no late work, no retakes. period.
advertisement

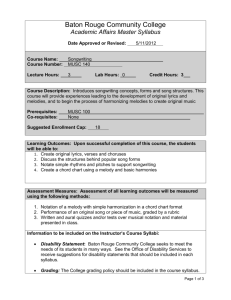
Advanced Placement Music – Syllabus M.J. Cotton – School Year 2010-2011 Course Description: The Advanced Placement (AP) Music Theory course enables highly motivated students to do college level work in the areas of reading and analyzing notated music and aural training. Particular emphasis will be placed upon developing listening skills, sight singing ability and knowledge of rhythm, melody, harmony, form and other compositional devices. The successful student will be endowed with the skills necessary to function intelligently in any musical situation. The work of the course will emphasize preparation for the advanced placement music theory examination. Course Objectives: The ultimate goal of the Advanced Placement Music Theory course is to develop a student’s ability to recognize, understand, and describe the basic materials and processes of music that are heard or presented in a score. The achievement of this goal may be best promoted by integrated approaches to the student’s development of: · Aural skills – through listening exercises · Sight-singing skills – through performance exercises · Written skills – through written exercises · Compositional skills – through creative exercises · Analytical skills – through analytical exercises The AP Music Theory Exam This course is designed to prepare you for the AP Music Theory Exam in May 2011. The AP Examination in Music Theory tests the student's understanding of musical structure and compositional procedures through recorded and notated examples. Strong emphasis is given to listening skills, particularly those involving recognition and comprehension of melodic and rhythmic patterns, harmonic functions, small forms, and compositional techniques. Most of the musical examples are taken from standard repertoire, although some examples of contemporary, jazz, or vernacular music, or music beyond the Western tradition are included for testing basic concepts. The examination assumes fluency in reading musical notation and a strong grounding in music fundamentals, terminology, and analysis. The AP Music Theory Exam is about two and a half hours long and consists of two sections. Section I consists of 75 multiple-choice questions, some of which are based on aural stimulus. Section II consists of written free-response questions and sight-singing exercises. Many of our in-class assignments and homework will be drill and practice types of assignments (formative) offered to help you master new skills. These will be graded on a pass/fail type of point system. Other assignments and tests will be standard assessment style assignments given to measure your level of mastery (summative). These will be graded using a four point “mastery learning” scale. Classroom Management The classroom rules are as follows: 1. Follow directions the first time they are given. 2. Respect all people and property 3. DO NOT lose materials you are provided. In the event you choose to not follow a classroom rule, you are subject to the following (not in any order of severity): isolation, detention, cleaning crew, and administrative referral. If you are asked to go out side for a moment, this is not necessarily a bad thing. This gives you and I the time to reflect before we tackle the real problem at hand. Please DO take the time to think about why I sent you out and be ready to have a conversation about ways we can fix these problems in the future. Computer Guidelines Students have the privilege, not the right, to use computers at STERN Mass. If you are caught using computers or adjusting the settings of a computer, you will be banned from the use of the computer for the entire semester. This is your ONLY warning about this. MAKE-UP WORK - It is YOUR responsibility to find out what you missed when you were absent. Homework is due the next class day after the date of absence. All exams missed due to excused absences must be made up within a week of the date of the absence. Written portions of exams will be administered only during office hours. Portions of the test requiring performance or listening will be administered by appointment after school. NO LATE WORK, NO RETAKES. PERIOD. Office Hours Students is AP Music Theory may come by my room Wednesday or Thursday after school from 3:30-4:30 by appointment for help. My e-mail address is mcotton@laalliance.org. Email is the BEST way to communicate with me. AIM: sternmassmusic CLASS ORGANIZATION Classes will be divided weekly into the following blocks: Monday Theory (1h 30m) Ear Training (ET) and Sight Singing (SS) 30 Min Wednesday Theory (1h 30m) ET and SS 30 Min Friday ET and SS Lab AP Music Class Standards (Links to National Music Standards [NMS]) I. II. III. IV. V. Musical Terminology (NMS 5) A. Terms for intervals, triads, seventh chords, scales, and modes B. Terms pertaining to rhythm and meter, melodic construction and variation, harmonic function, cadences and phrase structure, texture, small forms, and musical performance. Notational Skills (NMS 4, 5) A. Rhythms and meters B. Clefs and pitches C. Key signatures, scales, and modes D. Intervals and chords E. Melodic transposition Basic