Environmental Science: Unit 5 Human Population Dynamics
advertisement

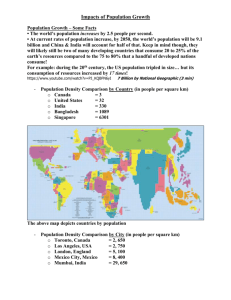
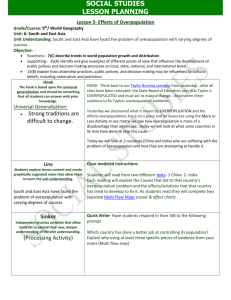
Environmental Science: Unit 5 Human Population Dynamics By Mrs. Shaw Day 1: Opening Assignment Before you start the questions below, please check your schedule to be sure you are supposed to be in this class. Also make sure you have 7 classes with a course code. (Senior Seminar and Career are not classes) What are 3 things that are necessary for a population to increase in size? What are 2 things that help to balance growth within a population? (things that happen that decrease the size at the same time that it is increasing) Remember that a POPULATION is the number of the same type of species within a specific area. Day 1: Opening Assignment ANSWERS What are 3 things that are necessary for a population to increase in size? Space, a reproductive strategy and capability, food (energy) source, access to water. What are 2 things that help to balance growth within a population? (things that happen that decrease the size at the same time that it is increasing) death and emigration (moving out of an area) Remember that a POPULATION is the number of the same type of species within a specific area. The Habitable Planet Unit 5: Human Population Dynamics http://www.learner.org/courses/envsci/unit/text .php?unit=5&secNum=1 Human Population Dynamics Video Review Copy the questions and answer 1. What survey is used to calculate the population in a specific area in the U.S.? 2. How is this information used and why is it important? 3. What are some limitations to this survey? 4. Why did the algae in Cape Cod increase and become a problem? Day 2: Opening Assignment If I wanted to create a graph to show how the human population has changed over time, how would I set it up? What goes on the x-axis? ________________ What goes on the y- axis? _______________ What type of graph would I use . . .bar or line? Day 1 Activity Human This Population Growth Activity assignment is due at the end of class today You can work together BUT each person needs to submit a separate activity sheet Population Clock http://www.census.gov/popclock/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E8dkWQVFAoA Day 3 Opening Assignment 1. In the Human Population Growth graphing activity we did yesterday what did you notice about the time span for doubling time as the population increased? 2. In Mexico the growth rate is much higher than in the U.S. What factors do you think contribute to this? Day 3 & 4 Activity Read Chapter 13 and answer the questions using the questions on your own notebook paper using complete sentences. Day 4 Opening Assignment 1. How has the agricultural and industrial revolution influenced human population growth? 2. Which is the highest population density of grasshoppers? A. 35 grasshoppers / 10 square meters B. 40 grasshoppers / 20 square meters C. 1 grasshopper / 1 square meter D. 50 grasshoppers / 30 square meters Overpopulation: The Future of Planet Earth https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hn5sEipg5tc Day 5 Opening Assignment What is the germ theory and how did it affect human population growth? Unit 5: Human Population Dynamics Student Learning Goals Students will be able to Describe the factors that influence human population growth trends Explain how population growth or decline impacts the environment Describe how demographers use statistics to make predictions of human population change and its subsequent environmental impact. Lesson 13.1 – History of the Human Population In 1798. British economist Thomas Malthus argued that population growth was not always desirable. Malthus believed that if the human population outgrew its resources it would lead to such conditions as famine, war, and other human suffering. (1) To try to solve this problem he proposed that people should marry later in life and have smaller families. (2) Increases in Growth Rate Scientists estimate that humans evolved on Earth approximately 100,000 years ago. The first humans were thought to be hunter – gatherers. During this time human population grew slowly for many reasons. Some of them were that it took more energy to get food so starvation, predation, and disease were common and the infant mortality rate was high due to lack of medical knowledge. (3) Increases in Growth Rate The population size started to increase mainly due to better food storage practices. Food storage reduced the starvation and death rate leading to a population increase. (4) Agriculture The agricultural revolution was a shift from harvesting wild food sources to producing food through techniques of farming and herding is known as the agriculture