N 4-5 Revision Questions unit 2

2.
National 4/5 Revision Questions
Unit 2 Nature’s Chemistry
1. Crude oil is a fossil fuel.
(a) Name another fossil fuel.
(b) Crude oil can be separated into fractions.
Identify the fraction in which butane is present.
The key below shows the name and general formula of some families of hydrocarbons.
Butyne is an alkyne with 4 carbon atoms.
Using the key, write the molecular formula for butyne.
1
3. Oil and natural gas are fossil fuels.
(a) Circle the correct words to complete the sentence.
(b) When burned, some fossil fuel produce a poisonous gas. This gas reacts with water in the atmosphere to produce acid rain. Name this poisonous gas.
4.
When butane burns in oxygen, carbon dioxide and water are produced. Write an equation using symbols and formulae for the burning of butane, C
4
H
10
.
5. Coal is a fossil fuel which burns, releasing energy.
6.
(a) What name is given to all chemical reactions which release heat energy?
(b) Coal is a finite resource. What is meant by the term finite ?
(c) Name another fossil fuel.
(a)
Some cars use the fuel “LPG” rather than petrol. What is meant by the term fuel?
(b)
“LPG” is a mixture of hydrocarbons. Name the two compounds produced when
“LPG” burns in a plentiful supply of air.
2
9.
8.
7. The higher the octane number of a fuel, the better it burns.
(a) How does the number of carbon atoms affect the octane number of the alkanes?
(b) Predict the octane number of the alkene with 3 carbon atoms.
The diagram shows a tower in which crude oil is separated.
(a) Name the process used to separate crude oil.
(b) As the boiling point of the fractions increases, what happens to the size of the molecules?
(c) As the molecules increase in size which fraction will have the highest viscosity?
Candle wax contains hydrocarbons.
(a) Name the elements present in a hydrocarbon.
(b) A student carried out this experiment.
(i)
(ii)
What gas is used up when the candle burns?
In the experiment, a gas was produced which turns lime water milky. Name the gas.
3
10. Information about the boiling points and colours of fractions of crude oil is shown below.
What colour is the fraction that boils at 260 o
C?
11. Octane is a hydrocarbon.
(a)
(b)
To which family of hydrocarbons does octane belong?
The diagram shows the apparatus used to crack octane.
Octane is cracked using an aluminium oxide catalyst. Bromine solution is used to show that some of the products are unsaturated.
(i) Copy the diagram and complete it by adding labels.
(ii) One of the reactions taking place is
C
10
H
18
Identify X.
C
3
H
6
+ X
4
14.
12. Long chain alkanes in diesel can be broken down using aluminium oxide as a catalyst.
(a) What is a catalyst?
(b) One reaction taking place is
C
16
H
34
C
7
H
14
+ Y
(i) Name this type of reaction
(ii) Name Y.
(iii) What effect would C
7
H
14
have on bromine solution?
13. The names of some hydrocarbons are shown in the grid.
(a) Identify the two saturated hydrocarbons .
(b) Identify the hydrocarbon with a boiling point of 36 o
C. You may wish to use your data booklet.
(c) Identify the hydrocarbon with molecular formula C
4
H
8
.
(a) Identify the hydrocarbon with six carbon atoms in the molecule.
(b) Identify the two hydrocarbons which are alkenes.
5
15. Cracking long-chain hydrocarbons produces smaller, more useful molecules.
One of the reaction taking place is:
(a) Draw a structural formula for octane.
(b) (Write the molecular formula for X.
(c) 0.1g of aluminium oxide was used as a catalyst.
(i) What mass of aluminium oxide will be present at the end of the experiment?
(ii) Write the formula for aluminium oxide.
16. Heptane can be cracked as shown.
(a) The product C
3
H
6
decolourises bromine solution quickly. Draw a structural formula for an isomer of C
3
H
6
, which would not decolourise bromine solution quickly.
(b) C
7
H
16 and C
4
H
10 belong to the same homologous series. What is meant by a homologous series?
(c) Ethylthioethane can be formed by the reaction of ethylthiol with ethane.
Suggest a name for the type of reaction taking place.
6
17. Use the grid to answer the questions.
(a) Identify the two hydrocarbons with the general formula C n
H
2n
, which do not react quickly with bromine solution.
(b) Identify the hydrocarbon which is the first member of a homologous series.
(c) Identify the two isomers of
18. Use the grid to answer the questions.
(a) Identify the two hydrocarbons with the general formula C n
H
2n
, which do not react quickly with hydrogen.
(b) Identify the compound which is an isomer of the compound in box A.
(c) Identify the compound which belongs to the same homologous series as the compound in box D.
7
19. 2-methylpentane and hexane have the same molecular formula (C
6
H
14
), but different structural formulae.
What term is used to describe this pair of alkanes?
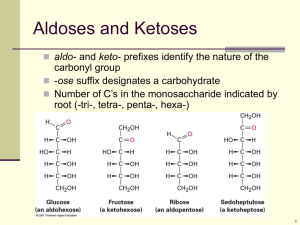
20. The carbohydrate glucose is made when green plants absorb light energy from the sun.
(a) Name the chemical, present in green plants, which absorbs light energy.
(b) Describe the chemical test, including the result, for glucose.
(c) Copy and complete the sentence by circling the correct words.
(d) Scientists have developed a method of producing hydrocarbons from carbohydrates. Name the element removed from a carbohydrate to produce a hydrocarbon.
21. Flowers produce a sweet-tasting liquid called nectar. Nectar contains a mixture of sugars such as glucose and sucrose.
