Economic instability
advertisement

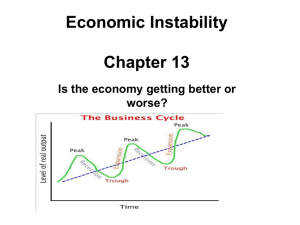
ECONOMIC INSTABILITY Chevalier Fall 2015 Economic Instability There are four (4) major causes of economic instability in the American economy. Business Cycles and Fluctuations Unemployment Inflation Poverty and distribution of income I. BUSINESS CYCLES and FLUCTUATIONS BUSINESS CYCLES- Systematic ups and downs of real GDP BUSINESS FLUCTUATIONS- Non-systematic rise and fall of real GDP; this interrupts economic growth Phases of the Business Cycle RECESSION- GDP declines for 6 consecutive mos. PEAK TROUGH- where real GDP stops going down EXPANSION- period of recovery from recession TREND LINE The Great Depression- severe recession Causes: 1. disparity between rich and poor; poor couldn’t stimulate the economy (poor distribution of income) 2. stock speculation by rich 3. drop of American exports due to tariffs The Business Cycle Business cycles since WWII have been pretty regular Avg. recession lasts 11 mos. Avg. expansion lasts 43 mos. Page 379 graph Causes of Business cycles 1. Capital Expenditures 2. Inventory Adjustments 3. Innovation and Imitation 4. Monetary factors Credit and loan policies Lower IR increase demand which pushes IR’s up 5. Increase in oil prices, war, WTC attacks Can we predict business cycles? Of course… Econometric model-macroeconomic model that describes how economy behaves Index of leading economic indicators (10 areas that closely resemble GDP) Turns down before real GDP turns down Turns up before real GDP turns up Avg. work week Order for durable goods II. Unemployment Unemployment rate- the number of unemployed individuals divided by the total number of persons in the civilian work force Unemployed=people available for work who made an effort to find a job in the past month. Goes up during recessions and down during expansions Unemployment Limitations-doesn’t account for people who haven’t tried to find a job in the last 4 weeks Too discouraged during recession to do so Employed doesn’t mean employed full-time Could be part time Kinds of Unemployment Frictional unemployment-people between jobs(short term) Structural unemployment-change in consumer tastes Military base closures, mergers, technology changes Happens when there is a fundamental change in an economy Cyclical unemployment-related to swings in business cycle Season unemployment Weather related Technological unemployment-automation Concept of full employment Some pros and cons Numerically when U.R. drops below 4.5% 2000=3.9% Healthy is 4-6% III. Inflation Measure by using the CPI 100K goods in over 400 categories; spits out a number Inflation rate = change in price level/beginning price levelX100 Rate of inflation graph p. 390 Inflation Deflation, and degrees of inflation Creeping, galloping, and hyper 1-3% 100-300% 500% a year Hungary during WWII 828,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 pengos=1 prewar pengo Causes of Inflation 1. demand-pull theory 2. blames inflation on federal gov’t deficit spending 3. rising input costs (costs of labor) tied to unemployment; could be non-labor too (oil) 4. spiral of prices and wages 5. excessive monetary growth Money supply grows faster than GDP Increases purchasing power Consequences of inflation Less purchasing power Hard on retirees; people with fixed income Causes people to change spending habits, disrupting the economy Alters distribution of income(lenders and borrowers) Hurts lenders Poverty and Distribution of Income The distribution of income p. 395 Reasons for income inequality Education Wealth- distribution of wealth 5th of Americans have 75% of the wealth in this country Top Discrimination-gender .82 to every dollar a man makes Ability The income gap in America Some reasons Unequal distribution of income Structural change in economy-goods to service production Growing gap in education Shift of the family structure Declining unions Poverty graph on page 397 Per capita graph per state on p. 399