Strategy: A View From the Top
advertisement

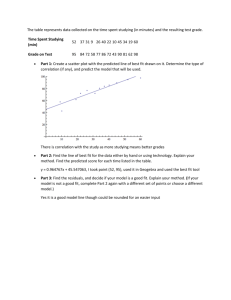
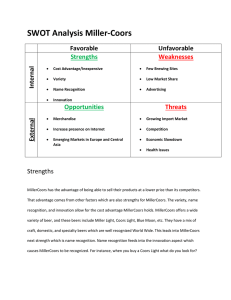
Strategy: A View From the Top TEAM 3 RANDY GREINERT MASON MITCHELL SARAH YELVERTON ALEC COOPER A View From the Top Positioning a company for competitive advantage by focusing on unique ways to create value for customers. Mission Vision Strategic intent Stretch Strategy Defined Slowing down the erosion process by protecting current sources of advantage against the actions of competitors. Investing in new capabilities that form the basis for the next position of competitive advantage. Good to Great into Strategy Level five leadership must be obtained before an overall strategy can be developed Financial gain is not as important as long term benefit of the company With the correct management in the correct places, management complications hurting the firm will cease. What can you be the best at the world at? Driving success towards a goal, or hedgehog. Going back to BOS and steering the firm to a blue ocean un dominated by the cut throat business world of today. Understand technology and the business environment. What drives you, $? CH. 4 Industry is defined in 4 dimensions Products (wine, beer, and spirits) Customers ( +21, Drinkers, segmented ) Geography Stage in the production-distribution Industry Structure, Concentration, and Product Differentiation Rule of Three and Four “Many stable markets will have only three significant competitors and the market shares of these competitors will roughly be proportioned as four-to-two-to-one, reflecting a concentration level of approximately 70% of total industry sales for the three competitors.“ 2007 Big three 78% Product Life Cycle Intro- High level of uncertainty Growth- Most intense competition Mature- Sales growth stagnant Declining- Industry considered unattractive Example- Bud Light Lime CH.5 To evaluate the relative worth of a company's strategic resources, 4 questions should be asked; 1- How valuable is a resource; does it help build and sustain competitive advantage? 2- Is this a unique resource or do other competitors have similar resources? 3- Is the strategic resource easy to imitate? 4- Is the company positioned to exploit the resource? Human Capital First and foremost – Companies are run by and for people Understanding people’s aspirations and concerns and capabilities is key to determine strategic position Dallas Cowboys Motorola Execs report that their company receives $33 for every $1 invested in employee education Organizational Strategic Resources Include a firm’s knowledge and intellectual capital base Reputation with customers partners suppliers and the financial community Specific competencies processes and skills sets And its corporate culture Ch.6 Introduction formulating business unit strategy • • • Involves creating competitive strategy within the industry. - SABMiller and Molson Coors merge US operations in 2007 Focus on how firms should compete in given setting. Factors Concerning Business Unit Strategy Nature of the Industry Company’s Mission, Goals and Objectives Current position Core competencies Competitors’ strategic choices Two Generic Strategies Low cost Differentiation Which one do you choose? Critique of Porter’s generic strategies Low cost production and differentiation are mutually exclusive, and when they exist together they result in sustained profitability. Differentiation can permit a firm to attain a low-cost position. The possibility of providing both improved quality and lower costs exists within the total quality management framework. CHAPTER 7 EMERGING INDUSTRIES - PRESENTS NEW OPPORTUNITIES EX: SOLAR ENERGY AND INTERNET TECHNOLOGY - G R O W T H I N D U S T R I E S - C H A L L E N G E S A R E FA C E D A S F I R M S T R A N S I T I O N T O M A R K E T M AT U R I T Y - M AT U R E A N D D E C L I N I N G I N D U S T R I E S - I M P O R TA N T T O C H O O S E B A L A N C E B E T W E E N D I F F E R E N T I AT I O N A N D C O S T S - F R A G M E N T E D I N D U S T R I E S - T H R I V I N G R E Q U I R E S C R E AT I V E S T R AT E G Y - D E R E G U L AT I N G I N D U S T R I E S - T H E R E M O VA L O F G O V E R N M E N T R U L E S A N D R E G U L AT I O N S T H AT C O N S T R A I N A M A R K E T F O R C E H A S RESHAPED SEVERAL INDUSTRIES E X : AT & T Q U I C K LY R E D U C E D P R I C E S T O H I G H - V O L U M E BUYERS TO COUNTER MCI AND SPRINTS AGGRESSIVE MARKETING EFFORTS -H Y P E R C O M P E T I T I V E I N D U S T R I E S - C O M P A N I E S D I S R U P T S T H E M A R K E T W I T H Q U I C K A N D I N N O V AT I V E C H A N G E T O G A I N A D V A N TA G E OVER COMPETITORS Business Unit Strategy Speed - Least understood critical success factor - Pace of progress that a company displays in responding to current or anticipated business needs - 4 sources of pressure to speed: customers, need for creating a new basis for competitive advantage, competitive pressures, and idustry shifts - Requirements of Speed: refocusing the business mission, creating a speed-compatible culture, upgrading communication, refocusing