Summary - The Scottish Government
advertisement

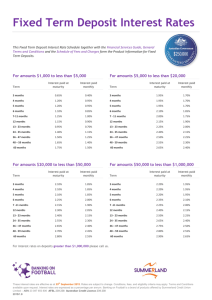
Scotland’s Digital Economy Maturity Index The Scottish Government’s vision The Scottish Government has a vision for all businesses in Scotland to have the • Availability of digital infrastructure, • Confidence, and • Skills required to embrace the internet and digital technologies. Whether they are large or small, working in Agriculture or in the Business activities sector, this will enable all businesses to make optimal use of digital technologies as appropriate for their specific sector, size and geographical location. Using data from the Digital Economy Business Survey 2014 (DEBS), the Scottish Government has developed a Digital Economy Maturity Index, which allows for the segmentation of businesses in Scotland according to their level of digitisation. Background – Business demographics and key findings from DEBS 2014 Business demographics – Sector and size Distribution of businesses by sector (%) The largest sectors were Distribution of businesses by size (%) • Most businesses are micro – with 1-9 employees. • Business Activities and • Wholesale/Retail Large 1 Medium 2 Small • This means micro businesses make up the majority of businesses in each maturity segment. Number of employees: Micro (1-9) Small (10-49) Medium (50-249) Large (250+) 15 Micro 82 0 50 100 Source: Digital Economy Business Survey 2014 Key findings – Internet take up • 92% of businesses have broadband – 19% of which have Next Generation Access** * Includes mobile networks such as 3G and 4G and dial-up. ** Download speed that is greater than 24Mbit/s. Key findings – Adoption and Benefits Adoption The most commonly adopted technologies were: • Having a website (73%) and • Using mobile internet and technologies (64%) Benefits Using different types of technologies bring a number of benefits to businesses. The most commonly cited were: • Generating exposure to the company; • Allowing greater flexibility and remote working for staff; and • Better targeted advertising. Key findings – Reasons for not using digital Among businesses that do not use various digital technologies, there was – a belief that the technology in question was of no relevance to the business; – a lack of understanding or knowledge of how to use technology; and/or – a lack of funds or lack of time. Scotland’s Digital Economy Maturity Index Purpose • To measure the level of digitisation of Scottish businesses and segment the business population into levels of digital maturity. • To establish the characteristics of businesses in each segment and identify the opportunities to develop their use of digital technologies based on their strengths and challenges. • To measure progress of digitisation of Scotland’s businesses over time. Methodology • Scotland’s Digital Economy Maturity Index (DEMI) has been constructed using a range of indicators from the Digital Economy Business Survey 2014* (DEBS). • The index consists of four main strands, under which there are a total of 12 indicators • Each indicator has been given a score based on its relative importance in terms of digital maturity. • A maximum score of 100 can be achieved. * Further details about the Digital Economy Business Survey 2014 can be found in the Annex. Indicators Digital Economy Maturity Index Adoption Usage Benefits Skills Type of internet conncetion Type of technologies used Benefits experienced from using digital technologies Digital technology skills gaps Overall importance of digital technology to current operations of the business Integration of technology into business Proportion of sales made over the internet Plans to develop employees' digital skills Engagement with public services online Internationalisation Strategy for use of digital in delivering business Digital technologies supporting product development Indicator weightings Benefits Digital Maturity Index – Indicators, sub-indicators and scores Score Max score * NGA (<24 Mbit/s) * Standard broadband * Internet not broadband * No internet connection 4 2 1 0 4 * Essential * Very important * Important 4 3 2 * Not important 0 Indicator Sub-indicator Adoption Type of internet connection Overall importance of digital technology to current operations of business 4 Usage * Website * Social media * Mobile internet and technologies Technologies used * Cloud computing * Data analytics * Management software 1 1 2 2 3 3 * Essential (9-10) * Very important (7-8) * Important (5-6) * Use but not important (3-4) * Use but not at all important (1-2) 5 4 3 2 1 30 * Obtain information * Obtain printable forms * Return filled in forms electronically * Carry out transaction digitally * eTendering 1 2 2 3 3 11 Integration of technology into business Engagement with public services online Strategy for use of * Yes digital in delivering * No business 1 1 2 2 3 3 * Researching competitor products online * Researching and gathering market data online * Collecting customer feedback via website or social media 1 Using digital technology to help innovation Proportion of sales made over the internet * All - 100% 5 * 80-99% * 60-79% * 40-59% * 20-39% * <20% * None 4 3 3 2 1 0 12 Internationalisation * Use of digital technology has increased the number of international markets exported to * Website tailored to international markets 2 12 6 3 4 5 8 4 Skills 2 0 * Website * Social media Benefits experienced * Mobile internet