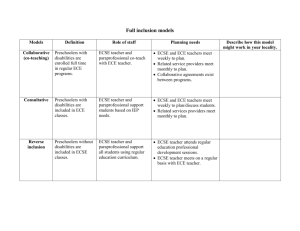
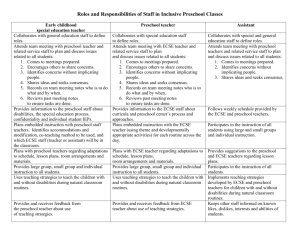
What are Blended Practices?
advertisement

Speech-Language Pathologists’ Importance in Early Childhood Special Education: Creating Supportive Learning Environments for Young Children with Disabilities – Part 1 Jane Minnema, Ph.D., SLP-CCC St Cloud State University jeminnema@stcloudstate.edu 320-308-3969 Preface to Part 1 Who I am … and where I’ve been Who you are … and where you’ve been What we “know” from daily professional experiences … to a much deeper understanding of the field of ECSE Jane’s approach to adult learning Session Outcomes – Part 2 What I hope for: I. Understanding EBP per ASHA and DEC II. Pondering current research findings for dual or multiple language learners What I wish I knew when teaching! III. The importance of SLPs for setting the ECSE learning environments! Session Outcomes What I hope for: Realizing our different ways of thinking about children and families Re-thinking service delivery within ECSE learning environments A deeper understanding of ECSE practices, settings, and the importance of the SLP Why is this important to me? Many, many years invested in our field! Always hoped to make a difference … But now … a Grammy! Ethan Isaiah, 7 mo At 18 mo – Delayed language skills Young Children Attend Variety of Learning Environments Various settings in which young children w/ disabilities receive services: Early Intervention – Birth to 3 years Family Home Visiting Programs Child Care Programs* Early Childhood Special Education – 3 to 7 years Secluded multi-categorical ECSE preschool* Inclusive preschool programs* Head Start* Child Care Programs* * Our focus today Starting with Definitions Supportive learning environments – those “natural” instructional delivery settings in which young children progress toward age appropriate developmental outcomes Natural – young children with disabilities attend EC programs with same aged peers Instructional delivery – service provision per IFSPs or IEPs Developmental outcomes – acknowledges uniqueness of sequence, rate, and proficiency I am most privileged to observe … Many wonderful program models that deliver high-quality services Highly proficient ECSE service providers, SLPs, and other IFSP/IEP team members For that, I am grateful! On the surface … IFSP and IEP education teams are providing effective, high-quality services Many models across MN in which SLPs provide services Seems simple … without much for us to learn?! But, let’s look more closely at various issues (Information that I wish I knew when I was teaching!) How did Ethan develop? Ethan, 12 mo Delayed language comprehension Delayed babbling w/ no jargoning Walking – quickly! Ethan, 3 yr, 11 mo Delayed language development Phonological delay Riding bicycle – no training wheels!!! Why would my son deny services? Because …. Ethan, age 4 yr Expressive language delay Phonological delay Cluttering (??) Attending Montesorri Preschool (Beginning Kg curriculum) Older brother, Sean, born at 35 weeks Abbot Northwestern NICU, Level 2 Two weeks Attended Montesorri Preschool Family looking for … Natural milieu language stimulation Normal language peer modeling But, were offered – Individualized therapy Table top activities w/ SLP in isolation Family involvement discouraged Professional “Ways of Thinking” ECSE/EC Pedagogy Applied CD Professional ethics and standards + competencies + principles Educational practices or Clinical practices Theoretical underpinnings that guide decision-making about children and families Approaches to intervention or teaching Crossing Speech/Language Services, ECSE, and EC Child ASHA: Knowledge & Skills per Topic DEC: Recommended Practices NAEYC: Developmentally Appropriate Practices Intervention Family Approaches to Service Delivery Child Speech/Language: Clinical Service Delivery to Remediate ECSE: Educational Service Delivery to Remediate EC: Educational Programming to Support Development Intervention Family So … View of Children Child Speech/Language: One Child Communication ECSE: Child w/in Family 5 Learning Domains EC: Groups of Children Curricular Content Intervention Family Speech Language Service Delivery My “old” SLP Training Assessment of child in isolation for diagnosis Focused on communication only Behavioral approach to speech/language remediation through IEPbased intervention Pull out intervention in “broom closet” Observed Today in ECSE Integrated SLP “therapy” Leading group activities (e.g., Circle Time) Leading small group activity (e.g., Center Time) Supporting child through activity (e.g., augmentative communication device) OR … my “old” SLP training??? ECSE Service Delivery My “old” ECSE Training Assessment of child in isolation for diagnosis Isolated learning domain focus Behavioral approach to learning + free play Remediation through IEPbased intervention Parent training Supported pull out intervention in “broom closet” Observed Today in ECSE Evaluation for eligibility Embedded learning opportunities Family systems approach Adapted learning through IEPbased intervention Parent partnerships Inclusive practice across all domains of learning Or … “old” ECSE training??? EC Programming My “old” EC Observations Some children attend (missing ELLs, children living in poverty except Head Start, children w/ disabilities) Considered all learning domains Understood play’s importance Assessment not present Parent training – if considered Supported pull out intervention in “broom closet” EC Pre-Service Training ‘11 More children included! Holistic view of children (integrated learning domains) Advocate for social-emotional importance w/ play-based learning Assessment measures learning Parent collaborations Or … “old” EC format??? What can we say about these differences? Cross-disciplinary practice impeded – communication, overlap or gaps in services, inefficient service delivery Present different child assessment, functional, or developmental information to families Can de-emphasizes the importance of play and social/emotional development of young children with and without disabilities Other suggestions? Audience Perceptions?!! In Pair Share: What is new information? Where do you agree? Where do you disagree? Where do you fall between the “old” and the “current?” What can we take forward? The BEST from each field: SLP: Systematic, technical, supported skill development in specialized area ECSE: Embedded