enzymes - A level biology
advertisement
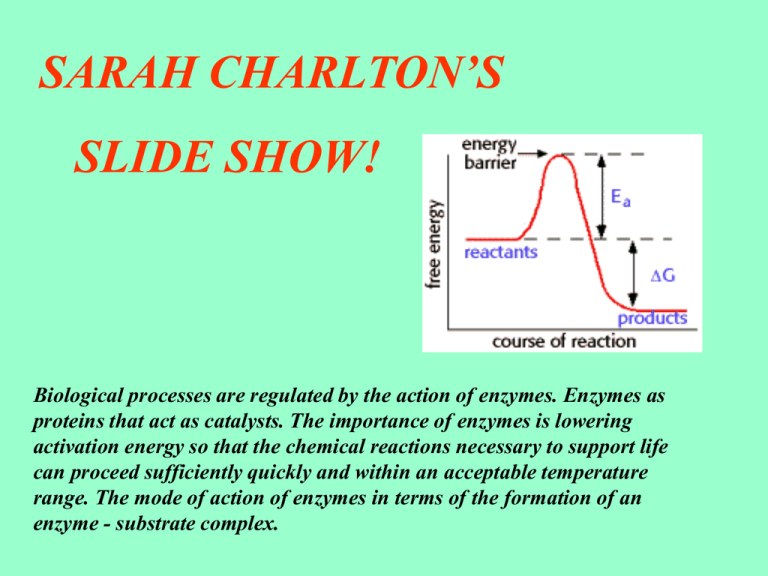
SARAH CHARLTON’S SLIDE SHOW! Biological processes are regulated by the action of enzymes. Enzymes as proteins that act as catalysts. The importance of enzymes is lowering activation energy so that the chemical reactions necessary to support life can proceed sufficiently quickly and within an acceptable temperature range. The mode of action of enzymes in terms of the formation of an enzyme - substrate complex. The way enzymes work can also be shown by considering the energy changes that take place during a chemical reaction. We shall consider a reaction where the product has a lower energy than the substrate, so the substrate turns into the product. Before it can change into the product, the substrate must overcome an “energy barrier” called the activation energy (EA). In a chemical reaction the larger the activation energy, the slower the reaction will be because only a few substrate molecules will by chance have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. When you are calculating activation energy it is useful to know how much energy is in the product and how much is in the reaction. The graph will then show you how it’s distributed. Most physiological reactions have the largest activation energies, so they simply don’t happen on a useful time scale. The activation energy of a chemical reaction is actually the energy required to form the transition state, so enzymes lower the activation energy by stabilizing the transition state, an they do this by changing the conditions within the active site of the enzyme. As you can see from this diagram the activation energy has been lowered by enzymes and this has stabilized the transition state to a peak, the energy barrier has been broken. When changing the conditions you can not lower the activation energy. However, enzymes seem to lower the activation energy of a reaction because they split the reaction into stages, each with a lower activation energy. The cells in the product supply this much small amount of energy from ATP which was produced in respiration from the enzymes. This allows many reactions to take place easily at the temperatures that normally occur in the body of an organism. Enzymes are biological catalysts in the human body also enzymes are proteins. Proteins are important compounds in living organisms - not just enzymes but in other ways. There are about 40,000 enzymes in a human cell each controlling a different chemical reaction. They increase the rate of reaction but decrease activation energy as it’s a barrier for the enzymes. Enzymes make it possible for chemical reactions to take place at normal temperatures. The temperature in the human body is about 350c. If the activation energy is high the enzyme reactions will be slower and the body will feel this, this is why the enzymes lower the activation levels otherwise the body temperature will drop. This is how a substrate fits onto an enzyme in a reaction. As you know the activation energy for many necessary biological reactions is simply too high for these reactions to proceed, however these reactions are vital to the life of an organism. Enzymes will therefore lower the activation energy barrier and allow these reactions to occur. It’s a key idea. Enzyme molecules have a complex tertiary structure. The substrate molecules of the enzyme must be precisely the right shape to fit it into part of the molecule called the active site. The substrate molecules are attracted to the active site and form an enzyme - substrate complex. This complex only exists for a fraction of a second, this is when the products of the reaction form. The activation energy is low in this reaction because it is controlled by enzymes and little energy is needed to bring the two substrate molecules together. This is a diagram to show an enzyme in action. THIS IS THE END OF MY SLIDE SHOW. HOPE YOU ENJOYED IT AND LEARNT A LOT!