1) Older adults are less willing to take financial risks than young adults (2) Ambiguity behavior changes with age (3) Young and older subjects gamble less in ambiguity conditions than in risk conditions. The study only partially confirms our hypotheses: As older adults seem to be equally willing to take risks as young adults are (refuting hypothesis) Ambiguity behavior effectively differs with age (confirming hypothesis 2) And young subjects do gamble less in ambiguous conditions than in risky conditions, but older adults show no significant difference between risk and ambiguity behavior (partially confirming hypothesis 3). http://www.uni-heidelberg.de/md/awi/forschung/dp508.pdf DECISION-MAKING MODELS CLASSICAL MODEL ADMINISTRATIVE MODEL POLITICAL MODEL Classical Model - A decision-making model based on the assumption that managers should make logical decisions that will be in the organization’s best economic interests. Views the manager as acting rationally in a certain world. Decision maker is fully informed about the possible alternative. Administrative Model - A decision-making model that describes how managers actually make decisions in situations characterized by non-programmed decisions, uncertainty, and ambiguity. Bounded Rationality - People have the time and cognitive ability to process only a limited amount of information on which to base decisions. Satisficing - To choose the first solution alternative that satisfies minimal decision criteria, regardless of whether better solutions are presumed to exist. Intuition - The immediate comprehension of a decision situation based on past experience but without conscious thought. Political Model –is useful for making nonprogrammed decisions when conditions are uncertain, information is limited and there are manager conflicts, what goals to pursue or what course of action to take. Coalition – is an informal alliance among managers who support a specific goal. Coalition Building – is the process of forming alliances among managers. THE DECISION - MAKING PROCESS Step 1: Identify and Define the Problem Step 2: Generate and Evaluate Alternative Solutions Step 3: Decide on Preferred Cause of Action Step 4: Implement the Decision Double check on ethical reasoning Step 5: Evaluate Results BARRIERS TO EFFECTIVE DECISION MAKING A. PSYCHOLOGICAL BIASES ○ Illusion of control ○ Framing effects ○ Discount the future B. TIME PRESSURES C. SOCIAL REALITIES PERSONAL DECISION FRAMEWORK Directive Style Analytical Style Conceptual Style Behavioral Style WHY DO MANAGERS MAKE BAD DECISIONS? Being influenced by initial impressions. Seeing what you want to see Overconfidence Rely Too Much on Past Experience Addicted to Corporate Politics Lack Clarity of goals Mismanage Resources Don’t See the Opportunity Don’t Trust Themselves to Lead WHAT CAN LEADERS DO TO INCREASE THEIR CHANCES OF AVOIDING PITFALLS? RED FLAG CONDITIONS M I S L E A D I NG E X P E R I ENCE S M I S L E A D I NG PREJUDGE MENT S I N A P P R O P RIAT E S E L F - I N T E REST I N A P P R O PRIA T E A T T A C H MENTS USING GROUPS TO IMPROVE DECISION MAKING METHODS AND TECHNIQUES ADVANTAGES AND PITFALLS OF GROUP DECISION MAKING STRUCTURED CONFLICT NOMINAL GROUP TECHNIQUE DELPHI TECHNIQUE STEPLADDER TECHNIQUE ELECTRONIC BRAINSTORMING ADVANTAGES Group can think better than individuals because they can view problems in multiple perspectives because group members usually possess different knowledge, skills abilities and experiences. They can perform better on complex tasks and make better decisions than individuals. Group can find and access much more information than individuals alone. With groups we can generate more alternative solutions People who participate in a group discussion are more likely to understand why the decision was made. They will have heard the relevant arguments both for the chosen alternative and against the rejected alternatives. Group discussion typically leads to a higher level of commitment to the decision. Buying into the proposed solution translates into high motivation to ensure that it is executed well. PITFALLS Groupthink – a barrier to good decision making caused by pressure within the group for members to agree with each other. It occurs in a highly cohesive group when group members feel intense pressure to agree with each other so that the group can approve a proposed solution. Groupthink is most likely to occur under the following conditions. The group is insulated from others with different perspective Sometimes one group member dominates the discussion The group leader begins by expressing a strong preference for a particular decision. The group has to established procedure for systematically defining problems and exploring alternatives. Group members have similar backgrounds and experiences Goal displacement often occurs in groups STRUCTURED CONFLICT Most people view conflict negatively. Yet the right kind of conflict can lead to