ANALOG CIRCUIT
AND DEVICES
Course Code:
EEE 3123
22/3/2016
Semester I
2013/2014
1
TOPIC:
VOLTAGE
REGULATORS
22/3/2016
2
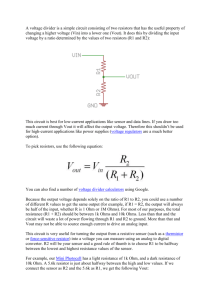
Power Supply Regulation
An ideal power supply provides a constant dc voltage despite
changes to the input voltage or load conditions.
The output voltage of a real power supply changes under load as shown
in the second plot. The output is also sensitive to input voltage changes.
Voltage
Voltage
VNL
VNL
VFL
Ideal power supply
0
Real power supply
Current
0
0
Current
0
Line Regulation
Example;
line regulation
0.05a %/V
means
Line regulation is A
a measure
of howofwell
power
supply is
the output
voltage
able to maintain thethat
dc output
voltage
for a changes
change in the ac
0.05formula
percentfor
when
input voltage
input line voltage. The
linethe
regulation
is
increases or decreases
by one volt.
V
Line Regulation = OUT 100%
VIN
Line regulation can also be expressed in terms of percent
change in VOUT per volt change on the VIN (%/V).
VOUT / VOUT 100%
Line Regulation =
VIN
Example 17.1
• Page 853
Load Regulation
Example;
A load
regulation
of well
0.01 a%/mA
Load regulation is
a measure
of how
power supply is
means
that the
output
voltage
able to maintain the
dc output
voltage
between
no load and
changes
0.01 constant.
percent when
load
full load with the input
voltage
It canthe
be expressed
as
current
increases
a percentage change
in load
voltage:or decreases by 1
mA.
VNL VFL
Load Regulation =
VFL
100%
Load regulation can also be expressed in terms of percent
change in the output per mA change in load current (%/mA).
Sometimes a maximum error voltage is given in the specification as
illustrated in the next slide for a commercial power supply.
Example 17.2
• Page 854
Load Regulation
Commercial power supplies, such as you have in lab, have
excellent line and load regulation specifications.
The BK Precision 1651A is an example of
a triple output supply (two 0-24 V outputs
and a fixed 5 V output). Voltage regulation
specifications for this power supply are:
Line regulation:
Load regulation:
≤0.01% +3 mV (Main supply)
≤5 mV (Fixed 5 V supply)
≤0.01%+3 mV (Main supply)
≤5 mV (Fixed 5 V supply)
Load Regulation
Sometimes the power supply manufactures use the equivalent
Thevenin resistance of a supply in place of a load regulation
Refer Page 854-855 for derivation.
specification.
In this case, VOUT can be found by
applying the voltage divider rule:
RL
VOUT VNL
R
R
L
OUT
In terms of resistances, load
regulation can be expressed as:
ROUT
Load regulation
100%
RFL
Power Supply
RTH = ROUT
VOUT
VTH = VNL
RL
Load Regulation
A power supply has an output resistance of 25 mW and a full
load current of 0.50 A to a 10.0 W load.
(a) What is the load regulation?
(b) What is the no load output voltage?
ROUT
0.025 W
Load
regulation
100%
(a)
100% = 0.25%
10.0 W
RFL
(b) By Ohm’s law, VOUT = 5.0 V.
VNL
VOUT
RL
R
R
L
OUT
5.0 V
= 5.013 V
10.0 W
0.025 W + 10.0 W
Series Regulators
Control element: a pass transistor in series with the load between
the input and output.
Sample circuit: senses a change in the output voltage.
A simple representation of a series
type of linear regulator:
Error detector: compares the sample voltage with a reference
voltage and causes the control element to compensate in order to
maintain a constant output voltage.
Series Regulator block diagram:
Control
element
VIN
Reference
voltage
Error
detector
VOUT
Refer Page 856 for full explanation.
Sample
circuit
Basic series regulator circuit:
Control element
VIN
VOUT
Q1
R1
+
VREF
The control element maintains
a constant output voltage by
varying the collector-emitter
voltage across the transistor.
–
D1
Error detector
R2
Sample
circuit
R3
Series Regulators
R
The output voltage for the series regulator circuit is: VOUT 1 2 VREF
R3
(a) What is the output voltage for the series regulator?
(b) If the load current is 200 mA, what is the power
dissipated by Q1?
R
(a) VOUT 1 2 VREF
R3
100 kW
1+
3.9 V
47 kW
= 12.2 V
(b) P = VI
= (18 V – 12.2 V)(0.2 A)
= 1.16 W
VIN
VOUT
18 V
Q1
R1
4.7 kW
VREF
+
–
3.9 V
D1
R2
100 kW
R3
47 kW
Series Regulators
Current limiting prevents excessive load current. Q2 will
conduct when the current through R4 develops 0.7 V across
Q2’s VBE. This reduces base current to Q1, limiting the load
current.
The current limit is:
I L(max)
0.7 V
R4
For example, a 1.4 W
resistor, limits current
to about 0.5 A.
