Propaganda and Persuasive Techniques
advertisement

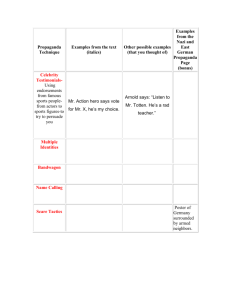
Propaganda and Persuasive Techniques English IA & IP Mrs. Spencer Definitions and Uses • Propaganda: Propaganda is ideas or information that is meant to influence people through their emotions, instead of with facts • Persuasive Techniques: In advertising, propaganda is sometimes called “Persuasive Techniques”, because someone is trying to persuade you to buy something. • 3 Common Uses of Propaganda – During Wars – In Politics – In Advertising Wartime Propaganda • Wartime Propaganda is used to appeal to the emotional stresses of military personnel and civilians as well. Many times propaganda flyers are dropped from planes into a war zone so they are easily accessible. Political Propaganda Propaganda, or Persuasive Techniques in Advertising Propaganda or Persuasive Techniques “Do You Buy It?” Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. M’m m’m good You deserve a break today, so get out and get away, at ______________. Just do it. ( a brand of athletic clothing) Snap! Crackle! Pop! Like a good neighbor, ______ is there. It’s finger lickin’ good I am stuck on ____, and _______s stuck on me. Have it your way, at __________ Leggo my _____________ Melts in your mouth, not in your hands They’rrrre GR-R-REAT! My bologny has a first name, it’s _____. My bologny has a second name it’s _______. Oh! I love to eat it every day and if you ak me why, I’ll say…Cause ______ has a way with B O L O G N A. I don’t want to grow up, I’m a ___________ kid. Give me a break, give me a break! Break me off a piece of that ____bar. The Uncola. Answers to “Do You Buy It” Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Campbell’s Soup McDonald’s Nike Rice Crispies State Farm Kentucky Fried Chicken Band-Aid Burger King Eggo Waffles M & Ms Kellogg’s Frosted Flakes Oscar Mayer Toys R’ Us Kit Kat Candy Bar 7-Up Technique Definition Example 1. Name Calling – Using negative words, usually in politics, to turn you against a competing person without giving evidence or facts “My opponent didn’t tell you the truth!” 2.Plain Folks Appeal – Trying to show that a person or product is good for “ordinary” people, because a person is “just like you” and understands you An ordinary looking family sits together at a table to eat a certain brand of macaroni. OR Politicians show pictures of themselves playing with a dog or with their children, wearing casual clothing. 3.Glittering Generality – Telling only positive things about something or someone, without giving evidence or facts “Pure, fresh, mountain spring water. Bottled especially for you in Utah from only our purest mountain springs.” 4. Bandwagon – Convincing us to accept someone or something because of its popularity Commercials that show everybody’s got one, or everyone’s doing it! 5. Testimonial – Using a famous person to try to make you buy or support something or someone Tiger Woods wears Nike clothing, and if you want to be like him, then you should, too! OR A famous actor is voting for a candidate, so you should, too. 6. Hidden Fears – Suggesting that a person or product will protect you against something unpleasant or dangerous If you don’t want “ring around the collar,” use a particular detergent. OR This person will protect America against terrorism. 7. Snob Appeal – Suggesting that association with a person or product can make you special The people who drive this kind of car wear fancy clothes, live in mansions, or go to great places. OR 8. Facts and Figures – Using tests, statistics or information that sounds “scientific” to prove that one product or person is better than another “Four out of five dentists recommend this toothpaste.” OR “73% of Americans believe this candidate will do a better job – can they all be wrong?” 9. Unfinished Comparisons – Comparing a product or person to another, without providing the other half of the comparison. “This soap cleans better!” – better than what? OR “This politician works harder for America.” – harder than whom? 10. Repetition – Repeating a name, slogan or product over and over in the same advertisement “Buy it for less at Jamisons” repeated at least four times in the same advertisement OR “He says he didn’t know” repeated over and over about a politician in the same advertisement. 11. Weasel Words, or 12. Empty Phrases – Using broad promises or phrases that don’t really mean anything “With this diet, you can loose up to 100 pounds.” OR “Vote for this politician. He’s a real American!” Test Your Knowledge Name the Technique Used in these Advertisements • Name Calling • Bandwagon Snob Appeal Hidden Fears Plain Folks Appeal Unfinished Comparisons Propaganda or Persuasive Techniques on Television • Television Commercials are typically geared toward a select group of viewers; therefore, businesses will wisely purchase time slots during the airing of particular television shows in order to reach their perspective buyers. Your Assignment • You are to watch 1 hour of television on a major network broadcast station and record your findings using the handout as a guide. Pay close attention to the target audience section. (teens, adolescents, families with small children, elderly, etc.) Select a Friend to Work With on the Next Assignment Magazine Advertisements • Choose a magazine to evaluate. Each couple working together should have two different magazines. • Count the number of pages with advertisements and then count the number of pages without advertisements. • Next, you and your partner will make a spread sheet using Excel to show your findings. Using Excel 1. Make a header: Go to View on the toolbar. Click “Header and Footer”. Click on “Custom Header”. Next, you should type in the heading “Magazine Data” and then type in both of your names in the Center section. Click “ok” when you are finished Label the Columns • Column A: Name of Magazine • Column B: Number of Pages with Ads • Column C: Number of Pages without Ads • Column D: Total Number of Pages • Column E: Percentage of Pages with Ads (You may make the columns wider by dragging your cursor over the adjoining vertical lines.) Column D and E • When typing in Column D for the first magazine line: you should type in =SUM(B2,C2) • When typing in Column E for the second magazine line: you should type in =B2*100/D2 • When you type in information for the second magazine you should adjust the line and column numbers accordingly. BEFORE YOU PRINT • GO TO FILE AND SELECT PRINT SETUP. SELECT A “LANDSCAPE” PRINT • GO TO FILE AND SELECT PRINT PREVIEW. • DO YOU HAVE A HEADING WITH BOTH OF YOUR NAMES? • ARE BOTH MAGAZINES ON THE SHEET? • If “yes” go ahead and print. Your Next Assignment • After drawing numbers, you and your partner will create an advertisement using the prompt and the technique given to you. • Your advertisement is due: Tuesday, March 1st. • You and your partner will present the advertisement to the class as you demonstrate the persuasion technique used and the prompt. • Don’t waste class time allotted and Good Luck!