much better group decision making Cognitive Conflict – C - Type conflicts - Focuses on problem and issue related differences of opinion. Two methods of introducing structured c-type conflict into the group decision making process. Devil’s Advocacy Dialectical Inquiry Affective Conflict – A- Type Conflict -Refers to the emotional reaction that can occur when disagreements become personal rather than professional. DELPHI TECHNIQUE A decision making method in which members of a panel of experts respond to questions and to each other until reaching agreement on an issue. STEPLADDER TECHNIQUE A decision making method in which group members are added to a group discussion one at a time (like a stepladder) the existing group members listen to each new members thought, ideas, and recommendations; then the group shares the ideas and suggestions that it had already considered, discusses the new and old ideas, and makes a decision. ELECTRONIC BRAINSTORMING Brainstorming - a decision making method in which group members build on each other’s’ ideas to generate as many alternative solutions as possible. Electronic Brainstorming – a decision making method in which group members use computers to build on each other’s ideas and generate as many alternative solution as possible. This overcomes the disadvantages associated with face-to-face brainstorming. Disadvantages: Production Blocking – a disadvantage or faced-to-faced brainstorming in which a group must wait to share an idea because another member is presenting an idea. Evaluation Apprehension – fears of what others will think of you. ORGANIZATIONAL DECISION MAKING MANAGEMENT SCIENCE APPROACH THE CARNEGIE MODEL INCREMENTAL MODEL GARBAGE SCAN MODEL MANAGEMENT SCIENCE APPROACH Use of statistics to identify relevant variables Remove human element Very successful for military problems Good tool for decisions where variables can be identified and measured A drawback of management science is that quantitative data are not rich and lack tacit knowledge CARNEGIE MODEL INCREMENTAL MODEL Managers select alternative courses of action that are only slightly, or incrementally, different from those used in the past. Focus on structured sequence of activities from discovery to solution Perceived to lessen the chances of making a mistake They correct or avoid mistakes through a succession of incremental changes Tries to explain how organizations improve their programmed decisions over time Large decisions are a collection of small choices Decision interrupts are barriers – Identification Phase – Development Phase – Selection Phase – Dynamic Factors GARBAGE CAN MODEL Model of organizational decision making depicting a chaotic process and seemingly random decisions Decision makers are as likely to start decision making from the solution side as the problem side Create decision-making opportunities that they can solve with readymade solutions based on their competencies and skills Different coalitions may champion different alternatives Decision making becomes a “garbage can” in which problems, solutions, and people all mix and contend for organizational action. Selection of an alternative depends on which person’s or group’s definition of the current situation holds sway. Consequences of the Garbage Can Model 1. Solutions may be proposed even when problems do not exist 2. Choices are made without solving Problems 3. Problems may persist without being solved 4. A few problems are solved REFERENCES: Williams, C. Effective Management: A Multimedia Approach, 5th Edition, 2012, South Western, Cengage Learning. Daft, Richard. New Era of Management, 9th Edition, 2010, South Western, Cengage Learning. Alec Sproten, Carsten Diener ,Christian Fiebach, Christiane Schwieren. University of Heidelberg Department of Economics Discussion Paper Series No. 508Aging and decision making: How aging affects decisions under uncertainty. December 2010 Bateman, Thomas S. and Snell Scott A. Management Leading & Collaborating in a Competitive World, 7th Edition, 2007, Mc Graw-Hill International Edition John R. Schermerhorn . Management ,11th Edition, Oct 18, 2010, John Wiley & Sons http://besatuva.com/2011/09/05/chrysler-case-study-managerial-decision-making/ http://www.forbes.com/sites/johnkotter/2012/05/02/barriers-to-change-the-real-reason-behind-thekodak-downfall/ http://www.uen.org/Lessonplan/downloadFile.cgi?file=555-6-3625 decision case studies.doc&filename=decision_case_studies.doc. https://www.google.com.ph/search?q=DECISION+MAKING+CASE+STUDIES&ie=utf-8&oe=utf8&aq=t&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&client=firefoxa&channel=sb&gfe_rd=cr&ei=nxoRVIP7C8uL8QeB34DYDA# Andrew Campbell and Jo Whitehead. The Ashridge Journal: Think again Spring 2009 3600 Erin White. Wall Street Journal -Business :Why do managers make bad decisions? 2009 http://www.hrpub.org/download/201309/csit.2013.010211.pdf Thank you for listening!!!!!!!!!!! Jhudz & Jen