Chapter 1 Section 1.3 – String Class
advertisement

Chapter 1 Section 1.3 – String Class
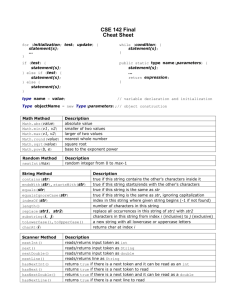
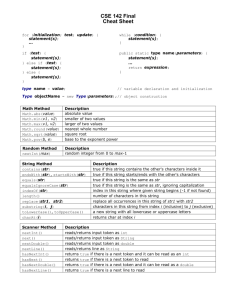
String methods:
o str.length()
o str1.equals(str2)
o str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2)
o str.toLowerCase( )
o str.toUpperCase( )
o str.trim( )
o str.charAt(integer)
o str.substring(start)
o str.substring(start, end)
o str1.indexOf(str2)
o str1.indexOf(str2, start)
o str1.lastIndex(str2)
o str1.compareTo(str2)
o str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2)
lexicographic order (ASCII character set): digit, uppercase letter, lowercase letter
Chapter 4
Defining Classes
Example creating a class: BankAccount
1 /**
2 A bank account has a balance that can be changed by
3 deposits and withdrawals.
4 */
5 public class BankAccount {
6
7
private double balance;
8
9
/**
10
Constructs a bank account with a zero balance.
11
*/
12
public BankAccount() {
13
balance = 0;
14
}
1
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 }
/**
Deposits money into the bank account.
@param amount the amount to deposit
*/
public void deposit(double amount) {
balance = balance + amount;
}
/**
Withdraws money from the bank account.
@param amount the amount to withdraw
*/
public void withdraw(double amount) {
balance = balance - amount;
}
/**
Gets the current balance of the bank account.
@return the current balance
*/
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
Driver (Testing) class for BankAccout: BankAccountTester
1 /**
2 A class to test the BankAccount class.
3 */
4 public class BankAccountTester {
5
6 /**
7
Tests the methods of the BankAccount class.
8
@param args not used
2
9 */
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11
12
BankAccount harrysChecking = new BankAccount();
13
harrysChecking.deposit(2000);
14
harrysChecking.withdraw(500);
15
System.out.println(harrysChecking.getBalance());
16
System.out.println("Expected: 1500");
17 }
18 }
Instance Variables
o Automatically initialized
Boolean to false
Primitive type to zero,
Class types (Objects) to null (includes sterings)
We prefer to explicitly initial them in a constructor
Constructors
o Called when an object is created of the class
o Can be multiple constructors for a class
o Can call other methods from constructor
o Use this parameter when you need to refer to the “current” object
o A no-argument is automatically created when you include no comnstructors
Chapter 10 File I/O
Sending Output to a Text File
3
Methods for Class PrintWriter
o println
o print
o printf
o close
o flush
Appending to a Text file
o outputStreamName = new PrintWriter( new FileOutputStream
(FileName, true));
4
Reading from a Text File
5
Testing for end of File
Reading a Text File Using BufferedReader
6
Methods for Class BufferedReader
o readLine (reads a line)
o read (reads a single character)
o flush
Chapter 6 Arrays
Declaring an array:
o double[ ] score = new double[5]; OR
o double[ ] score;
score = new double[5];
o String str = new String[6];
o BankAccount myChecking = new BankAccount[3];
Initialize an array: int[] age = {2, 12, 1};
Array instance variable: length
o score.length returns the length (number of elements) of the array
Array method sort: Arrays.sort(str); java.util.Arrays
7
Need to use for loop to initialize, update, or read an array
double[ ] score = new double[100];
for (int index = 0; index < score.length; index++)
score[index] = 0;
Convert an array of char to String
char[ ] a = {'A', 'B', 'C'};
String s1 = new String(a);
s1 = “ABC”
String s2 = new String(a,0,2);
s2 = “AB”
Arrays are objects
o Creating an array of objects:
Triangle[ ] triangleList = new Triangle[5];
This does not create 5 objects of the class Triangle
All are initialized to null
for (int i = 0; i < triangleList.length; i++)
triangleList[ i ] = new Triangle( );
Both array indexed variables and entire arrays can be used as arguments to
methods
public void myMethod1(int [ ] score);
public void myMethod2(int score);
Making two arrays, a and b, equal:
myMethod1(score);
myMethod2(score[2]);
for ( int i = 0; (i < a.length) && (i < b.length); i++ )
b[ i ] = a[ i ];
Checking if two arrays are equal: (java.util.Arrays)
Arrays.equals(a, b);
Arguments in main : public static void main(String[] args) args[0], args[1], etc.
8
Additional Topics
Enhanced for loops (for-each loop):
“Regular” for loop:
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
a[ i ] = 0.0;
–
Enhanced for loop:
for (double element : a)
element = 0.0;
Variable Number of parameters
printNumbers(1, 2, 3);
printNumbers(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
printNumbers( );
public static printNumbers( int … args) {
for ( int i = 0; i < args.length; i++ )
System.out.println(args[ I ];
Input/Output Classes
Scanner keyboard
= new Scanner(System.in);
Scanner inputStream
= null;
PrintWriter outputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = new Scanner(FileInputStream(“inputFile.txt”));
outputStream = new PrintWriter(FileOutputStream(“outputFile.txt”));
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(“File not found.”);
System.exit(0);
}
9