(a) To which family of compounds do glucose and sucrose belong?
(b) Glucose can be broken down to produce alcohol.
(i) Name this type of chemical reaction.
(ii) What is the chemical name for the alcohol produced?
22. Starch and sucrose are carbohydrates.
(a) Describe the chemical test, including the result, for starch.
(b) Starch is made by joining glucose molecules together. Name the type of chemical reaction taking place.
(c) Harry set up an experiment to investigate the burning of carbohydrate.
His results are shown below:
(i) Which carbohydrate, starch or sucrose, released the most heat energy?
(ii) Harry used the same volume of water in each experiment. Suggest another variable which should be kept the same to make a fair comparison.
8
23. The grid shows the names of some processes.
Identify the process which is used to increase the alcohol concentration of fermentation products.
24. Saliva contains an enzyme which breaks down starch.
(a) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place when starch breaks down.
(b) A student carried out an experiment to break down starch.
He repeated the experiment using water at 100 o
C.
What effect would this have on the activity of the enzyme?
(c) The monosaccharide glucose is produced when starch is broken down.
Name another monosaccharide.
25. (a) Ethanol, for alcoholic drinks, can be made from glucose. Name this process.
(b) The table below shows the relationship between the percentage of ethanol and the density of alcoholic drinks.
Write an general statement describing how the percentage of ethanol affects the density of the alcoholic drink.
9
26. (a) Write the molecular formula for sucrose.
(b) Name an isomer of sucrose.
(c) (i)
What is meant by the term “enzyme”?
(ii) The graph shows how the temperature affects the activity of an enzyme.
State one other factor which has a similar effect on enzyme activity.
27. The grid shows the names of some carbohydrates.
(a) Identify the condensation polymer.
(b) Identify the two monosaccharides.
28. Alcohol can be formed from glucose.
(a) Name the process by which alcohol is formed from glucose.
(b) Name the gas given off during this process.
29. The equation for the reaction taking place during fermentation is:
Copy this equation and balance it.
10
30. Ethanol, C
2
H
5
OH, is the alcohol found in whisky.
A bottled of whisky contains 230 g of ethanol.
Calculate the number of moles of ethanol present in the whisky.
31. Ethanol can be used to make esters which can be used as flavourings for food. The following ester is used to given ice cream a rum flavour.
Name this ester.
32. Butan-2-ol is a member of the alkanol family.
Draw the full structural formula for an isomer of butan-2-ol.
33. Starch is hydrolysed by the enzyme amylase during digestion.
(a)
(b)
What is produced when starch is hydrolysed?
Name another substance which can be used to hydrolyse starch.
34. Name the process by which plants make glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
35. The shortened structural formula for an organic compound is
Which of the following is another way of representing this structure?
11
37.
36. In which of the following experiments would both carbohydrates give an orange precipitate when heated with Benedict’s solution?
38. Fermentation of glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast stops when the ethanol concentration reaches about 13%.
12
39.
40. Scientists have replaced oils in gloss paints with synthetic polyesters. This has improved the drying quality of paint. The first step in the production of the synthetic polyester is shown.
(a) Copy the triglyceride structure and circle the ester link.
(b) Name X.
41. Hydrolysis of an ester gave an alkanol and an alkanoic acid both of which had the same molecular mass of 60.
The structure of the ester was
13
42. Calculate the enthalpy change in the following reactions;
(a) 0.5g of methanol burns to heat 250cm
3
of water and produces a temperature change of 15 o
C.
(b) 4g of propanol burns to heat 1000cm 3 of water and produces a temperature change of 45 o C.
(c) 2.5g of butanol burns to heat 500cm
3
of water and produces a temperature change of 20 o
C.
43. Silver jewellery slowly tarnishes in air. This is due to the formation of silver(I)sulphide.
The silver(I)sulphide can be converted back to silver using aluminium.
Calculate the mass of silver produced when 0.135g of aluminium is used up.
44. (a) Copy this equation and balance it.
(b) Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced when 1400kg of carbon monoxide is used.
45. Some clothes should be dry-cleaned. Many different compounds, such as carbon chloride, perchloroethylene and trichloroethane, have been used as solvents in the dry-cleaning process over the years.
(a) Name the elements present in carbon chloride.
(b) Perchloroethylene was first used in the dry-cleaning industry in 1925.
The chart shows the use of perchloroethylene over a 20 year period.
In which year did the use of perchloroethylene first fall below 75 kilotonnes?
14
46. An experiment was set up to investigate photosynthesis. The number of oxygen bubbles produced by a plant in one minute was counted.
The experiment was repeated with the lamp at different distances from the plant. The results are shown.
(a) Write a general statement about how the distance of the lamp from the plant affects the number of bubbles of oxygen produced in one minute.
(b) Predict the number of bubbles of oxygen produced if the lamp was placed
120cm from the plant.
47. The protein content of some foods is shown in the table.
Show this information as a bar graph.
15
48. The following bar graph shows the nutritional content in 100g of pizza.
(a)
(b)
What mass of carbohydrate is in this pizza?
A person eats a 200g pizza. What mass of protein was eaten?
49. Ibuprofen is the active ingredient in Paineeze.
10g of Paineeze contains 1 gram of Ibuprofen.
Use the relationship below to calculate the percentage of Ibuprofen in 10 grams of
Paineeze.
50. When petrol is burnt, carbon dioxide is produced. The graph shows that the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is falling.
In what year will the UK reach the government target?
16