Study Guide – Unit 1 Test
advertisement

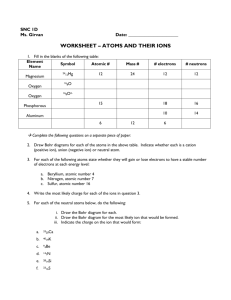
Study Guide – Unit 1 Test Name ___________________________ Pg ______ Nature of Science / Measurement 1. A measure of the amount of matter in a substance is called its ___________________________________. 2. The measure of the force of gravity on a substance is called ______________________________________. 3. A measure of the amount of mass in a given volume is called _____________________________________. 4. The amount of space that a substance takes up is called _________________________________________. 5. In scientific notation, 3.6 nanometers would be written as _________________________________meters. History of Atomic Theory 6. List a discovery and 2 important ideas that each theorist is given credit for: Discovered Idea 1 Idea 2 Dalton Thompson Rutherford Bohr Schrodinger 7. Who discovered which atomic model? Place a in the appropriate box: Who came 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th? Planetary model Billiard ball model Blueberry muffin model Electron Cloud model Bohr Dalton Schrodinger Thompson 8. Label each particle as either positive, negative, or neutral: Proton Neutron Electron 9. According to modern atomic theory, all elements are made of extremely small particles called __________. 10. According to the Particle Theory of Matter, ___________________ and ________________ are in the nucleus and __________________ orbit around on energy __________________. Density 11. A rock with a mass of 8 grams is placed in a graduated cylinder with 50 mL of water. The water level rises to 52 mL. What is the density of the rock? _______________________ 12. A rectangular block of wood that is 1 cm long, 2 cm high and 3 cm wide has a mass of 3 g. What is its density? ___________________ Will it sink or float in water? _____________ States of Matter 13. Label each of the following states of matter. _______ _______ _______ 14. Place the words in the Word Bank onto the graph in the appropriate place. Boiling point Gas Melting point Solid Liquid 15. The state of matter where the atoms are moving so fast that their electrons are stripped off the atom is called _______________________. 16. Which state of matter spreads out to completely fill its container, from top to bottom? _______________ 17. When carbon dioxide is frozen into a solid (called dry ice) and then allowed to warm up, it immediately changes to a gas (CO2). This process is called _____________________________________. 18. Place a in the appropriate box: Definite Shape Definite Volume Indefinite Shape Indefinite Volume Ionized Solid Liquid Gas Plasma Mixtures & Solutions 19. Place a in the appropriate box: 18 diff. gases in the air Heterogeneous mixture Homogeneous mixture Messy closet Chocolate chip cookie Kool-Aid in glass pH 20. Place a in the appropriate box: Sour taste Bitter taste Looks chalky Feels slippery Corrodes metal Turns blue litmus red Turns red litmus blue pH is 0-6 pH is 7-14 Acid Base 21. When you combine an acid and a base, what two substances will you get? ____________ and _________ Chemical & Physical Changes 22. Place a in the appropriate box: True False All kinds of matter have the same properties Each substance can be identified by its properties The properties of a specific type of matter can change All properties of all mixtures are all the same 23. Place a in the appropriate box: Acidic reaction Rusting iron Baking cookies Boiling water Cutting paper Crushing a can Slicing bread Burning gasoline Physical Change Chemical Change 24. What is the mass on the triple beam balance? ___________ 25. Ms. Williams wants to know the effect of Slushies on the behavior of 8th graders. On Monday, she allows first lunch to have them and 2nd lunch isn’t allowed. IV: ____________________, DV ________________, What are the 2 levels? __________________________________ and ______________________________ 26. Scientifically, how could Ms. Williams make her experiment better? _______________________________ 27. Gold is a metal found in the ground. You can sometimes find it in streams among the rocks and dirt at the bottom. When you scoop out a pan of dirt and put it under running water, the dirt and other rocks are washed away but the gold stays at the bottom of the pan. What property of gold makes “panning” for gold a good way to find it? _______________________________________________ 28. For your answer to #27 above, is this a physical or chemical property? _____________________________ 29. The cubes in both images below are all exactly alike, but they were put together into different shapes. Now how do they compare in mass and volume? a. Both objects have the same mass and same volume b. Mass is the same, but volume has changed c. Volume is the same, but mass has changed d. Both mass and volume are now different 30. The track coach wants to see which type of shoe affects the amount of time it takes to sprint 100 meters. She has the same boy try 3 different brands and clocks him running in each type of shoe 5 times. What is the IV? ____________________________, DV? _________________________ 31. In question 30, what would be the best type of graph to use? ____________________________________ 32. The diagram to the right is the design of a simple system. An example might be you eating a hamburger, digesting it, and then having the energy to run around. Another example is a computer: electrons go in, they are processed, then light, sound, and information comes out. Write down 2 other (different) examples of input/process/output systems. a. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 33. In systems, random variables occur that may or may not affect the output. In the 1 st example of a hamburger, a random factor might be that you are walking while eating. This does not change the fact that you get energy from the hamburger. In the second example, you might increase the volume so the sound is easier to hear. Again, this does not change the fact that electrons went in and sound came out. For each of YOUR examples above, give one random example that might appear to be a part of the process, but does NOT really affect the BASIC input/process/output system. a. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________