Six Sentence Combining Options to Correct Fused Sentences and
advertisement
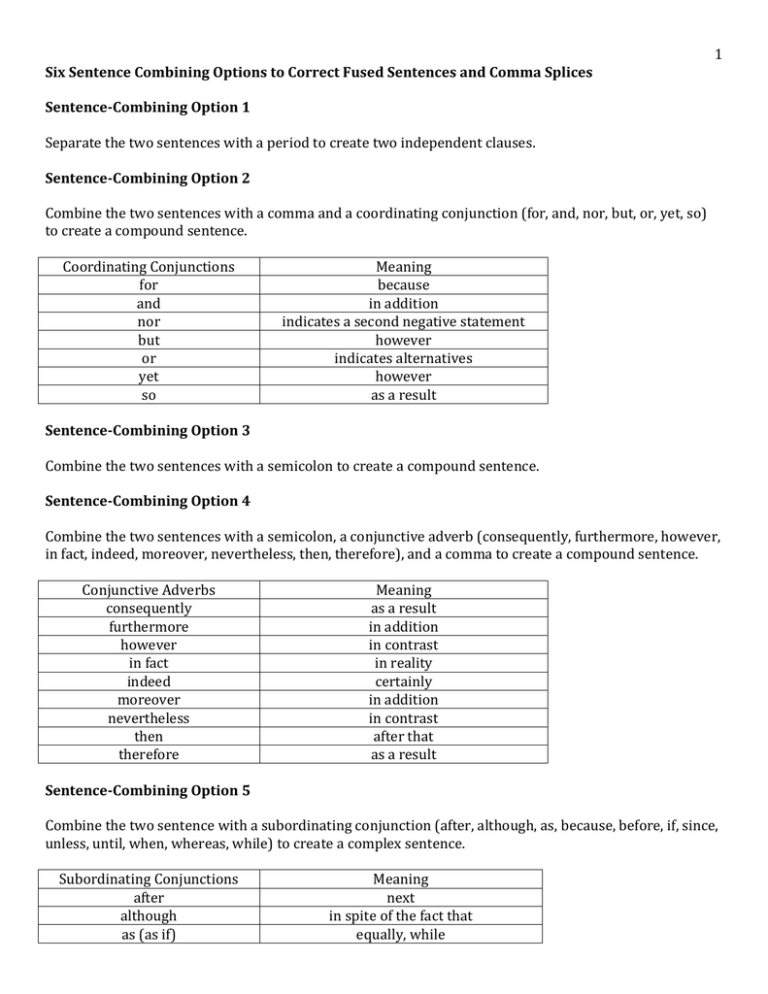
1 Six Sentence Combining Options to Correct Fused Sentences and Comma Splices Sentence-Combining Option 1 Separate the two sentences with a period to create two independent clauses. Sentence-Combining Option 2 Combine the two sentences with a comma and a coordinating conjunction (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) to create a compound sentence. Coordinating Conjunctions for and nor but or yet so Meaning because in addition indicates a second negative statement however indicates alternatives however as a result Sentence-Combining Option 3 Combine the two sentences with a semicolon to create a compound sentence. Sentence-Combining Option 4 Combine the two sentences with a semicolon, a conjunctive adverb (consequently, furthermore, however, in fact, indeed, moreover, nevertheless, then, therefore), and a comma to create a compound sentence. Conjunctive Adverbs consequently furthermore however in fact indeed moreover nevertheless then therefore Meaning as a result in addition in contrast in reality certainly in addition in contrast after that as a result Sentence-Combining Option 5 Combine the two sentence with a subordinating conjunction (after, although, as, because, before, if, since, unless, until, when, whereas, while) to create a complex sentence. Subordinating Conjunctions after although as (as if) Meaning next in spite of the fact that equally, while 2 because before if since unless until when (whenever) whereas while for the reason or cause that in advance, prior to on condition that from then until now, because except if up to the time of at the time that but on the other hand during or through the time that Additional subordinating conjunctions and dependent words include the following: afterward, even though, even if, even since, ever since, how, in order that, just as, just as if, now that, once, provided that, rather than, so, so that, than, that, though, till, what, whatever, where, wherever, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whose, why. Sentence-Combining Option 6 Combine the two sentences by starting with a subordinating conjunction (after, although, as, because, before, if, since, unless, until, when, whereas, while) and inserting a comma between the clauses to create a complex sentence. Subordinating Conjunctions Meaning although in spite of the fact that because for the reason or cause that if on condition that since from then until now, because until up to the time of Example Option #5: The morning remained calm although a breeze swept through the camp in the afternoon. Option #6: Although a breeze swept through the camp in the afternoon, the morning remained calm. Option #5: He paints rural settings because he prefers to depict tranquil scenes. Option #6: Because he prefers to depict tranquil scenes, he paints rural settings. Option #5: The work can be done if we upgrade the computers. Option #6: If we upgrade the computers, the work can be done. Option #5: The population has doubled since poachers have been prosecuted. Option #6: Since poachers have been prosecuted, the population has doubled. Option #5: The company produced a profit until the cost of raw materials soared. Option #6: Until the cost of raw materials soared, the company produced a profit.