Chapter 7
advertisement

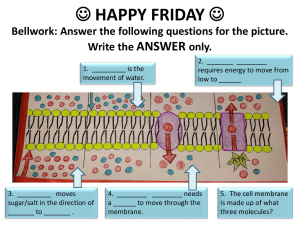
Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function Chapter 7.3 Cell Structures and Organelles The Cell is a Factory for Making PROTEINS!! Cell Organelles Cell Part Function Cytoplasm Semifluid material that surrounds the organelles and provides a place for chemical reactions to take place. Cytoskeleton A network of long, thin protein fibers that form a framework and support system for the cell; anchors all the organelles Nucleus Control center of the cell; contains the cell’s DNA; surrounded by nuclear membrane (envelope) Ribosomes Produces proteins Nucleolus Produces ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Folded membrane system that is the site for protein and lipid production Smooth ER Area with no ribosomes attached; place where many carbohydrates and lipids are produced Rough ER Ribosomes are attached and produce proteins Cell Organelles Cell Part Function Golgi Apparatus Flattened membranes that modified, sorts, and packages proteins Vacuoles Temporary storage for the cell; used to store food, enzymes, and other materials needed for the cell Lysosomes Structure containing enzymes used to digest waste Centrioles Used in cell reproduction Mitochondria Produce energy by breaking down sugars Chloroplasts Capture light energy and convert it to chemical energy (food); found in plant cells Cell wall Thick, rigid fibers that surround the plasma membrane and protects the cell Cilia and Flagella Used for cell movement in some eukaryotic cells Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Semifluid material that surrounds the organelles and provides a place for chemical reactions to take place. Cytoskeleton A network of long, thin protein fibers that form a framework and support system for the cell; anchors all the organelles Nucleus and Nucleolus Nucleus Control center of the cell; contains the cell’s DNA; surrounded by nuclear membrane (envelope) Nucleolus Produces ribosomes Ribosomes Ribosomes Produces proteins Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum Folded membrane system that is the site for protein and lipid production Smooth ER Area with no ribosomes attached; place where many carbohydrates and lipids are produced Rough ER Ribosomes are attached and produce proteins Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus Flattened membranes that modified, sorts, and packages proteins Vacuole Animal Cell Plant Cell Vacuoles Temporary storage for the cell; used to store food, enzymes, and other materials needed for the cell Lysosomes Lysosomes Structure containing enzymes used to digest waste Centrioles Centrioles Used in cell reproduction Mitochondria Mitochondria Produce energy by breaking down sugars Chloroplasts Chloroplasts Capture light energy and convert it to chemical energy (food); found in plant cells Cell Wall Cell wall Thick, rigid fibers that surround the plasma membrane and protects the cell Cilia and Flagella Cilia and Flagella Used for cell movement in some eukaryotic cells p. 199 Chapter 7.4 Cellular Transport Predict • Food coloring demonstration – Drops of red and blue food coloring are added to opposite ends of a container of water. • Hypothesize: – What will happen when the food colorings are added? – What will happen after 5 minutes? Observation & Explanation • Observe: – What happened to our food colorings? • Explain: – How can this result be explained? Figure 7.20 © Glencoe-McGraw Hill (2007) Diffusion • Substances dissolved in water (solutes) move constantly in random motion; this is call Brownian Motion • Causes diffusion – net movement of particles from an area where there are many particles of the substance (high concentration) to an area where there are few particles of the substance (low concentration) • There are two components of solution: – Solvent – a substance in which another substance is dissolved – Solute – the substance that is dissolved Diffusion • Movement of substances from high concentration to low concentration • Caused by the RANDOM movement of particles • Requires no energy input! http://www.indiana.edu/~phys215/lecture/lecnotes/lecgraphics/diffusion.gif http://www.indiana.edu/~phys215/lecture/lecnotes/lecgraphics/diffusion2.gif • Interactive Diffusion Activity: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP1903 Dynamic Equilibrium • Once a uniform purple color is reached, the food coloring particles continue to move randomly. • However, at some point, all particles of a substance (in this case food coloring) will be as spread out as they can and there will no longer be areas of high and low concentration. • When this occurs, dynamic equilibrium has been reached. Diffusion in Cells Factors that Affect Diffusion • Three main factors affect the rate (speed) of diffusion: – Concentration of the diffusing particles – Temperature – Pressure • If any of these three increases, the diffusion rate will increase. Why? Facilitated Diffusion A. Water can pass easily through the plasma membrane – most substances cannot B. In facilitated diffusion, special transport proteins move ions and small molecules across the plasma membrane Transport Processes • Passive transport – movement of a substance across the plasma membrane without the use of the cell’s energy. • Active transport – requires the use of the cell’s energy to move substances into or out of a cell across the cell membrane. No Energy Required Requires Energy Cellular Transport Videos http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1ZFqOvxXg9 M&feature=related Osmosis is the DIFFUSION OF WATER Osmosis • The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Figure 7.22 © Glencoe-McGraw Hill (2007) – Cells must regulate this in order to maintain homeostasis. – One of three situations exists. • http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flasha nimat/transport/osmosis.swf • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sdiJtDRJQ Ec Isotonic Solution • Cell is in a solution that has the same concentration of water and solutes Iso – Greek meaning “equal” cell is in dynamic equilibrium with environment Water enters and leaves the cell at the same rate. Figure 7.23 © Glencoe-McGraw Hill (2007) Hypotonic Solution • Cell is in a solution that has a lower concentration of solute than the cell hypo – Greek meaning “under” Net movement of water is into the cell Causes osmotic pressure In animals – cell could burst In plants, cell wall prevents bursting; cell becomes firmer Figure 7.24 © Glencoe-McGraw Hill (2007) Hypertonic Solution • Cell is in a solution that has a higher concentration of solute than the cell. hyper – Greek meaning “above” Net movement of water is out of the cell Results: In animals – cells shrivel In plants, central vacuole pulls away from cell wall; plant wilts Figure 7.25 © Glencoe-McGraw Hill (2007) Red Blood Cells – A Comparison • Is your blood pure water? • What would happen to your red blood cells if pure water were to be injected into your blood stream? Osmosis Examples Example Pickles are made by immersing cucumbers in a concentrated saltwater solution. Spraying plants with a solution that contains too high a concentration of fertilizer might cause them to dry out and die. Patients undergoing surgery are given 0.9% saline (saltwater) solution. One of the oldest methods of preserving food is to pack them in saline solutions, which kill the bacteria that cause foods to spoil. Organisms that live in seawater have specialized mechanisms that prevent them from becoming dehydrated. Florists store fresh flowers in cold water to help the flowers keep their original appearance. Solution