revolution. (5) Farming and the establishment of a social structure helped increase the Earth’s human population. Farming provided an increased and steady food supply which led to increase in populations. Social structure caused a rise in the standard of living which also help with population growth. (6) Industry The Industrial Revolution which has happened over the past 300 years, influenced population growth in many ways. Technological advances have led to improved food production and distribution, reduced the length of the work day, and provided people with a safer work environment. (7) Health Care The germ theory is the theory (evidence based) that disease identified bacteria and other microorganisms were the agents responsible for many diseases. It’s development has led to improved hygiene, sterile surgical practices, better methods of waste disposal and water treatment. (8) Decline in Growth Rate Three factors that have played a role in population declines over the past 800 years have been diseases like the plague, famine and war. These have all led to decline in growth rates over the past 800 years. Lesson 13.2: Growth and Changing Needs Measuring Growth Rate Growth rate is calculated by the following equation: Birth rate – death rate = growth rate (1) Doubling time is the time it takes a population to double in size. (that is wild! ) (2) As the human population has increased, the doubling time has decreased because there are more people available to reproduce. (3) Measuring Growth Rate Other than birth and death rates, other factors need to be considered when measuring growth rate for a specific area. Emmigration (people moving out of an area) and Immigration (people moving into an area) both need to be factored in to measure growth rate for a specific area. (4) Demography Demography is the science and study of the changing vital statistics in a human population. (5) Look at the charts that compare the percentages of populations in each age group in 3 different countries. Make 2 quantitative observations about these charts. In Mexico (Kenya) the average lifespan is much shorter. More people in Sweden live longer than in the US. (6) 7. Why do you think the U.S. has a slower growth rate than Mexico? Mexico is a poorer country and therefore has less money for medical care and education on health and reproduction. That has also led to the shorter life span in Mexico. (7) Changing Needs The least developed nations of the world are expected to experience the greatest growth in the coming decades due to less money, medical care, and education. (8) Lesson 13.3: Challenges of Overpopulation List 4 negative effects of overpopulation. Diseases spread faster, carbon emissions are greater in more populated areas so there is an increase in pollution, diseases related to malnutrition, poor hygiene, and lack of medical care are increased. 2. What is being done in under-developed countries to help control the birth rate? Increasing medical care to provide effective birth control and also education on reproduction. 3. What are 2 ways new technology is working to solve these sustainability problems? New technology is giving us new sources of renewable energy, new strains of crops that are developed through genetic engineering, and other scientific breakthroughs are being discovered to solve some of the space and resource issues that come with overpopulation. 1. How Many People Can Live on Our Planet? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dN06tLRE4WE Day 6 Opening Assignment Copy the chart on your paper and fill in Infectious diseases Definition Examples Noninfectious diseases Infectious vs. Noninfectious Place the following diseases in the correct column – infectious or noninfectious. Chicken pox migraines cancer influenza Hepatitis appendicitis diabetes Strep throat STD’s heart disease measles plague Disease Transmission Lab Remember: Even I don’t know who has the disease! You can only mix “bodily fluids” with 3 people and you must document who they are. FOLLOW the DIRECTIONS! Don’t forget to mix thoroughly Day 7 Activity Overpopulation is NOT the Problem Article Review Title a blank piece of paper “Overpopulation in NOT the Problem Article Review”. Then read the article and write a 2 paragraph summary. Be sure to explain these three points; How does this view of the “problem” differ from what we have been learning about when it comes to overpopulation. Explain what “Anthropocene” is. Explain where our focus should be and make predictions on how job careers have to evolve into this new area. Turn your paper in to be graded when you have finished


![[标签:标题]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007514640_1-d06ca384d6a6efac05ae8c0c925f8675-300x300.png)