and technologies from using digital * Cloud computing technologies * Data analytics * Management software 2 Digital technology skills gaps * No skills gaps * Some skills gaps * Considerable skills gaps * Not applicable 3 2 1 0 Doing anything to develop employees' digital skills * Yes * No, but planning to in future * No, and not planning to in future 3 1 0 Total max 3 3 100 Maturity segments and scores Segment Digital Economy Maturity Index Score Disconnected Doubters 0-10 Basic Browsers 11-30 Tentative Techies 31-49 Enthusiastic Explorers 50-66 Digital Champions 67-80 Digital Pioneers 81-100 Digital Maturity of Scottish Businesses – Results Distribution of businesses by maturity segment • The vast majority of Scotland’s businesses are classified as Basic Browsers (38%) and Tentative Techies (30%). • Only 3% are classified as Digital Champions or Digital Pioneers. • 92 is the highest score achieved by any business. How the maturity segments differ - General characteristics Characteristic Disconnected Doubters Digital Champions Size Small and micro businesses are overrepresented in this segment. Medium businesses are overrepresented in this maturity segment. Sector Wholesale/retail, agriculture and construction sectors are overrepresented in this segment. Transport/Communications, Manufacturing and Other services are overrepresented in this segment. Age Are often over ten years old (84%*) Are often between 3-10 years old (48%) Growth expectations Expect to stay about the same size in the coming year (62%) Expect to grow moderately (50%) or expect to grow substantially (22%) in the next 12 months. Turnover Relative to other segments tend to have an annual turnover of less than £100,000 (37%) Tend to have an annual turnover of more than £250,000 but below £1 million (31%) Export Tend not to export (5%) Tend to be exporters (57%). Adoption of digital Tend to have adopted one technology – either website or mobile technologies. Tend to have adopted most of the six technologies. * All percentage figures throughout exclude don’t knows Disconnected Doubters (13%) Key characteristics Sectors Size Small (7%) Medium (1%) Micro (92%) Wholesale/Retail Agriculture are overrepresented in this maturity segment compared with their overall presence in the business population. Disconnected Doubters tend to … … have been established for over ten years (84%). … expect to stay about the same size in the coming year (62%). … have an annual turnover of less than £100,000 (37%). … not export (5%). Construction Disconnected Doubters (13%) Digital characteristics Current Future • Likely not to have an internet connection (34%). • Are unlikely to consider getting an internet connection. • If using technologies at all, it tends to be mobile technologies or have a website. • Have no intentions of using digital technologies in the future. Attitudes Do not see the need to go online or use digital technologies. Do not see how it could benefit the business. Disconnected Doubters (13%) Barriers No need and lack of a strong business case are the biggest barriers to future digitisation of the business. Opportunities • Changing attitudes towards digital. - Need to create a desire among Disconnected Doubters to explore the use of digital technologies to become more efficient, improve their competitiveness and grow. - Need to promote the benefits of adopting internet. Basic Browsers (38%) Key characteristics Size Sector Construction Agriculture Health/Social work Medium (1%) Small (15%) Micro (84%) are overrepresented in this maturity segment compared with their overall presence in the business population. Basic Browsers tend to … … have been established for over 10 years (70%). … expect to remain about the same (51%) or expect to grow moderately (35%) over the next 12 months. … have an annual turnover of between £50,000 and £250,000 (46%). ... not export (7%). Basic Browsers (38%) Digital characteristics Current Future • Tend to have a standard broadband connection. • Tend not to have any plans to develop digital skills of staff. • Most have adopted 1 or 2 technologies – most commonly a website or mobile technologies. • • Some make use of public services online – mainly to look for information. However, a majority hope to develop the use of their websites and social media. Some wish to expand their use of mobile technologies, cloud computing and data analytics. Attitudes Tend not to consider technologies important to the running of the business. Do not think that technologies are of any relevance to the business. Basic Browsers (38%) Barriers Lack of funds and lack of skills pose the greatest barriers to future digitisation of the business. Opportunities • Encourage take up of improved broadband connections and a wider range of technologies. • Learn from businesses in more digitally mature segments about how effective use of digital technologies can benefit the business. • Equip staff with the appropriate skills to further develop use of the technologies in place. Tentative Techies (30%) Key characteristics Sector Size Micro (79%) Small (18%) Medium (3%) Large (1%) Manufacturing Business Activities Health/social work Other services are overrepresented in this maturity segment compared with their overall presence in the business population. Tentative Techies tend to … … have been established for over 10 years (66%). … expect to grow moderately (44%) or remain about the same (36%) over the next 12 months. … have an annual turnover of between £50,000 and £250,000 (43%). … have started to export (23%). Tentative Techies (30%) Digital characteristics Current Future • Tend to have standard broadband connections. • Consider digital technologies to be very important to the future competitiveness of their business. • Most have adopted 3 of the key digital technologies. • Expect to start or increase the sales made over the internet in the next 2-3 years. • Tend to use public services online to obtain information and return filled in forms online. • Tend to make at least some sales online. Attitudes Consider technologies to be important to the current running of the business. However, they tend not to see the full potential of how technologies can benefit the business. Tentative Techies (30%) Barriers Lack of time and lack of funds are the biggest barriers to future use of digital technologies. Opportunities • Encourage a more structured approach to the use of digital by promoting the adoption of a digital strategy. • Promote the use of technologies as a means of increasing their international presence. Enthusiastic Explorers (15%) Key characteristics Size Large (2%) Sector Business Activities Transport/Communications Medium (4%) Small (17%) Micro (76%) Enthusiastic Explorers have the greatest representation of large businesses. Other services Manufacturing are overrepresented in this maturity segment compared with their overall presence in the business population. Enthusiastic Explorers tend to … … have been established for over 10 years (58%) … expect to grow moderately (47%), or remain about the same size (26%) over the next 12 months. … have an annual turnover of between £100,000 and £500,000 (44%). … be likely to export (42%). Enthusiastic Explorers (15%) Digital characteristics Current • • • • • Tend to have adopted at least 4 of the key digital technologies. Likely to have a digital strategy. Tend to be exploring new ways of communicating with customers through a range of social media channels. Most have started using digital technologies to aid product development. Will use digital technologies to increase their exports. Future • Consider digital technologies to be very important or essential to the future competitiveness of the business. • Expect to start selling or significantly increase the proportion of sales made online. • Hope to develop the use of their existing technologies. • Tend to have plans to develop the digital skills of their staff. Attitudes Consider technologies to be very important or essential to the running of the business. Enthusiastic Explorers (15%) Barriers Cost, lack of time and lack of skills are the biggest barriers to future use of digital technologies. Opportunities • Build on existing desire to digitise: Need to build on these businesses’ established desire to develop their use of digital technology. Further promote the use of digital technologies to aid product development and to increase their international presence. • There is still scope for further exploitation of digital technologies for Enthusiastic Explorers to become more efficient, increase their turnover and improve their competitiveness. Look towards the Digital Champions to learn from them. • Promote the case for wider adoption of Next Generation Access, presenting the opportunities that follow from having a fast and reliable internet connection in place. Digital Champions (3%) Key characteristics Sector Size Transport/Communications Manufacturing Micro (65%) Other services Small (26%) Medium (7%) Large (2%) are overrepresented in this maturity segment compared with their overall presence in the business population. Digital Champions tend to … … have been established for between 3-10 years (48%). … expect to grow moderately (50%) or expect to grow substantially (22%) in the next 12 months. … have an annual turnover of between £250,000 and £1 million (31%). … be exporters (57%). Digital Champions (3%) Digital characteristics Current Future • Among the most likely to have adopted NGA (29%). • Tend to have plans in place to develop staff’s digital skills. • Tend to have a digital strategy. • • Tend to use all digital technologies and use them extensively. Have a desire to develop the use of the digital technologies already adopted. • Most are using digital technologies to aid product development and have also increased the number of international markets they have been able to export to. • Expect to start selling or significantly increase the proportion of sales made online in the next 2-3 years. Attitudes Digital technologies are essential to the running of the business. Digital Champions (3%) How do Digital Champions differ from the rest? Exploitation of digital technologies • Digital Champions do not only make use of most of the key digital technologies, but also make more extensive use of the technologies. For example, they tend to: • Allow customers to place orders and make payments over the internet via their website; • Communicate with customers and promote the business through a range of social media channels; • Use social media to help recruit; • Use data analytics to provide better targeted marketing. Benefits • Digital Champions are more likely to experience benefits from digital technologies in terms of: • Improved sales, turnover and/or profits • Increased responsiveness to customers • Increase efficiency. Digital