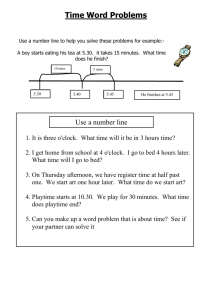
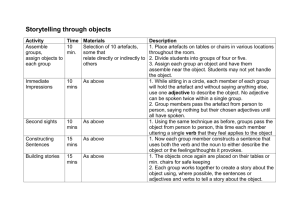
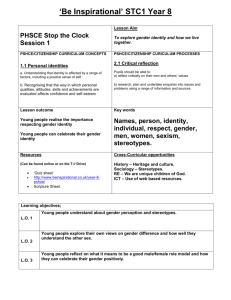
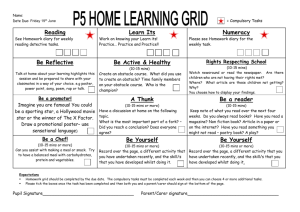
Basic mathematical economics
advertisement

Lesson Plan Guideline Superior University 1 Lesson Plan Guideline Business Mathematics and Statistics (BBA/B.Com Hons) Module Handbook Contents Staff and Course Delivery Arrangements 02 Course Introduction 04 Course Objective 05 Outcomes 06 Student Gain 07 Teaching and Learning Methodology 09 Assessment criteria 09 Lecture Plan 11 Penalties 16 Assessment Grades and Percentages 17 2 Lesson Plan Guideline STAFF AND COURSE DELIVERY ARRANGEMENTS 1. Teaching Staff Course Team Name Muhammad Zia Ullah Khan Room and Building MS department Phone Number 0333-4265478 Email pme@superior.edu.pk Consultation Hours On appointment Course Name and code: Business Mathematics & Statistics Credit Hours: 3 3 hours per week for the 15-week semester Program: BBA/B.Com Hons Semester: 1st Pre Requisites: Follow Up: Text Book: Session: 2014 – 2017 Business Mathematics & Statistics NA Introductory Mathematical Analysis for Business, Economics, and the life and social sciences (by Ernest F. Haussler, 3 Lesson Plan Guideline Richard S. Paul) Applied Mathematics for Business, Economics and the Social Studies (By Frank S. Budnick) Business Mathematics and statistics (By Mirza Mohammad Hassan & Mohammad Ali Mirza) (By Abdullah) Introduction: This course is designed to learn basic concepts and techniques of mathematics. A thorough knowledge in the areas of basic mathematics is an essential skill for management sciences. In view of the need to estimate the uncertainties of business decisions, the management This course also gives provides understanding of mathematical techniques applied for, forecasting in corporate planning and Financial Management. To represent and evaluates basic mathematical information verbally, numerically, graphically and symbolically. To use appropriates technology to enhance mathematical thinking and understanding and to solve mathematical problem and judge the reasonable results. To interpret mathematical models such as formulas, graphs, tables and schematics, and draw inference from them. To recognized the limitations of mathematical models. To develop the view that mathematics an evolving discipline, interrelated with human culture and understand its connections to other disciplines. The statistics plays an important role in every field of human inquiry. When statistics is applied in economics, it called econometrics, when it applied in 4 Lesson Plan Guideline Biological science it is called Biometry and others. Statistics are the eye of administration. Various problems such as unemployment, crime, poverty etc. require statistical investigation in order to study their causes. The structure of insurance is based on statistics. Statistics is a source of making forecasts about many facts. Past knowledge of statistics helps in comparing the result for year to year and in finding out the reasons for changes and the effect of such changes in future. Mathematics and Statistics A combined subject: Mathematicians and statisticians use symbols, graphs, and diagrams to help them find and communicate patterns and relationships, and they create models to represent both real-life and hypothetical situations. These situations are drawn from a wide range of social, cultural, scientific, technological, health, environmental, and economic contexts. Course Objectives The Objective of the mathematics and statistics components of the core curriculum is to develop a quantitatively literate for university student. Every student should be capable to apply accounting and economics mathematically and statistically. Every student should be able to apply “basic Mathematical and Statistical Tools” in the solution of real world problems. The broadly stated objectives of this course are listed below To equip students with basic tools of mathematics and statistics that can be applied in solving complex mathematical and statistical information. To make students equipped with the skill of applying derivatives in the form of maxima and minima to find out minimum cost, maximum profit and point of equilibrium. 