Unit7EvolResPg
advertisement
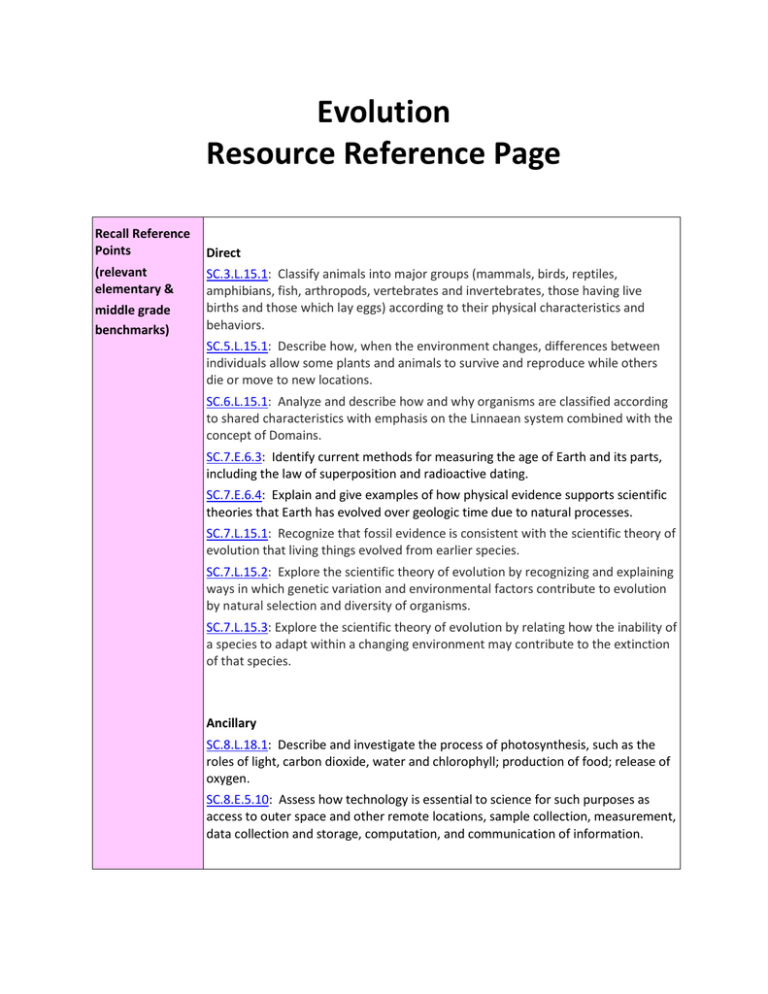
Evolution Resource Reference Page Recall Reference Points (relevant elementary & middle grade benchmarks) Direct SC.3.L.15.1: Classify animals into major groups (mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, arthropods, vertebrates and invertebrates, those having live births and those which lay eggs) according to their physical characteristics and behaviors. SC.5.L.15.1: Describe how, when the environment changes, differences between individuals allow some plants and animals to survive and reproduce while others die or move to new locations. SC.6.L.15.1: Analyze and describe how and why organisms are classified according to shared characteristics with emphasis on the Linnaean system combined with the concept of Domains. SC.7.E.6.3: Identify current methods for measuring the age of Earth and its parts, including the law of superposition and radioactive dating. SC.7.E.6.4: Explain and give examples of how physical evidence supports scientific theories that Earth has evolved over geologic time due to natural processes. SC.7.L.15.1: Recognize that fossil evidence is consistent with the scientific theory of evolution that living things evolved from earlier species. SC.7.L.15.2: Explore the scientific theory of evolution by recognizing and explaining ways in which genetic variation and environmental factors contribute to evolution by natural selection and diversity of organisms. SC.7.L.15.3: Explore the scientific theory of evolution by relating how the inability of a species to adapt within a changing environment may contribute to the extinction of that species. Ancillary SC.8.L.18.1: Describe and investigate the process of photosynthesis, such as the roles of light, carbon dioxide, water and chlorophyll; production of food; release of oxygen. SC.8.E.5.10: Assess how technology is essential to science for such purposes as access to outer space and other remote locations, sample collection, measurement, data collection and storage, computation, and communication of information. Textbook Direct Biology (Pearson) Chapter 16 Darwin’s Theory of Evolution (p. 448-479) Chapter 17 Evolution of Population (p.480-507) Chapter 19 (Section 2 & 3) History of Life (p. 546-569) Chapter 26 Section 3 Primate Evolution (p. 765-779) Biology (Glencoe) Chapter 14.2 The History of Life (p. 401-409) Chapter 15 Evolution (p. 416-443) Chapter 16. 2 & 16.3 Primate Evolution (p.461-475) Ancillary Biology (Pearson) General Animal Evolution: Chapter 25.2 Invertebrate Evolution: Define phyla and provide examples from Chapters 26, 27 & 28 Vertebrate Evolution: Define classes and provide examples from Chapters 26, 27 & 28 Biology (Glencoe) General Animal Evolution: Chapter 24.1 & 24.2 Invertebrate Evolution: Define phyla and provide examples from Chapters 24.3, 25, 26 & 27 Vertebrate Evolution: Define classes and provide examples from 28, 29 & 30 FCIM Lessons Direct SC.912.L.15.1 Evidence of Change SC.912.L.15.2 Molecular Clocks SC.912.L.15.3 Speciation and Extinction SC.912.L.15.8 Origin of Life SC.912.L.15.9 Explain the role of reproductive isolation in the process of speciation SC.912.L.15.10 Identify basic trends in hominid evolution from early ancestors six million years ago to modern humans SC.912.L.15.11 Discuss specific fossil hominids and what they show about human evolution SC.912.L.15.13 The conditions required for natural selection SC.912.L.15.14 Discuss mechanisms of evolutionary change other than natural selection such