Kohlberg's PPT - The Payne Page
advertisement

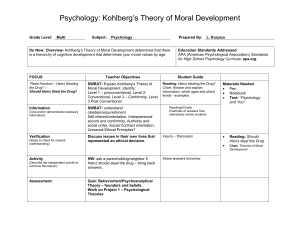
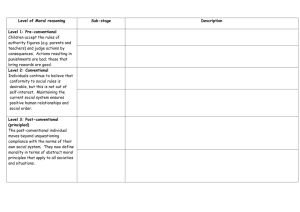
What would you do? Kohlberg’s theory of moral development Who? ► Lawrence Kohlberg (1927-1987) was a well known theorist in the field of moral development. He posed moral dilemmas (e.g. Heinz Dilemma) to his subjects and then asked questions to probe their reasons for recommending a specific course of action. What? Moral Dilemma ► Dilemma: a problem involving a difficult choice; often, there is no “clear” or even desirable solution—whatever you choose will result in some possible negative consequences ► Moral: of or relating to principles of right or wrong behavior Why? play we are about to read, Antigone, focuses on a moral dilemma. The characters must make difficult choices and are motivated by different types of morality. This will help us to analyze them. ► The Directions ► Partners ► Read the scenario ► Discuss the dilemma ► Determine what the person should do ► Discuss why that choice is a moral choice Scenario 1 ► ► ► ► ► A woman was near death from a unique kind of cancer. There is a drug that might save her. The drug costs $4,000. The sick woman’s husband, Heinz, went to everyone he knew to raise money and tried every legal means, but could only get together $2,000. He asked the doctor who discovered the drug for a discount or to let him pay later, but the doctor refused. Should Heinz break into the laboratory to steal the drug for his wife? Why / why not? Scenario 2 ► Heinz broke into the laboratory and stole the drug. ► The next day, the newspapers reported the breakin and theft. ► Brown, a police officer and a friend of Heinz, remembered seeing Heinz last evening, behaving suspiciously near the laboratory. Later that night, he saw Heinz running away from the laboratory. ► Should Brown report what he saw? Why or why not? Scenario 3 ► Officer Brown reported what he saw. Heinz was arrested and brought to court. ► If convicted by jury, he faces up to two years in jail. ► Heinz was found guilty. ► Should the judge sentence Heinz to prison? Why or why not? Stages of Moral Development ► Kohlberg proposed stages of moral development. Stage 1 & 2: Selfish Obedience ► 1) Rules followed to avoid punishment; obedience and concern for physical consequences. ► 2) Doing things for others because it will result in others doing things in return; concern for reward, equal sharing and benefit to self. Stage 3 & 4: Conforming to Traditions ► 3) Whatever pleases the majority is considered morally right; other viewpoints can be seen, conformity is prized, desire to do things for others. ► 4) Group authority, law, duty and rules of society prized; concern for maintaining social order for its own sake; social disapproval avoided; emphasis on the inherent 'rightness' of rules and duties. Stage 5 & 6: Moral Principles Beyond Conformity ► 5) Internal commitment to principles of personal conscience; concern with individual rights within standards set by consensus; emphasis on fair procedures for reaching consensus and for evaluating principles and rules. ► 6) Concern with universal ethical principles and abstract morality affecting all beings regardless of conventional views; emphasis on universality, consistency, and logical comprehensiveness. Which stage? ► Read the explanations for choices Heinz could make. ► With your partner, determine which stage is represented by this choice. Explain why you believe that is the stage. A A) Heinz should steal the medicine, because he will be much happier if he saves his wife, even if he will have to serve a prison sentence. ► Stage 2: Self-interest B B) Heinz should steal the medicine, because everyone has a right to choose life, regardless of the law. Or: Heinz should not steal the medicine, because the scientist has a right to fair compensation. ► Stage 5: Human Rights C C) Heinz should not steal the medicine, because he will consequently be put in prison. ► Stage 1: Obedience D D) Heinz should not steal the medicine, because the law prohibits stealing making it illegal. ► Stage 4: Law and Order E E) Heinz should steal the medicine, because his wife expects it; he wants to be a good husband. ► Stage 3: Conformity F F) Heinz should steal the medicine, because saving a human life is a more fundamental value than the property rights of another person. Or: Heinz should not steal the medicine, because others may need the medicine just as badly, and their lives are equally significant. ► Stage 6: Universal Human Ethics Sources ► Kohlberg’s Stages – Explained and Illustrated,” Blessed to Be a Blessing, Sep 2000, 3 Oct. 2006 <http://www.vtaide.com/blessing/Kohlberg.htm>. ► “Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development,” Austega Gifted Resource Center, 15 Feb 05, Austega Pty Ltd., 3Oct 06 <http://www.austega.com/gifted/moralKohlberg.h tm>.