Q1
R4
VOUT
VIN
R1
Q2
+
R2
Current limiter
–
R3
Example 17.4
• Page 859
Series Regulators
Fold-back current limiting drops the load current well
below the peak during overload conditions. Q2 conducts
when VR5 +VBE = VR4 and begins current limiting. VR5 is
found by applying the voltage-divider rule:
R5
VR5
VOUT
R
R
6
5
An overload causes VR5 to
drop because VOUT drops.
This means that less
current is needed to
maintain conduction in Q2
and the load current drops.
Q1
R4
VOUT
+VIN
R5
R1
+
–
R2
R6
Q2
D1
R3
Shunt Regulators
A simple representation of a shunt
type of linear regulator;
Shunt Regulator block diagram:
R1
VIN
VOUT
Reference
voltage
Error
detector
Control
element
(shunt)
Basic shunt regulator circuit:
Sample
circuit
VOUT
VIN
R1
R2
–
VREF
The control element maintains
a constant output voltage by
varying the collector current in
the transistor.
Error detector
Control
element
Q1
+
RL
R3
D1
Sample
circuit
R4
Q1 in parallel with the load.
R1 in series with the load.
Regulation is achieved by controlling the current through the
parallel transistor Q1.
Shunt Regulators
Shunt regulators use a parallel transistor for the control
element. If the output voltage changes, the op-amp senses
the change and corrects the bias on Q1 to follow. For
example, a decrease in output voltage causes a decrease in
V
VB and an increase in VC. V
OUT
IN
R1
Although it is less efficient
than the series regulator, the
shunt regulator has inherent
short-circuit protection. The
maximum current when the
output is shorted is VIN/R1.
R2
Error detector
–
VREF
Control
element
Q1
+
RL
R3
D1
Sample
circuit
R4
Example 17.5
• Page 862
Switching Regulators
All switching regulators control the output voltage by
rapidly switching the input voltage on and off with a duty
cycle that depends on the load. Because they use high
frequency switching, they tend to be electrically noisy.
Andecrease
A
increaseininthe
theduty
dutycycle
cycledecreases
increasesthe
theoutput
outputvoltage.
voltage.
on/off
control
tonton ton
tofftoff toff
VC
VC
VC
VOUT
tonton ton
tofftoff toff
tonton ton
tofftoff toff
tonton ton
Switching Regulators
A step-down switching regulator controls the output
voltage by controlling the duty cycle to a series transistor.
The duty cycle changes depending on the load requirement.
Because the transistor is
either ON or OFF on all
switching regulators, the
power dissipated in the
transistor is very small
and the regulator is very
efficient. The pulses are
smoothed by an LC filter.
Q1
VIN
C Lcharges
reversesLpolarity
off
on
+
+
RL
C
D1
R1
VOUT
Variable
pulse-width
oscillator
R2
–
+
R3
D2
VREF
Switching Regulators
In a step-up switching regulator, the control element
operates as a rapidly pulsing switch to ground. The switch
on and off times are controlled by the output voltage.
Step-up action is due to
the fact the inductor
changes polarity during
switching and adds to
VIN. Thus, the output
voltage is larger than
the input voltage.
VIN
+
L field
L field
collapses
builds
charges
discharges
on
off C C
+V
OUT
+
R1
+
Variable
pulse-width
oscillator
–
D2
L
D1
C
on
off
Q1
RL
R2
+
R3
Switching Regulators
In a voltage-inverter switching regulator, the output is the
opposite polarity of the input. It can be used in conjunction
with a positive regulator from the same input source.
Inversion occurs
because the inductor
reverses polarity
when the diode
conducts, charging
the capacitor with
the opposite polarity
of the input.
off
on
Q1
+VIN
off
on
D1 C discharges
+
L
R1
Variable
pulse-width
oscillator
C
C charges
+
L field collapses
builds
R2
+
–
R3
D2
–VOUT
RL
IC Voltage Regulators
Integrated circuit voltage regulators are available as
series regulators or as switching regulators. The popular
three-terminal regulators are often used on separate pc
boards within a system because they are inexpensive and
avoid problems associated with large power distribution
78XX Regulators
systems (such as noise pickup).
The 78XX series is a fixed
positive output regulator
available in various
packages and with
standard voltage outputs.
TO-220 case
D-PAK
4
1 2
1
2
3
3
Type number
Output voltage
7805
7806
7808
7809
7812
7815
7818
7824
+5.0 V
+6.0 V
+8.0 V
+9.0 V
+12.0 V
+15.0 V
+18.0 V
+24.0 V
IC Voltage Regulators
The only external components required
with the 78XX series are input and output
capacitors and some form of heat sink.
These IC’s include thermal shutdown
protection and internal current limiting.
The 78XX series are
primarily used for fixed
output voltages, but with
additional components, they
can be set up for variable
voltages or currents.
Positive
input
(1)
Heat-sink surface
4
1 2
1
2
3
(3)
78XX
(2) Gnd
3
Positive
output
IC Voltage Regulators
The 79XX series is the negative output counterpart to the
78XX series, however the pin assignments are different
on this series. Other specifications are basically the same.
