unit 4 notes
advertisement

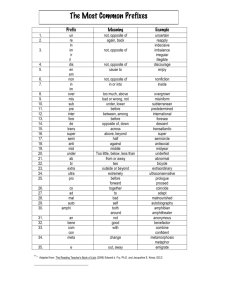
Social Inequality & Change Collective behavior • Definition: activity involving a large number of people; often spontaneous, sometimes controversial • Collectivity: lg. # of people whose activity occurs in the absence of well-defined & conventional norms (examples: crowds, riots, public opinion, rumors, fashion)—can be localized or dispersed RIOT CROWD Localized collective behavior • Crowd: temporary gathering of people who share a common focus & influence each other • Mob: highly emotional crowd that pursues a violent or destructive goal • Riot: social eruption that’s highly emotional, violent & undirected • Flash mobs (result of modern technology) 5 Types of crowds • • • • • • Casual: little/no interaction (beach) Conventional: planned (funeral) Acting: intense purpose/emotional (riot) Expressive: emotional (New Year’s Eve) Protest: political (marching, die-ins) CAN CHANGE from one type to another! MOB FLASH MOB http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=GBaHPND2QJg Sabadell Friends with Benefits flash mob (Grand Central Station): “New York New York” https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=AcF1AMace2s Christmas Hallelujah Chorus flash mob https://www.youtube.com/wa tch?v=ohagajJvzhU Dispersed collective behavior • Rumor: unsubstantiated information people spread informally, often by word of mouth • Gossip: rumor about people’s personal affairs • Public opinion: widespread attitudes about controversial issues • Propaganda: information presented with the intention of shaping public opinion • Panic: form of localized collective behavior by which people react to a threat or other stimulus with irrational, frantic & often selfdestructive behavior • Mass hysteria (moral panic): form of dispersed collective behavior by which people react to a real or imagined event with irrational and even frantic fear • Fashion: social pattern favored by lg. # of ppl • Fad: unconventional social pattern people embrace briefly but enthusiastically Social Movements & Change • Defined: transformation of culture & social institutions over time • Exist to encourage or resist change • Examples: civil rights movement, child labor laws, women’s rights, environmental laws, gay rights (same-sex marriage), marijuana legalization movement • Result of technology improvements: TV, cable, satellite, cell phones, social networks • Unites people like never before Social Change • Causes: inventions/technology, discoveries, diffusion (spread of info/cultures); conflict, ideas (religion), demographics (women, child birth rates, migration) • Modernity: social patterns resulting from industrialization (less small communities, more personal choices, more diversity, oriented towards the future more than the past) Modernity • Mass society: society in which prosperity & bureaucracy have eroded traditional social ties • Class society (Marx): capitalist society with pronounced social stratification • Postmodernity: social patterns characteristics of postindustrial societies • Race: category of people who share biologically transmitted traits that society considers important (black, white, Hispanic, Asian) • Ethnicity: shared cultural heritage (Christian Xmas) • Prejudice: rigid & unfair generalization about a category of people (all whites/blacks…) • Racism: the belief that one racial category is innately superior to another (Asians are smarter.) • Generalization: use facts to draw conclusions about a group of people (most cops are white, so all cops are white) • Discrimination: treating various categories of people unequally (Preferring an Asian doctor because they’re “smarter.”) • Stereotype: an exaggerated description applied to every person in some category (black male=thug)