Survey of Life The Nature of Science and the Scientific Method
advertisement

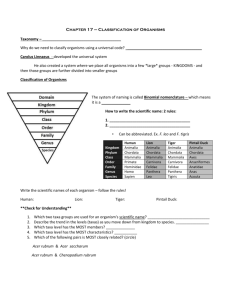
Survey of Life The Nature of Science and the Scientific Method What is the cartoonist trying to communicate? Science is knowledge gained from observing with the senses and experiments . Topics studied in a scientific way must have 3 characteristics: 1. Measurable: you can measure it. 2. Observable: you can use your senses to “feel” it. 3. Objective: it is a FACT. Check the boxes of the topics that are OBJECTIVE. NOT IN NOTES! Which items below that can be studied by Science? Earthquakes Viruses Angels Cells Stars Mind Reading Flowers Beautiful Music Delicious Food Summary: Decide whether each question below can be answered by science. What is the most beautiful type of Flower? Are Fish afraid of the Dark? How does temperature affect the growth of bacteria? Place a check mark next to the topics which can be studied scientifically? What is the most Are fish afraid of ✖ ✖ beautiful type of flower? ✓ Observable? Measurable? ✖ Objective? ✖ ✓ does temp. How affect the growth of bacteria? ✓ ✓ ✓ Observable? Measurable? Objective? the dark? Observable? ✖ Measurable? ✖ Objective? ✖ Tools & Precision Scientists use the metric system whenever they measure. a. Scientists measure length by using a ruler Meter (m) _______. The unit is the __________. Volume a. Scientists measure _________ by using a graduated cylinder. The unit Milliliter (mL) is the __________________. Tools Continued c. Scientists measure mass by using a balance ___________________. The unit is the Gram (g) ___________. Prefixes used with the Metric System. kilo a. __________ means 1000 times b. __________ means 1/1000th milli centi c. __________ means 1/100th Measurements need to be PRECISE. 1. Precision: close the measured values are a. How ________ each other. to _______ Smaller units (increments) allow b. ___________ for more precision. smallest c. The tool that measures the __________ amount and with the most increments . _____________ How Do Scientists Discover Truth? How do scientists study things scientifically? Remember: To scientifically study something, it must be-- Measurable 1.M -- ______________ Observable 2.O -- ______________ Objective 3.O -- ______________ The Scientific Method is A systematic approach to problem solving. There are not a set number of steps. One possible set of steps is shown below: 1. State theProblem what is the question you will answer? 2. Gather Information what is already known about the problem? 3. Form a Hypothesis 4. Perform.Experiment an educated guess based on what is known. testing the hypothesis. The Scientific Method (Cont’d) 5. Record and Analyze Data The information that is gathered (observations, measurements, times, etc.) 6. Form a Conclusion A statement based on data from your experiment stating whether or not your hypothesis was supported 7. Share results and Repeat! Making Good Hypotheses testable •A hypothesis must be _____________. Experiments ___________ are performed to test hypothesis. Therefore it must have the following characteristics: • Measurable • Observable • Objective Keywords often associated with hypotheses Believe, expect, think, predict Write a Hypothesis about different liquids to water plants. Ex: If plants are watered with koolaid, then they will not grow as well as plants with water, because there is added sugar. . Is this hypothesis testable? “Scientists think that acid rain decreases the ability of a plant to grow because plants don’t like acids.” Is this hypothesis testable? Conclusions I. A conclusion is a logical decision based on _______. data Data is information or observations ____________ taken from experiments. IV. Words that are associated with conclusions include: Conclude Decide Find Out Infer Deduce Look at the example in your notes… What do you think is the cause? Is this based on observations or data? Is this a valid conclusion? Why is it important for scientists to be objective when it comes to examining scientific data? Scientific Conclusions should be based on facts not opinions or beliefs so that the outcomes are reliable. Recall the steps of the scientific method Problem/question 1. _________________ Gather info 2. _________________ Hypothesize 3. _________________ 4. _________________ Experiment Record/analyze data 5. _________________ 6. _________________ Form a conclusion 7. _________________ Share results and repeat * Stop here for practice * Complete the practice scenarios of the scientific method. Keep these as part of your notes. Characteristics of Life BIO =Life All Living things share 7 primary characteristics. In order to be considered alive, all seven characteristics must be present. 