Negative
input
(2)
(3)
79XX
(1) Gnd
Negative
output
Type number
Output voltage
7905
7905.2
7906
7908
7912
7915
7918
7924
–5.0 V
–5.2 V
–6.0 V
–8.0 V
–12.0 V
–15.0 V
–18.0 V
–24.0 V
IC Voltage Regulators
The LM317 is a adjustable positive output IC regulator.
There is a fixed reference voltage of +1.25 V between the
output and adjustment terminals. There is no ground pin.
R
The output voltage is calculated by: VOUT VREF 1 2 I ADJ R2
R1
What is VOUT?
(Assume IADJ = 50 mA.)
+20 V
Positive
input
(3)
LM317
(1) Adjustment
2 kΩ
VOUT 1.25 V 1
50 μA 2 kW
150 W
= 16.8 V
+16.8
V
Positive
(2)
output
R11
150 W
C11
C3
C22
R22
2 kW
IC Voltage Regulators
IC regulators are limited to a maximum allowable current
before shutting down. The circuit shown is uses an
external pass transistor to increase the maximum available
load current.
Rext sets the point where
Qext begins to conduct:
Rext
0.7 V
I max
Qext
VIN
Rext
C1
VOUT
78XX
For example, if Imax is
1.0 A, Rext = 0.7 W
What minimum power rating is required for Rext?
P = I2R = (1 A)2(0.7 W) = 0.7 W
C2
RL
IC Voltage Regulators
The 78S40 is an IC containing all of the elements needed to
configure a switching regulator, using a few external parts.
It is a universal switching
regulator subsystem
because it can be configured
as a step-down, step-up, or
inverting regulator by the
user. The data sheet shows
typical circuits for these
configurations.
Here is the step-down
configuration.
RCS
VIN
Noninvert Invert
input
input
9
10
Gnd
CT
Timing
cap
11
12
Ipk
Driver Switch
VCC
VCC sense collector collector
13
14
S
Oscillator
15
16
16
Q1
Q
Flip-flop
–
Comp.
++
1.25 V
V
reference
–
D1
+
8
7
66
5
4
Reference Invert Noninvert VCC
Output
Rvoltage
input
input op-amp
2
R1
Q2
R
3
Switch
emitter
2
1
Anode Cathode
L
VOUT
CO
Selected Key Terms
Regulator A electronic circuit that maintains an
essentially constant output voltage with
changing input voltage or load current.
Line regulation The percentage change in output voltage for a
given change in input (line) voltage.
Load regulation The percentage change in output voltage for a
given change in load current.
Linear regulator A voltage regulator in which the control
element operates in the linear region.
Switching A voltage regulator in which the control
regulator element operates as a switch.
Quiz
1. The load regulation of an ideal power supply is
a. 0%
b. 25%
c. 50%
d. 100%
Quiz
2. A correct formula for load regulation is
a.
VOUT
Load Regulation =
100%
VIN
b.
VNL VFL
Load Regulation =
100%
VFL
c.
VFL
Load Regulation =
100%
VNL VFL
d. Load Regulation =
VOUT / VOUT 100%
VIN
Quiz
3. An alternate way to express load regulation is in terms of
the
a. output resistance and the full-load resistance
b. output resistance and the shorted-load resistance
c. input resistance and the full-load resistance
d. input resistance and the shorted-load resistance
Quiz
4. In the circuit shown, R4 = 0.7 W. The output current will
be limited to
a. 0.5 A
b. 0.7 A
c. 1.0 A
d. 1.4 A
Q1
VIN
R4
VOUT
0.7 W
R1
Q2
+
R2
Current limiter
–
R3
Quiz
5. The block diagram for a series voltage regulator is
shown. The yellow box represents a
a. control element
VIN
VOUT
b. sample circuit
c. error detector
d. reference voltage
?
Quiz
6. The block diagram for a shunt voltage regulator is
shown. The yellow box represents a
a. control element
R1
VIN
VOUT
b. sample circuit
c. error detector
d. reference voltage
?
Quiz
7. The circuit in the blue shaded area is a
a. high speed switching circuit
b. fold-back current limiter
c. reference source
d. shunt regulator
Q1
R4
VOUT
+VIN
R5
R1
+
–
R2
R6
Q2
D1
R3
Quiz
8. A major advantage of all switching regulators is
a. low noise
b. high output impedance
c. high efficiency
d. all of the above
Quiz
9. The type of regulator circuit shown is a
a. series linear
b. series switching
c. shunt switching
onoffD
Q1
+VIN
1
offon
+
R1
C
discharges
L
C
C
Variable +
charges
pulse-widthL L
field
field
collapses
builds
R2
oscillator
+
d. none of the above
–
R3
D2
–VOUT
RL
Quiz
10. The output voltage from a 7912 is a regulated
a. +5 V
b. +12 V
c. 5 V
d. 12 V
• Thomas L. Floyd, “Electronic Devices Conventional
Current Version, Ninth Edition (International Edition)”,
Pearson Prentice Hall, 2012
22/3/2016
References
40