as genetic drift and gene flow SC.912.L.15.15 Describe how mutation and genetic recombination increase genetic variation Ancillary SC.912.L.15.4 Describe how and why organisms are hierarchically classified and based on evolutionary relationships SC.912.L.15.5 Explain the reasons for changes in how organisms are classified SC.912.L.15.6 Distinguishing characteristics of the domains and kingdoms of living organisms SC.912.L.15.7 Representatives of vertebrates & invertebrates SC.912.L.15.12 Conditions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium Labs REQUIRED TOPIC/SUGGESTED LAB: Survival of the Fittest — Variations in the Clam Species Clamys sweetus (student) (teacher) (http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/activities/index.html) Chapter 17 Lab B: Competing for Resources (BIOR_LBS_Lab17_V01.pdf) Icebreakers/Introductory activities: Ch. 16: Amino Acid Sequence: Indicators of Evolution (Pearson , p.474) Peppered Moth Peppered Moth Simulation (http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/pepperedmoth.html) Why is there variation in Peppers? (Pearson p. 457) (BIOR_AYS_PepVar_V01.pdf) Launch Lab Ch. 15 (Glencoe) How Does Selection Work? (BIOH_AYS_LaunchLab15_V01.pdf) Allele Frequency Lab Inquiry (From Pearson Lab Manual) (BIOH_AYS_AllFre_V01.pdf) Function of Opposable Thumb (Glencoe) (BIOR_AYS_OppThumb.pdf) Launch Lab Ch. 16 (Glencoe) What Are the Characteristics of Primates? (BIOH_AYS_LaunchLab16_V01.psf) Additional Labs and Hands-On Activities: Lab Manual (old Pearson) Making Coacervates (Lab Manual A, p. 143) Comparing Adaptations of Birds (Lab Manual A, p. 131) Modeling a Gene Pool (Lab Manual A, p. 137) Modeling Camouflage and Natural Selection (Lab Manual B, p. 119) Lab Manuals (Pearson) Comparing Bones (BIOR_AYS_ComBones_V01.pdf) Modeling Natural Selection (BIOR_AYS_ModNatSel_V01.pdf) Chapter 16 Lab B: Amino Acid Sequences: Indicators of Evolution (BIOR_LBS_Lab16_V01.pdf) Chapter 19 Lab B: Using Index Fossils (BIOR_LBS_Lab19_V01.pdf) Ecosystems and Speciation (BIOR_LBS_EcoSpec_V01.pdf) Investigating Hominid Fossils Lab B (BIOR_LBS_InvHomFos_V01.pdf) Lab Manuals (Glencoe) How is Camouflage an Adaptive Advantage? (Pre-AP Lab Manual, p. 35 38) (BIOH_LBS_PApLab11_V01.pdf) Biochemical Evidence for Evolution (Pre-AP Lab Manual, p. 39 - 42) (BIOH_LBS_PApLab12_V01.pdf) Biology Textbook Darwin’s Voyage (Pearson p. 451) Fossil Variety Activity (Glencoe, p. 393) BioLab Ch.16 (Glencoe p. 475): What Can You Learn about Bipedalism from Comparing Bones (BIOH_LBS_BioLab16_V01.pdf) Honors Extension **SUGGESTED: Activities Unit 4 STEM Web Quest (Glencoe): Playing Paleontologist (Student: BIOH_AYS_StemEvol_V01.pdf) and (Teacher: BIOH_AYT_StemEvol_V01.pdf) Open Inquiry Project 5 (Glencoe): History and Classification of Life (BIOH_LBS_HxClaLife_V01.pdf) Demos ** SUGGESTED Who wants to live for a million years natural selection game: (http://science.discovery.com/interactives/literacy/darwin/darwin.h tml) Natural Selection Interactive Simulation (http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/natural-selection) Chapter 16.3 Demo (Glencoe, p. 467): Tool Users Gizmos explorelearning.c Direct Human Evolution: Skull Analysis om (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=576) Evolution: Natural and Artificial Selection (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=575) Evolution: Mutation and Selection (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=554) Microevolution (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=521) Rainfall