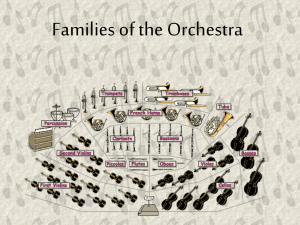
Sections of the Orchestra
advertisement

Unit 3 Time Periods; The Evolution of the Orchestra The Beginning of the Orchestra Orchestra dates back from the beginning of mankind. Primitive people had instruments made of natural resources. Do Now: What do you think their music sounded like? Do you think that their music was more melodic or rhythmic? Explain your answer. The Beginning of a Modern Orchestra. The orchestra began its slow growth about 400 years ago. Real orchestras did not appear until bowed stringed instruments; Late Renaissance Period /Baroque Period. Do Now: What are bowed stringed instruments? In an orchestra, the wind instruments would double /play along with the strings. Baroque Period; 1659-1695 Composers started to write special parts for wind instruments. flute Oboe Trumpet (Brass) bassoon The French Horn was included. (Brass) Do Now: What kind of music did Brass instruments play? For what occasions? J.S. Bach and G. F. Handel From 1685-1759 these composers had 2 flutes 2 oboes 1 or 2 bassoons 2 horns (brass) 2 trumpets (brass) Drums Strings: violins, violas, cello and contra bass. Classical Period, 1700-1800 The orchestra grew immensely during this music era. Composers Mozart, Beethoven and Haydin enlarged the orchestra further. The clarinet was added to the orchestra. Special percussion instruments were also added. Do Now: Name some of the percussion instruments that belong in the symphonic orchestra? Stringed instruments were doubled in numbers. Romantic Period, 1800’s The trombone and tuba were added to the orchestra. The number of horns were increased. The string section was enlarged further. By the end of the 1800’s, the symphonic orchestra was established with 90-100 players. Sections of the Orchestra Orchestral instruments are usually divided into four families: strings, woodwind, brass and percussion. These families normally sit together in an orchestra. The strings sit at the front, then the woodwind, and the brass and percussion in two groups at the back. Do Now: Why do your think these families sit in this order? Explain Your Answer Strings Common instruments: violin, viola, cello, double bass. There are almost always two sections of violins, one viola section, one cello section and one double bass section. The first violin is the concert master and the leader of the orchestra next to the conductor. This player plays all the violin solos. Sits first chair, for Best violin player. Woodwinds Common instruments: flute, oboe, clarinet, bassoon. The woodwind instruments usually sit in two rows in the center behind the strings. Mostly, there is a pair of each instrument: for instance, a 1st and 2nd flute. Unlike the strings, each player has a separate part to play. In addition to these, you often see a piccolo, contra-bassoon in music from the 19th century onwards. Brass Common instruments: trumpet, trombone, bass trombone, tuba, french horn. The brass section normally sits in two groups: the french horns and the other instruments. The brass section sits behind the woodwind section. Percussion Common instruments: suspended cymbal, crash cymbal, tambourine, triangle, side-drum, bass drum, timpani, xylophone, glockenspiel. The percussion section has the highest number of possible instruments, but usually only a small number are used in a piece of music. When composers want a special sound, like cow-bells, thunder or wind, the percussion section has to make it! There are only about 4 players in this section, so they need to be very flexible. This section sits behind the brass section.