Compositional Skills (NMS 4, 5) A. Four-voice realization of figured-bass symbols and Roman numerals B. Composition of a bass line (with chord symbols) for a given melody Score Analysis (with or without aural stimulus) (NMS 6) A. Small-scale and large-scale harmonic procedures, including: 1. identification of cadence types 2. Roman-numeral and figured-bass analysis, including nonharmonic tones, seventh chords, and secondary-dominant chords 3. identification of key centers and key relationships; recognition of modulation to closely related keys B. Melodic organization and developmental procedures 1. scales (e.g., major, minor, pentatonic, whole-tone, modal) 2. motivic development and relationships (e.g., inversion, retrograde, sequence, imitation) C. Rhythmic/metric organization 1. meter type (e.g., duple, triple, quadruple, irregular) and beat type (e.g., simple, compound) 2. rhythmic devices and procedures (e.g., augmentation, diminution, hemiola) D. Texture 1. types (e.g., monophony, homophony, polyphony) 2. devices (e.g., imitation, canon) E. Formal devices and/or procedures 1. phrase structure 2. phrases in combination (e.g., period, double period, phrase group) 3. small forms Aural Skills (NMS 1, 2, 6, 7) A. Sight-singing (major and minor modes, treble and bass clefs, diatonic and chromatic melodies, simple and compound meters) B. Melodic dictation (major and minor modes, treble and bass clefs, diatonic and chromatic melodies, simple and compound meters) C. Harmonic dictation (notation of soprano and bass lines and harmonic analysis in a four-voice texture) D. Identification of isolated pitch and rhythmic patterns E. Detection of errors in pitch and rhythm in one- and two-voice examples F. Identification of processes and materials in the context of music literature representing a broad spectrum of genres, media, and styles 1. melodic organization (e.g., scale-degree function of specified tones, scale types, mode, contour, sequences, motivic development) 2. harmonic organization (e.g., chord function, inversion, quality) 3. tonal organization (e.g., cadence types, key relationships) 4. meter and rhythmic patterns 5. 6. 7. instrumentation (i.e., identification of timbre) texture (e.g., number and position of voices, degree of independence, presence of imitation, density) formal procedures (e.g., phrase structure; distinctions among literal repetition, varied repetition, and contrast; small forms) AP MUSIC COURSE CALENDAR (Monthly Calendars will be more detailed and may reflect adjustments to the following): September Theory: Unit 1: Physics of Sound: Overtone series, Properties of Sound, Vibration Elements of Music Unit 2: Fundamentals of Melody, Timbre, Meter, Harmony, Texture, Rhythm Unit 3: Rhythm and Pitch: Meter, basic notation, clefs, accidentals, enharmonic equivalents, grand staff, writing music manuscript Unit 4: Scales and Modes: Major, minor, modal, pentatonic, whole-tone scales, others, relative keys, parallel keys, tonality, circle of 5ths Unit 5: Intervals and inversions ET: Melodic and harmonic intervals, rhythm patterns SS: Learning Solfege October Theory: Review Units 1-5 Unit 6: Harmony, chord spelling, triads and inversions, roman numerals, scale degree names, figured bass, analysis symbols, seventh chord symbols Unit 7: Cadence types, non-harmonic tones ET: Chords and Chord Inversions SS: Introduction to melody and chords November Theory: Review Units 6-7 Unit 8: Voice Leading in Two Voices, Species Counterpoint Chapter 9: Texture and texture types Chapter 10: Melodic Organization: Motive, Sequence, Phrase, Period, Melodic Structure ET: Cadences, Simple progressions SS: Simple chord progressions, more complex or longer melodies including skips and more advanced rhythms by group and individually December Theory: Review Units 8-10 Unit 11: Voice leading rules, soprano/bass lines, four-part texture, doubling, parallelism, 6/4 chords, common chord progressions, realization of a Roman numeral progression and harmonic analysis Unit 12: Harmonic progressions, root relationships, descending 5th relationships, harmonization of melody, realization of a Roman numeral progression. ET: Melodic and harmonic intervals, rhythm patterns SS: Simple chord progressions, more complex or longer melodies including skips and more advanced rhythms by group and individually January Theory: Review Units 11-12 Unit 13: Seventh chords and resolutions, realization of Roman numeral progressions. ET: More Melodic dictation and chord progressions SS: More melodies including minor February Theory: Review Unit 13 Unit 14: Modulation, pivot chords, other types of modulation Unit 15: Secondary Dominants, secondary leading tone chords ET: More Melodic dictation and chord progressions SS: More melodies including minor March Theory: Review Units 14-15 Unit 16: Form ET: Samples from Previous AP Tests. SS: Samples from Previous AP Tests. Take Sample AP Exam April Theory: Review Unit 16: Form ET: Samples from Previous AP Tests. SS: Samples from Previous AP Tests. Take Sample AP Exam May Theory: Review for and Take the AP Music Test Major Analysis Project ET/SS: June Concert Music June Theory: Composition Project and Performances @ CSULA ET/SS: June Concert Music