5 Lesson Plan Guideline To make students learn solution of equations and use of graphs in order to estimate and represent loss, profit, sales, revenues, variable cost, fixed cost and break-even point. To represent and evaluate mathematical information verbally, numerically, graphically and symbolically. To make students understand the concept of regression and correlation and relationship between independent and dependent variables and analysis of result because these concepts are applied in the course of Quantitative Techniques of business in order to generate analysis. To expand questions based upon mathematical reasoning, skills and formal logic to develop convincing mathematical argument. To apply and interpret statistical techniques such as formulas, graphs, tables and schematics, and draw inference from them. To recognize the limitations of mathematical and statistical models. To develop the view that mathematics and statistics are interlinked disciplines, interrelated with human culture and understand its connections to other disciplines. Outcomes: On completion of this course, students should be able to: Successful completion of this course will enable the student to: 1. Apply arithmetic and algebraic skills to everyday business problems. 2. Use ratio, proportion and percent in the solution of business problems. 3. Solve business problems involving commercial discount, markup and markdown. 4. Solve systems of linear equations graphically and algebraically and apply to cost volume- profit analysis. 5. Apply Statistical Representation of Data, Correlation, Time Series and Exponential Smoothing methods in business decision making 6 Lesson Plan Guideline 6. Use elementary probability theory and knowledge about probability distributions in developing profitable business strategies. In the pursuit of the above objectives, students should achieve excellence in the following specific areas. Understand the nature of mathematical economics, mathematical accounting. Understand the relations, functions, graphics approach, economic and accounting analysis Understand the linear equation and problems related to linear equation. Show understanding of quadratic equation of different methods Show understanding of matrix algebra theory and model based Determining the “derivative using the rules for differentiation” Determining the depreciation by straight line method and declining balance method Solving business application problems involving Student Gain Classification Knowledge Topics and Student will be able to Comprehension Demonstrate a broad knowledge of mathematics in the core areas of economics, accounting, finance and medical. Make a link of mathematical queries in subjects other than mathematics to the concepts taught to them. Apply techniques of mathematics and statistics in other business subjects. Understand the concepts of all business courses 7 Lesson Plan Guideline where mathematical or statistical would be required. Topics like pro forma financial statements, estimation, forecasting, analysis of market share, all accounting topics require students to be efficient in mathematics so that they can effectively perform all these tasks. This course will enable to do it. Demonstrate more in depth knowledge and skills of quantitative of theoretical modeling areas of economics and accounting. Application and Skills Select and apply appropriate techniques to solve problems Justify conclusions based upon logical reasoning in subjects of economics and accounting. Apply mathematical, statistical techniques amalgamated with the graphical representation in an appropriate manner. Communicate effectively and clearly in written and oral formats. Analysis Apply skills and mathematical tools to solve complex problems. It would allow students to convert their ideas on paper using mathematical estimation and calculations. To produce logical and reasonable results. Perform with high level of accuracy. 8 Lesson Plan Guideline Teaching and Learning Methodology Lectures: Previous lecture quiz and quires Lecture includes, introduction of problems, basic principles and same example will be discussed the solution to examples and questions students are given problem sets etc. Discussion on queries and difficulties raised by students’ group discussion, class participation, home assignment. Assessment Criteria: Up to Mid Term Marks Distribution Assignment 10% Mid Term paper 20% Total Mid Term Evaluation 30% Up to Final Term Marks Distribution Final Project 30% Final Term paper 40% Total Final Term Evaluation 70% Total Marks (Mid + Final) 100% Assessment Detail: The quizzes part in the assessment criteria would enable students to prepare themselves for mid-term and final term papers. While preparing for the quizzes, students would go through all the course content, solve problems related to the topics, prepare them and most importantly they would be able to rectify their mistakes. It would also enhance the capability of the students to understand the concepts which were taught to them; moreover mathematics is all about practicing the problems