Champions (3%) Barriers Cost and lack of time pose the biggest barriers for these businesses to further develop their use of digital in the next 12 months. Opportunities • Build on existing desire to digitise: Need to build on the established desire to develop their use of digital technology to maintain their competitiveness in the increasingly digitised world. • Promote the case for wider adoption of Next Generation Access, presenting the opportunities that follow from having a fast and reliable internet connection in place. • Lessons to learn: Embrace the lessons available to learn from these companies to encourage greater and more efficient use of digital among businesses in the other maturity segments. Digital Pioneers (0.2%) • Businesses with a Digital Economy Maturity Index score of between 81-100 are classified as Digital Pioneers. • 0.2 per cent of businesses receive a DEMI score of between 81-100 at the moment. • This suggests significant untapped potential in many Scottish businesses to further develop their use of digital technologies to fully reap the benefits that the digital age has to offer. • The following pages provide a description of what Digital Pioneers might look like. Digital Pioneers – digital characteristics Adoption and Usage • Digital Pioneers have adopted Next Generation Access and are making extensive use of a range of key digital technologies. • They communicate with their customers and other businesses using a number of digital channels, and they are likely to offer customers the choice to order products and make payments online. Strategy • They have a strategy for digital, with a clear idea of their current level of digitisation and how to improve in this area. Digital Pioneers – digital characteristics Benefits • Digital Pioneers successfully exploit digital technologies and reap benefits from this in terms of improving their competitiveness, increasing their efficiency and increased growth of their business. • They are improving working conditions for their staff through offering flexible working using mobile technologies and cloud computing. They also use technologies to increase their responsiveness to customers. • They are also using digital technologies to innovate and develop new products and services and effectively use technology to reach out to international markets. Skills • Digital Pioneers recognise the need to continuously develop the digital skills of their staff and have plans in place to do so. Digital Economy Maturity Index - Summary Summary • The vast majority of Scottish businesses are to be found in the second lowest or middle maturity segments. • Only around 3% of businesses are classified as Digital Champions or Digital Pioneers. • There is further potential for businesses to increase their digitisation to: - Improve their competitiveness - Increase innovation - Improve efficiency - Grow. Summary of characteristics of the maturity segments* Enthusiastic Digital Champions Explorers Tentative Techies Basic Browsers Disconnected Doubters Size Large Medium Small Micro Size Size Size Size Size Sector Agriculture Manufacturing Construction Wholesale/Retail Hotels/Restaurants Transport/Communications Business Activities Health/Social Work Other services Sector Sector Sector Sector Sector Age Between 3-5 Between 5-10 years Older than 10 years Age Age Age Age Age Growth expectations Growth expectations Growth expectations Growth expectations Growth expectations Characteristic Growth expectations Grow substantially Grow moderately Stay about the same Contract moderately Contract significantly or close down * Digital Pioneers have been excluded as the sample size is too small to draw any conclusions with regards to their characteristics. Summary How the maturity segments differ Businesses in the different maturity segments differ in terms of : • Take up of internet and the type of connection. • Number of digital technologies adopted. • Extent of the exploitation of the technologies used. • Attitudes to digital. • Extent of benefits experienced from using digital technologies. • Extent to which digital is used to aid product development and expand international presence. • Plans to develop use of digital in the future. Disclaimer The results presented here are broad conclusions and generalisations made based on the results from the Digital Economy Maturity Index and the wider Digital Economy Business Survey. The results may not describe every business in the respective maturity segments and should be seen as indicative only. Annex Digital Economy Business Survey 2014 • The Scottish Government, in partnership with Scottish Enterprise, Highlands and Islands Enterprise and Skills Development Scotland, commissioned IFF Research to carry out a Digital Economy Business Survey in the summer of 2014. • The aim of the survey was to establish a baseline on the current level of digitisation by Scottish businesses and to allow digital progress to be measured and tracked over time. • In total, 4,002 businesses (excluding sole traders) in Scotland took part in the research via a telephone survey. 1,809 of these interviews were carried out with businesses in the Scottish Enterprise (SE) area, while 2,193 interviews were undertaken with businesses in the Highlands and Islands Enterprise (HIE) area. • A report on the High Level Results from the survey can be found here: http://www.gov.scot/Topics/Economy/digital