Chapter 5 Political Parties
advertisement

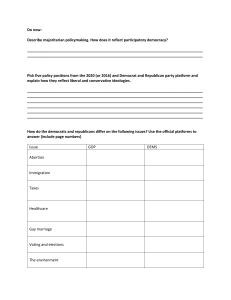
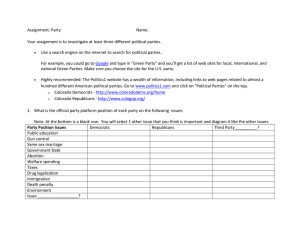
October 21, 2013 • Objectives: Students will be able to define a political party, and the functions. • What are the differences between a Democrat and Republican? CHAPTER 5 POLITICAL PARTIES Section 1: Political Parties and What They Do ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN YOUR NOTEBOOK: • 1. Name 2 political parties in the American political system. • 2. Which political party is the oldest in American history? • 3. Which political party favors less involvement by the government in our daily lives? • 4. Which political party favors social welfare programs? What is a political party? »It’s NOT what you attend at a friend’s house WHAT IS A POLITICAL PARTY? (2 DEFINITIONS) 1. Election oriented• A group of persons who seek to control government through the winning of elections and the holding of public office. WHAT IS A POLITICAL PARTY? (2 DEFINITIONS) 2. Principle or issue oriented• A group of persons joined together on the basis of common principles • seek to control government in order to affect certain public policies and programs. THE 2 MAJOR PARTIES IN AMERICAN POLITICS ARE: 1. Republicans THE 2 MAJOR POLITICAL PARTIES IN AMERICAN POLITICS ARE: 2. Democrats WHAT DO PARTIES DO? 1. The vital link between the people and the government. 2. a.k.a. “Power brokers”- they bring conflicting groups together by encouraging compromise between contending groups. 5 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF POLITICAL PARTIES ARE: 1. Nominating Candidates for public office • They select candidates and present them to voters. • They work to help their candidates win elections 5 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF POLITICAL PARTIES: 2. Informing and Activating Supporters • Parties campaign for candidates • take stands on issues • criticize the opponent’s positions on issues • try to activate people’s interest and participation in public affairs • Use pamphlets, signs, buttons, stickers, speeches, rallies, media advertisements. 5 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF POLITICAL PARTIES ARE: 3. The Bonding Agent Function • Ensure the good performance, good character, and qualifications of its candidates and officeholders 5 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF POLITICAL PARTIES ARE: 4. Governing • Congress and state legislatures conduct their business on the basis of partisanship • Political parties provide channels between the legislative and executive branches of government. • Constitutional change 5 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF POLITICAL PARTIES ARE: 5. Acting as Watchdog • The “party out of power” criticizes the behavior of the “party in power”- the party that controls the executive branch of government. • This criticism tends to keep the party in power more responsive to the wishes and concerns of the people. Who is Earl Dodge? The Prohibition Parties candidate for President of the US in 1984, 1988, 1992, 1996, and 2000. Why don’t you know him? What does it mean? Democrats and Republicans dominate American politics CHAPTER 5, SECTION 2: WHY A 2 PARTY SYSTEM?: • Throughout most of our history, the U.S. has been a 2party nation (the 1 st two political parties were the Federalists and Anti-Federalists) • The Constitution contains no provisions for political parties. • Single-member districts (aka SMD’s)-help to promote a two-party system, and they tend to discourage minor parties (most voters think of a vote for a minor party candidate as a “wasted vote.”) THE AMERICAN IDEOLOGICAL CONSENSUS: • Similarities: Both political parties are considered to be moderate, built on compromise, and seek the same goal of winning the majority of votes in the electorate. • Republicans and Democrats regularly act in a bipartisan manner. DIFFERENCES: EACH PARTY TENDS TO VOTE IN FAVOR OF: • Republicans • Democrats -Private market economies -Social welfare programs -Less Government regulation of business -More Government regulation of business -Less Government involvement in social programs -More Government involvement in social programs -Improve status of minorities MULTI-PARTY SYSTEMS • Multi-party systems have historically been a feature of European democracies. • Various parties are based on particular interests such as: • • economic class • religious belief • political ideologies Coalitions ex: Italy and France ONE PARTY SYSTEMS • One party system= “no party system” PARTY MEMBERSHIP PATTERNS: -Membership in a party is strictly voluntary -Each party has always been composed of a cross-section of the nation’s population. -No person or group is tied permanently to either party STEREOTYPICAL ALIGNMENT OF VOTING PATTERNS: Republicans Democrats • White Males • African Americans • Protestants • Catholic (until 2000) & Jewish People • Business Community • Business Union Members • Red: Republican • Blue: Democrat MAJOR SOURCES OF PARTY IDENTIFICATION: • Family • Major events • Economic status • Work environment • Age • Level of Education • Media FINAL 5 • Explain the 2 of the main functions of a political party & 2 differences between a Republican and a Democrat