so through practice they will grasp the content more accurately. It would be totally on the discretion of the instructor to decide the 9 Lesson Plan Guideline number of quizzes. The number of quizzes would be announced in the class but the overall percentage of the quizzes would remain same. Reference Books Business Mathematics By Abdullah and Miraj Din Mirza Journal: a. Quarterly Journal of Economics b. Bell Journal Economics c. The Journal of Human Resources d. Journal of Management Sciences e. Journal of Common Market Studies f. Journal of Economic Perspective 10 Lesson Plan Guideline Study Week Learning Outcome Session Break Up Opening Discussion (ice breaking session & module discussion) use of substitution and Equations The concept of linear equations elimination method use of substitution and Break 15 Mins. 30 Mins. 20 mins elimination method Solving linear equations 1 Students Would be able to : Learn the concept of linear equation and the solution through factorization, quadratic formula and graphical representation. simultaneously with graphical representation. Concept of Quadratic Solving linear equations simultaneously with graphical representation. 50 mins Factorization by completing square and quadratic formula. Equations Factorization By completing Square 65 mins method By Quadratic Formula. Session Topic Learning Outcomes Session Break Up Concept and nature of matrices 2 Matrix Algebra: Concept and nature of Students would be able to: Learn the concept and nature of Addition, subtraction and multiplication Break 15 Mins. 65 Mins. 15 Mins. 11 Lesson Plan Guideline matrices Addition, Subtraction, matrices and how matrices are used in order to solve the linear equations. Inverse of matrices and Application of matrices in solving linear equations 85 Mins. Multiplication. inverse of matrices Application of matrices in solving linear equation (up to three variables) and finding cost of commodities in different scenarios. Session Topic Learning Outcomes Session Break Up Opening Discussion (ice breaking session & module discussion) 3 Understanding of simple interest. Application and solution of question of simple interest. Students Would be able to : Learn the concept of Understanding of simple interest. Application and solution of question of simple interest. Learn the concept of 15 mins 30 Mins. Understanding of simple interest. Break 20 mins 12 Lesson Plan Guideline Session Topic 4 50 mins 60 mins Learning Outcome Session Break Up Students would be able to: Understand and learn the concept of differentiation. and differentiation. Concept of derivative and differentiation Application of derivative by basic definition method Break Application of Basic rules of differentiation 50 Mins. Chain Rule 35 mins Differentiation: Application Solution of compound interest Concept of derivative 30 Mins. 65 Mins. 15 Mins. derivative by basic definition method. Basic rules of differentiation. Chain Rule. Session Topic Learning Outcomes Instantaneous rate of change 5 Students would be able to: Application of maxima and minima, rate of change. Session Break Up Instantaneous rate of change Partial derivatives Application of maxima Partial Derivatives 50 mins 40 mins 13 Lesson Plan Guideline and Minima in figuring out optimum level of profit, minimum costs, concerned rate of Break Application of maxima and minima in figuring out optimum level of profit, minimum costs change in order to create efficiency. Session Topic Learning Outcomes 15 mins 75 mins Session Break Up Comprehensive Quiz for Mid Term Exam 6 14 Lesson Plan Guideline Mid Term Exam Session 7 Topic Session Integration : Learning Outcomes Students would be able to : Integration and its rules and application of integrals Session Break Up Rules of integration 40 Mins. Change in variable 40 Mins. Rules of Integration Change in Variable Break 15 Mins. Application of Integrals Application of integrals 85 Mins. in measuring areas 8 between the curves, volume and surface area of solids. Session Topic 9 Learning Outcomes Session Break Up Students would be able to: Grasp the concept of statistics as a Usefulness of Statistics subject, its importance and in real life and its application in numerous fields. Statistics as a subject and its application Relation of statistics with mathematics application in Break 20 Mins. Frequency distribution and statistical graphs 120 mins. Introduction to Statistics: 20 Mins. 20 Mins. numerous fields. Relation of Statistics and Mathematics. Management of Data 15 Lesson Plan Guideline Frequency distribution Statistical Graphs (Pie Chart and Histogram) Session Topic Measures of Location and Dispersion : Ungrouped and Grouped Data 10 Learning Outcomes Students would be able to: Ungrouped and grouped data Learn and calculate arithmetic Arithmetic mean, median and mean, median and mode , standard mode deviation and variance. Break 20 Mins. 60 Mins. 15 Mins. Arithmetic mean, median and mode, Session Break Up Quartile, Percentile and Deciles, mean deviation, standard deviation and variance. Quartile, Percentile and Deciles. 