and Bird Beaks (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=404) Natural Selection [Peppered Moth] (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=447) The Effect of Environment on New Life Forms (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=397) Rabbit Population by Season (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=380) Chicken Genetics [Artificial Selection] (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=453) Ancillary Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=517) The Effect of Temperature on Gender (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=376) Food Chain: Reactions (http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspDetail&Resou rceID=381) Websites NOVA PBS Human Evolution (http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/07/index.html) NOVA Evolution Interactive Web resources (http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/teachers/resources/subj_06_02.html#life_29) NOVA Genetic Drift and the Founder Effect (http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/tdc02.sci.life.gen.foundereffect/) NOVA The Advantage of Sex: Why Did Sex Evolve (http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/tdc02.sci.life.evo.advantage/) NOVA Killer Microbe (http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/biot09.biotech.concpt.kmicrobe/) PBS The Red Queen (http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/tdc02.sci.life.evo.redqueen/) Exploratorium’s Which Embryo is Human? (http://www.exploratorium.edu/exhibits/embryo/embryoflash.html) Becoming Human Interactive Resources (http://www.becominghuman.org/) A Case Study in Human Origins (http://www.exploratorium.edu/evidence/) Biological Evolution Resources (http://www.learningscience.org/lsc3cevolution.htm) Population Genetics and Evolution LabBench Activity (http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab8/intro.html) Biology4Teachers Evolution Resources Website (http://www.biology4teachers.com/evolution.php) Video Snippets: Teosinte to Corn ( Artificial Selection Videos.zip ) Wolf to Woof ( Artificial Selection Videos.zip ) Stickleback Evolution ( HHMI Stickleback Fossil Primer.zip ) PBS: The evolution of Camouflage: (http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/01/1/l_011_03.html) PBS: Mutation: Sickle Cell Evolution (http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/01/2/l_012_02.html) HHMI Holiday Lecture Series: Evolution: Constant Change and Common Threads (http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/videosearch.html) HHMI Evolution: Fossils, Genes, and Mousetraps (http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/videosearch.html) Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (BIOH_VOE_Hardy_V01.ram) Molecular Clocks (BIOH_VOE_MolClo_V01.ram) Full Length: National Geographic’s Naked Science: Birth of Life (http://channel.nationalgeographic.com/series/naked-science/3151/Overview) NOVA: Judgment Day: Intelligent Design on Trial (full video available here: http://video.pbs.org/video/980040807/) PBS/NOVA Video Resources (http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/teachers/resources/subj_06_06.html) National Geographic: Morphed: Dinosaur to Turkey or When Whales had Legs (http://channel.nationalgeographic.com/series/morphed/all/Overview) History Channel’s Evolve Series [Eyes, Guts, Jaws, Skin, Flight, Communication, Size, Speed, Venom, Shape] (available at the public library or http://shop.history.com/detail.php?p=70393)