learning practices EC: Holistic view of child with integration of all learning domains Where does this take us? Blended Practices Brown-Grisham, J., Hemmeter, M., & Pretti-Frontczak, K. (2005) One current recommended approach for c reating authentic learning environments Blend of ECSE + EC instructional practices Can we add SLP service delivery? What are Blended Practices? ECSE primarily influenced by special education – individualized approach to meet the unique needs of one child at a time With the advent of inclusive practice … a movement toward blending EC & ECSE teaching and licensure pre-service training programs How to blend SLP service delivery? Think intentionally about authentic learning environment by analyzing the important critical elements Determine communicative critical skill(s) from speech/language instructional objectives Embed these critical skills into the daily preschool routine In other words, let’s take a step forward from integrated speech/language service delivery! Integrated Therapy “Integrated therapy is the coordination of therapies or consultative special education within the ongoing routines of the classroom. While the therapists are working with the child and classroom teachers in the classroom, those teachers have the opportunity to see what the therapist does with the child and implement those same strategies into the rest of the week when the therapist is not present. When therapists and teachers work together to provide services and education to a child, the child benefits by receiving well-coordinated intervention.” McWilliams, R. (1993) Legal Aspects of Integrated Therapy EI/ECSE programs are required by law to offer a range of services. No one approach to service delivery is appropriate for every child. · As used in this part, the term special education means specially designed instruction, at no cost to the parents, to meet the unique needs of a child with a disability, including (i) Instruction conducted in the classroom, in the home, in hospitals and institutions, and in other settings. (IDEA, Sec. 300.26) · To the maximum extent appropriate to the needs of the child, early intervention services must be provided in natural environments, including the home and community settings in which children without disabilities participate. (IDEA, Sec. 303.12 (b) Integrated Therapy … Meets continuum of educational needs Isolating portion of classroom may be necessary (e.g., alternative feeding, articulation therapy) Provides opportunities for consultative services “in real time” Maximizes classroom routine-based learning (e.g., snack time, circle time, table top activity) May be isolating for child – even within classroom activity A deeper level of Practice Activity-based Intervention Activity-based intervention is defined as a "child-directed, transactional approach that embeds intervention on children's individual goals and objectives in routine, planned, or child-initiated activities, and uses logically occurring antecedents and consequences to develop functional and generative skills" (Bricker & Cripe, 1992). Activity-based Intervention Terms Defined The first key element of activity-based intervention (ABI) is based on the premise that activities and actions initiated by children are more likely to attract and hold a child's attention and as a result maintain their involvement. The term transactional refers to the child acting upon his or her environment and the social and physical environment responding in a reciprocal manner (Bricker & Carlson, 1980; Sameroff & Chandler, 1975). When an child reaches out to his parent and the parent responds by smiling back and giving him a ball, the interaction is considered to be transactional. The child initiated the interaction and, because the adult responded in a positive manner the child will be more likely to make future social gestures. Activity-based Intervention More Terms Defined The second element of ABI involves the embedding of training and intervention (addressing IFSP/IEP goals and objectives) within routine, planned, or child-initiated activities. Routine refers to those events that occur on a predictable or regular basis. Planned activities are those which the adults in the environment organize and prepare for the children's participation. Child-initiated activities are simply activities which the children initiate on their own. Important to Remember … The focus of ABI is not on the activity itself, but rather on the opportunity for the child to practice target skills during ongoing activities throughout the classroom day. Speech/language an EC/ECSE learning domain – element of developmental practice Communicative target behaviors can be embedded in daily preschool instructional delivery to be meaningfully learning experiences for children Blending Speech/Language Services w/ ABI Advantages … Leave skills with teaching team Generative skills without targeted programming Service delivery in natural learning environment Challenges … Time New practices – change! Others’ misperceptions How to embed S/L targets into classroom learning environment Understand what the routine, planned, or child-directed activities OR … Think carefully about instructional and directional language used in the classroom Meaningfully embed instructional objectives! By consulting, modeling, direct intervention For example … Imitating a simple sentence, embed as: At leave taking – T: “I wanna go home.” During Circle Time – T: “I’m gunna sing.” At Play Time – T: “I wanna play with Sophie.” Completing a classification activity: During Art Time – T: “Can you find everything we use for art?” Articulating /s/: During Circle Time – Surprise Box of all “S” items How would you apply ABI to your SLP practice? Pair-Share or Multiple Share for application activity by: Think of a speech or language instructional objective. Select – a) routine preschool activity, b) planned preschool activity, or c) child-directed activity. How would you embed the instructional objective (communicative target) into the preschool activity? EBP – Where to Begin??! From a research perspective: Sam Odom, Indiana University “Teachers begin using a strategy exactly as it is proposed. As the teacher gains experience and collects information about the students’ performance, he or she may make modifications where needed.” Remaining Questions … Just like kittens … SLPs can accomplish anything NEW! Where are the boys now?!