85 mins Mean Deviation, Standard Deviation and Variance. Session Topic Learning Out Come Session Break Up 16 Lesson Plan Guideline Index Numbers: 11 Price Relative Link Relative Chain Indices (Mean, Students Should be able to: Learn and apply the concept of index numbers. Median and Geometric Mean) Price Relative and Link Relative 50 mins Break 20 mins Chain Indices (Mean, Median and Geometric Mean ) 80 mins Family Budget Method ( Application of Index Numbers) 30 mins Family Budget method (Application of Index Numbers) Session Topic Probability and Probability Distribution: 12 Factorial, Permutation, Combination Sample Space and Event. Learning Outcome Student would be able to: Learn factorial, permutation and combination Sample space and event Session Break Up Factorial, Permutation and Combination 40 mins Sample Space and Event Break Probability with coin, dice and cards, mean and variance 40 mins 20 mins 80 mins Probability with coin, 17 Lesson Plan Guideline dice and cards. Mean and Variance. Session Topic Learning Outcome 13 Test of Hypothesis: Null and Alternative hypothesis ( One Tail Student would be able to: Learn and Calculate Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis, and Two Tail test) Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis 40 mins Population Data and Sample Data 30 mins Break 20 mins Population Data and Level of Significance , Z test and T test Sample data Session Session Break Up Level of Significance Z test and T test Topic Learning Outcome 90 mins Session Break Up 18 Lesson Plan Guideline 14 Regression And Correlation Learn the concept of coefficient of correlation, independent and dependent variables Co-efficient of Correlation 50 mins Independent and Dependent Variables 30 mins Independent and 20 mins Break Dependent Variables. Co-efficient of Correlation Analysis: Student would be able to : Regression Line ( X ON Y, Y ON X) Regression Line (X ON Y, Y On X) 80 mins Comprehensive Quiz 2 15 Revision FINAL EXAMINATION 19 Lesson Plan Guideline Penalties Late Submission: According to the University policy an assessment item submitted after the due date, without an approved extension, will be penalized at a rate of 10% per day of the possible maximum mark for the assessment item for each day or part day that the item is late. Assessment items submitted more than five days after the due date will be awarded zero marks. Absenteeism: Late coming and shortage in attendance i.e. continual 3 absents from class, the students will be struck off from the relevant subject. Plagiarism: University policy prohibits students plagiarizing any material under any circumstances. A student plagiarizes if he or she presents the thoughts or works of another as one’s own. This definition may include: Using another’s ideas without due acknowledgement; Working with others without permission and presenting the resulting work as though it was completed independently. Aiding another student to plagiarize is also a violation of the plagiarism Policy and may invoke a penalty. Assessment GPA and Percentages: (80-100%) 20 Lesson Plan Guideline This is an outstanding standard knowledge and understanding of indicating comprehensive the relevant materials; demonstration of an outstanding level of academic ability; mastery of skills (as identified in the assessment task); and achievement of all assessment objectives. (70-79%) This is an excellent standard indicating a very high level of knowledge and understanding of the relevant materials; demonstration of a very high level of academic ability; sound development of skills (as identified in the assessment task); and achievement of all assessment objectives. (65-74%) This is a very good standard indicating a high level of knowledge and understanding of the relevant materials; demonstration of a high level of academic ability; reasonable development of skills (as identified in the assessment task); and achievement of all assessment objectives. Pass (50-64%) This is a satisfactory standard indicating an adequate knowledge and understanding of the relevant materials; demonstration of an adequate level of academic ability; satisfactory development of skills (as identified in the assessment task); and achievement of most assessment objective 21