Sec (1.2):
advertisement

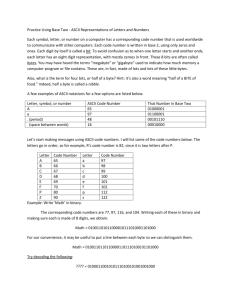
Sec (1.2): Main memory Memory: Stores data and instructions in the beginning, intermediate and final stages of the processing. Technology of memory building: There are two significant types for technologies used in memory building ( design ): 1. Magnetic core 2. Semiconductor memory 1- Magnetic core: Consists of million of rings, each ring in the size of pinhead, these rings connected to each other forming a mesh, electricity flows through these rings, the rings are magnetized. If the electricity flows in clock wise, the ring represents 1 but in counter clock wise it represents 0. In this kind of technology data are not lost even if the power goes off. Note: magnetic core is non-volatile memory Magnetic core: 1 0 2- Semiconductor memory: Is an integrated circuit, is put on a silicone board, each cell contains transistor which works as switch and a capacitor which keeps the charge. If the capacitor is charged, it means the value stored is 1, other wise the value is 0. Advantages of semiconductor: less bulky than the magnetic core. survive for a longer period (less damage) data can be stored in a smaller size less cost faster in information retrieval Disadvantages of semiconductor: it is volatile, it losses its contents as soon as the power goes off. For this purpose UPS is used 3- Bubble memory: It has come to take the advantages of magnetic cores and semiconductor technology Memory contains: 1. 2. 3. 4. Address register: contains the address of the data to be brought or put in the memory ( the address value is brought from the CPU ) Word register: it contains the data brought or to put from/in the memory LCU (local control unit): supervises all the parts of the memory The memory cells ( matrix ) ( The cell size is eight bits ) Memory contains: Least significant bit ( Lower order end ) Most significant bit ( High order end ) CPU ADDRES S REGISTE R LCU MATRIX WOR D REGIS TER Measuring Memory capacity: Bit = 0 or 1 Byte = 8 bits KByte = 1024 Byte = 210 byte MByte = 1024 * 1024 Byte = 220 byte GByte = 1024 * 1024 * 1024 Byte = 230 byte Ex: given the address register of length 16 bits and the length of the word is 4 bits, computes the size of the memory in bytes Sol.: No. of address locations = 216 = 65536 No. of bits in the memory = 65536*4 = 262144 bits Size of the memory in bytes = 262144 / 8 = 32768 bytes Types of memory: RAM ( Random Access Memory ) It is a memory where data can be read or written. It is a volatile memory It is important in putting the computer specification DRAM ( Dynamic RAM ) or SDRAM ( Synchronous DRAM ): Is used in reference to DRAM that applies additional techniques to decrease the time needed to retrieve the contents from its memory cells ROM ( Read Only Memory ) It is only for reading, it comes from the manufacture on a chip. For example the ASCII code is store in ROM This memory is non-volatile PROM ( Programmable Read Only Memory) Can be programmed by the manufacture or by the user (can be programmed for one time only ) EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory ) Can be erased and reprogrammed