business process reengineering, and committing to new performance metrics - Methods to Speed: streamlining operations, upgrading technology, and forming partnerships (Ford Motor Company with GM and DaimlerChrysler) Innovation - Value creation greatly depends on innovation - “MillerCoors will have more flexibility and resources for brandbuilding initiatives and increased levels of innovation in taste, product attributes and packaging” - Disruptive innovation: launching new products that are not as good as existing products but are cheaper (IMB personal computer disrupted the minicomputer) - Sustaining innovation: focuses on “better” products - Creating a culture of innovation that time and effort - Innovation does not always create profitable performance 1. Products must be truly innovative 2. Innovative products must be commercialized once one the market 3. Products must be introduced into the market in a timely manner - To improve performance through innovation: plan synergy between strategy and innovation, and involve customers early and often CHAPTER 8 Global Strategy Formulation Globalization is needed and important because some countries or regions of the world are more efficient that others in producing particular goods Ex: Australia-Mining and US-Agriculture - In the absence of natural comparative advantages industrial clustering occurs - Factor conditions match a countries endowments to the characteristics and requirements of the industry Include: climate, minerals, skill levels, capital, infrastructure, etc. - Demand Conditions demand in home country - The presence of related and supporting industries - Competitiveness- the more domestic competition, the more successful firms will likely be competing globally - - Molson Coors operates in the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada Industry Globalization Drivers 1.) Market Drivers: Evolution of customer needs, Global Channels and Transferability There is an important need to meet customers expectations, Hamburgers in India 2.) Economic Drivers: Nature of the industry, Economies of scale/ location, Differences in country costs 3.)Competitive Drivers: Interdependence between countries/ regions and globalization of competitors 4.)Government Drivers: trade barriers, regulatory climate, and technology/standards Global opportunity- went global because there was a need to grow Target Markets- focused on most attractive markets such as the Americas for the first 5 years Mode of Entry- Acquisition, Start-Up, and Joint Venture Local Adaptation- China, smaller satellite stores fit better with local needs Local Competition- launching a frontal attack on the incumbent, took over (Woolco) a weak player Gains and Setbacks- Not all global moves were successful but overseas was the only place with markets that offer Wal-Mart the room it needs to grow Economies of scale and scope Economies of scale- unit cost of performing an activity decreases as the scale of the activity increases Economies of scope- when the unit of cost of an activity falls because the asset used is shared with some other activity Core Most valuable customers Most valuable products Most important channels Their distinctive capabilities Defining core is important because there is a tendency to under exploit the full potential. There is increasing returns to leadership instead of a linear relationship Molson Coors started defined cost reduction as part of the core. Saving 178 million in 2007 Growth strategies Build Buy or Bond -Organic or internal growth -growth through acquisitions -growth through alliance-based initiatives MillerCoors alliance started in order to compete with Anheuser Busch Concentrated growth- a corporation that continues to direct its resources to the profitable growth of a single product category in a well defined market Vertical integration- if Coors were to buy farms to grow hops Horizontal integration- if Coors started making and selling Koozies also if they set up a wider number of plants Diversification strategies- were good at making beer we would be good at making cars Diversification implementation Mergers and Acquisitions Cooperative Strategies- joint ventures, strategic alliances and other Why would you do this - Risk sharing - Funding limitations - Market access - Technology access Disinvestments Sell offs Spin offs And liquidations Managing a portfolio Early perspective: structure follows strategy and set up the company to follow strategy BCG approach -growth/share matrix -build General electric business screen -uses long term industry attractiveness MACS Matrix -recognizes that a corporations ability to extract value from a business unit should be benchmarked Life cycle matrix Plots business on stage of industry's evolution and strength of company’s competitive position How to decide Deciding on an overall, theoretically consistent, quantitative methodology for evaluating a complex corporate strategy proposal involving multiple options is not a simple undertaking. How to run a company will always require keen managerial insight, intuition, and creativity.