1. Living Things are made up of: Cells Basic unit of life; collection of living matter surrounded by a barrier 2. Living things — Reproduce Producing new organisms similar to parent 3. Living things are based on universal genetic code carried in a molecule called DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid 4. Living things grow and ________. develop _____ 5. Living things obtain and use energy materials __________ and __________ (metabolism). 6. Living things maintain a stable internal environment _______ (homeostasis). Balanced internal conditions (ex: water content, temperature, pH) 7. As a group living things Change over time ______________________ (evolve). ***Circle the items below that are LIVING: Tornado Mushroom Flower Fire Rock You Computer Ant Volcano Bacteria Fish Car History of Biological Classification Classification – The Process of Grouping ______________ organisms based on Similarities ________________. Scientists classify organisms to help them determine Relationships between organisms. _____________ Scientists use the same criteria to choose characteristics to classify organisms as they use to determine what science can study: the characteristics must be Objective _______________, Measurable, and Observable _____________. Example: If you want to classify members of your biology class it would NOT be good to group them as “tall” and “short.” Why not? What could you use instead? Under 5’6” an over 5’6” ***Circle all of the terms below that would be appropriate criteria for classification. Height in cm Number of legs Most beautiful Classifying Taxonomy—the science of __________ Naming living things. and _________ How are relationships between living things determined? Physical Similarities— external and internal anatomy Chemical Similarities— DNA and other molecules Behavior— how organisms react to their environment How are living things classified? Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778), a Swedish botanist developed a system __________ called binomial nomenclature. In this system each species is assigned a two part scientific name. This system includes seven levels or taxa. Why is it important for scientists to have a universal naming system? Since there are many different languages, this provides a common way for all scientists to discuss organisms. Also avoids confusion due to slang. TAXA Example Kingdom General/Broad Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Order Primate Family Hominidae Genus Homo Species Specific/Inclusive sapiens Scientific Names According to Linnaeus’ system, every scientific name species has a Latin _______________ composed of the genus and species names. genus is always The first letter of the _________ species is capitalized. The first letter of the ________ lowercase. The entire scientific name is Underlined italicized or ___________. Species— group of living things that are capable of producing fertile offspring Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Human Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primate Hominidae Homo sapiens Cat Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Felis domesticus Lion Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Panthera leo Dog Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Canidae Canis familiaris 1. Which 2 organisms are the most closely related? Cat and Lion 2. Which organism is least similar to the others? Human 3. What is the scientific name for a cat? A dog? A lion? Felis domesticus Canis familiaris Panthera leo The Six Kingdoms of Life Objective 15 6 Today organisms are grouped into ____ kingdoms based on the following characteristics: Cell Type All living things are made of one or moreCells ______. Cytoplasm (mostly water) All cells are made of ___________ and are surrounded by a barrier called a Cell Membrane DNA _________________. All cells also have _______ ribosomes which stores genetic information and ____________ which are structures that make proteins 1. Cell Type: Prokaryotic— cells that do not contain a Nucleus ; DNA is found floating in the cytoplasm Draw an arrow to point to the DNA. 1. Cell Type cont. Eukaryotic— cells that contain a nucleus; the nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the DNA. Draw an arrow to point to the nucleus. 6 Kingdoms 1. Archaebacteria or Archaea 2. Eubacteria 3. Protista 4. Fungi 5. Plantae 6. Animalia Prokaryotic Kingdoms 1. Archaebacteria 2. Eubacteria Eukaryotic Kingdoms 1. Protista 2. Fungi 3. Plantae 4. Animalia Discovery Video