lesson 1.1 Energy Fixation
advertisement

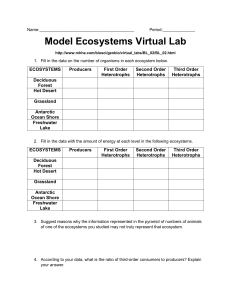
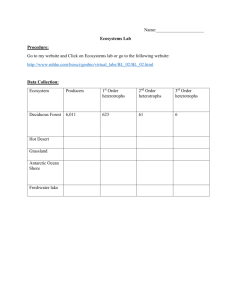
In groups define/ discuss the following words • • • • Habitat Population Community ecosystem • Producers • Primary consumers • Secondary consumers • decomposers Use the information below to draw a food web. Along the shallow water close to our beaches, producers such as brown algae, diatoms and dinoflagelates provide food for limpets and copepods. These in turn are eaten by carnivores such as starfish and arrowworms. Energy Flow in Ecosystems 1.1 Energy fixation Before looking through this powerpoint, Read: Pupil Monograph – Introduction and Page 1 –2 Scholar – 1.2 Energy Fixation Learning Intentions By the end of this section you will: 1. Understand what an autotrophs and heterotrophs. 2. Be able to explain the difference between Net Primary Productivity and Gross Primary Productivity and be able to do some calculations involving these. 3. Be able to define Biomass and describe how it is measured. 4. Have learned which factors can affect productivity and why the type of ecosystem will determine which factors will be most important. 5. Understand the relationship between water depth and photosynthetic production. Photosynthesis = conversion of energy from SOLAR ENERGY CHEMICAL ENERGY (CHO) • No ecosystem could exist without this initial energy conversion • This transformation is crucial to all life Energy capture SOLAR ENERGY Gross primary production = the total energy captured by the plant Producers Some energy used by the plant for cell processes (15 - 70% depending on species) Net primary production = the energy available for the primary consumer How to measure NPP? • increase in dry mass (Biomass) per unit time (because water content varies) (usually a year) • note NPP values from major ecosystems (p2 monograph) Which is most productive? Which is least productive? Which is most significant globally? Factors affecting primary productivity:- • availability of nutrients lack of nitrogen in tundra - slow rate of production upwelling zones in coral reefs - high productivity • light intensity • temperature • availability of water (rainfall!) Energy Flow in an Ecosystem OUTPUT: INPUT: HEAT, MOVEMENT, ENERGY SOLAR ENERGY Producers (autotrophs) Primary Consumers (heterotrophs) Secondary Consumers (heterotrophs) Decomposers Notes and Questions You may choose to make notes on what you have learned. You may make notes on the reading, then the powerpoint or you may like to combine to make 1 note. You may choose NOT to make any notes on this. If you make any notes PUT THEM IN YOUIR OWN WORDS. The learning intentions should help guide you! The questions and activities that follow are designed to test your understanding and recall of the key facts and ideas. Questions 1. In your notes or on flash cards provide the definitions for the following terms. Secondary consumer Heterotroph Primary consumer Producer Gross primary production Net primary production Biomass Autotroph (photoautotroph, chemoautotroph) 2. Circulation in Ecosystems Worksheet Q1-7 3. Scholar Pg 10 Q1-6